ppt
... • Stereoisomer are “handed” • Thalidomide, given for morning sickness in Europe in late 1950s. Sedative. Found to be teratogen Was found in some animals that only the S stereoisomer is teratogenic – but turns out they both are. ...
... • Stereoisomer are “handed” • Thalidomide, given for morning sickness in Europe in late 1950s. Sedative. Found to be teratogen Was found in some animals that only the S stereoisomer is teratogenic – but turns out they both are. ...
Organic Nomenclature - Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes
... Naming Ketones (–C=O group) = -one ending Ketones are very similar to aldehydes. The only difference is that the C=O in a ketone is in the middle of a chain - not on the terminal carbon. To name a ketone, use the -one ending and specify the position of the C=O with a number at the beginning of the n ...
... Naming Ketones (–C=O group) = -one ending Ketones are very similar to aldehydes. The only difference is that the C=O in a ketone is in the middle of a chain - not on the terminal carbon. To name a ketone, use the -one ending and specify the position of the C=O with a number at the beginning of the n ...
Pre AP Chemistry Chapter 6: Bonding Homework #2
... Write the appropriate formula for the ion formed by the elements from question 8. Use a + or a minus sign to indicate what charge the ion assume when electrons are gained or lost a. strontium____________ b. nitrogen____________ c. zinc__________ d. bromine_____________ ...
... Write the appropriate formula for the ion formed by the elements from question 8. Use a + or a minus sign to indicate what charge the ion assume when electrons are gained or lost a. strontium