Functional Groups
... A specific arrangement of atoms in an organic compound that is capable of characteristic chemical reactions. In other words, a substituent group other than an alkyl group. Most organic chemistry is functionalgroup chemistry. We will do one functional group. ...
... A specific arrangement of atoms in an organic compound that is capable of characteristic chemical reactions. In other words, a substituent group other than an alkyl group. Most organic chemistry is functionalgroup chemistry. We will do one functional group. ...
File
... Sodium Hypochlorite ( bleach) – sanitization – dairies; food processing equipment, utensils, dialysis machines; drinking water; surfaces contaminated with blood or body fluids - use 10% bleach 2. Iodine - one of the oldest & most effective disinfectants; inactivates proteins ...
... Sodium Hypochlorite ( bleach) – sanitization – dairies; food processing equipment, utensils, dialysis machines; drinking water; surfaces contaminated with blood or body fluids - use 10% bleach 2. Iodine - one of the oldest & most effective disinfectants; inactivates proteins ...
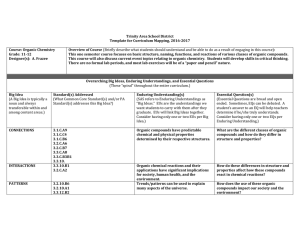
COURSE: Organic chemistry ACADEMIC YEAR:2016/2017 TYPE
... The course wants to give basic information on the principal properties of the organic compounds, allowing the student to understand the physical properties and the chemical behavior of every organic compounds. PRE-REQUIREMENTS General and inorganic chemistry SYLLABUS Electronic configuration. Bonds. ...
... The course wants to give basic information on the principal properties of the organic compounds, allowing the student to understand the physical properties and the chemical behavior of every organic compounds. PRE-REQUIREMENTS General and inorganic chemistry SYLLABUS Electronic configuration. Bonds. ...
Nomenclature of Polyfunctional Organic Compounds
... methyl bromide and half under "B"for bromomethane. Furthermore, a CAS name must be strictly systematic so that it can be assigned and interpreted by computers; common names are not allowed. People,however,have different requirements than computers. For peoplewhich is to say chemists in their spoken ...
... methyl bromide and half under "B"for bromomethane. Furthermore, a CAS name must be strictly systematic so that it can be assigned and interpreted by computers; common names are not allowed. People,however,have different requirements than computers. For peoplewhich is to say chemists in their spoken ...
How to study organic chemistry?
... Effect of H-Bond on acidity,basicity,B.P. Order,H-Bonding during tautomerism. ...
... Effect of H-Bond on acidity,basicity,B.P. Order,H-Bonding during tautomerism. ...
Origins of Life - Yale University
... Types of Organic Compounds • Vast majority of over 20 million known compounds are based on C: organic compounds. • Generally contain C and H + other elements • Great variety of compounds ...
... Types of Organic Compounds • Vast majority of over 20 million known compounds are based on C: organic compounds. • Generally contain C and H + other elements • Great variety of compounds ...
energies
... carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids The properties of carbon atoms make them extraordinary versatile, able to form the backbones of the large variety of organic compounds essential to life: A- Each C atom can form 4 covalent bonds with 4 other atoms, single, double, or triple bonds. ...
... carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids The properties of carbon atoms make them extraordinary versatile, able to form the backbones of the large variety of organic compounds essential to life: A- Each C atom can form 4 covalent bonds with 4 other atoms, single, double, or triple bonds. ...
Alcohols, Penols, and Thiols
... • Why does t-butyl alcohol react at equal rates with HI, HBr, and HCl? • Why does 1-butanol’s rate of reaction vary with HI, HBr, and HCl? ...
... • Why does t-butyl alcohol react at equal rates with HI, HBr, and HCl? • Why does 1-butanol’s rate of reaction vary with HI, HBr, and HCl? ...
Solid phase reactions II
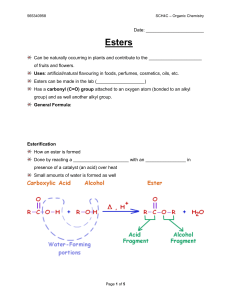
... Reduction of carboxylic acids (Weinreb amide) Oxidation of alcohols ...
... Reduction of carboxylic acids (Weinreb amide) Oxidation of alcohols ...
Functional Groups
... These rotations give rise to different conformations. However, with the exception of small-ring molecules, the alkanes, as compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen, are relatively weakly reactive substances. Most organic molecules which exhibit chemical reactivity have an incorporated active st ...
... These rotations give rise to different conformations. However, with the exception of small-ring molecules, the alkanes, as compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen, are relatively weakly reactive substances. Most organic molecules which exhibit chemical reactivity have an incorporated active st ...
Organic Chemistry: Functional Groups and Nutrients Objectives
... similar features also share similar properties. There are many more. Many of these have substituted groups that produce these properties. These substituted groups are called functional groups. One of these functional groups is the hydroxyl group (OH). When a hydroxyl group is attached to the carbon ...
... similar features also share similar properties. There are many more. Many of these have substituted groups that produce these properties. These substituted groups are called functional groups. One of these functional groups is the hydroxyl group (OH). When a hydroxyl group is attached to the carbon ...
Biological Molecules Power Point
... Living things depend on biochemical processes that involve chemical reactions among biochemical compounds. 6 elements make up 99% of all living tissue and combine to form the molecules that are the basis of cellular function ...
... Living things depend on biochemical processes that involve chemical reactions among biochemical compounds. 6 elements make up 99% of all living tissue and combine to form the molecules that are the basis of cellular function ...
Chapter 22 Organic chemistry
... Aldehydes and Ketones Substituted hydrocarbons with a carbonyl group ...
... Aldehydes and Ketones Substituted hydrocarbons with a carbonyl group ...
Review Chapters 8-18 - Bakersfield College
... 14. Which of these compounds show cis-trans isomerism? For each that does, draw structural formulas for both isomers. Which one has a higher boiling point (cis or trans)? a) 2-methyl-2-butene ...
... 14. Which of these compounds show cis-trans isomerism? For each that does, draw structural formulas for both isomers. Which one has a higher boiling point (cis or trans)? a) 2-methyl-2-butene ...
PPT
... PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF ALCOHOLS, cont. • Larger alkanes have greater hydrophobic regions and are less soluble or insoluble in water. • Water interacts only with the –OH group of ...
... PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF ALCOHOLS, cont. • Larger alkanes have greater hydrophobic regions and are less soluble or insoluble in water. • Water interacts only with the –OH group of ...
PDF
... • The –OH group can hydrogen bond between alcohol molecules leading to relatively high boiling points. • Hydrogen bonding in pure ethanol: ...
... • The –OH group can hydrogen bond between alcohol molecules leading to relatively high boiling points. • Hydrogen bonding in pure ethanol: ...
Jordan University of Science and Technology
... compounds, with considerable attention to stereochemistry, reaction mechanisms, synthetic organic chemistry and Surveys the chemistry of functionalized organic compounds emphasizing mechanisms and multi-step syntheses.. Emphasis will be on substitution and elimination reactions , the chemistry of hy ...
... compounds, with considerable attention to stereochemistry, reaction mechanisms, synthetic organic chemistry and Surveys the chemistry of functionalized organic compounds emphasizing mechanisms and multi-step syntheses.. Emphasis will be on substitution and elimination reactions , the chemistry of hy ...
Elements Found in Living Things
... in organisms. Amino acids contain two functional groups, the carboxyl group (-COOH) and the amino group (-NH2). ...
... in organisms. Amino acids contain two functional groups, the carboxyl group (-COOH) and the amino group (-NH2). ...
Phenols

In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest of the class is phenol, which is also called carbolic acid C6H5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule.Synonyms are arenols or aryl alcohols.Phenolic compounds are synthesized industrially; they also are produced by plants and microorganisms, with variation between and within species.Although similar to alcohols, phenols have unique properties and are not classified as alcohols (since the hydroxyl group is not bonded to a saturated carbon atom). They have higher acidities due to the aromatic ring's tight coupling with the oxygen and a relatively loose bond between the oxygen and hydrogen. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids (their pKa is usually between 10 and 12).Loss of a positive hydrogen ion (H+) from the hydroxyl group of a phenol forms a corresponding negative phenolate ion or phenoxide ion, and the corresponding salts are called phenolates or phenoxides, although the term aryloxides is preferred according to the IUPAC Gold Book. Phenols can have two or more hydroxy groups bonded to the aromatic ring(s) in the same molecule. The simplest examples are the three benzenediols, each having two hydroxy groups on a benzene ring.Organisms that synthesize phenolic compounds do so in response to ecological pressures such as pathogen and insect attack, UV radiation and wounding. As they are present in food consumed in human diets and in plants used in traditional medicine of several cultures, their role in human health and disease is a subject of research.ref name=Klepacka Some phenols are germicidal and are used in formulating disinfectants. Others possess estrogenic or endocrine disrupting activity.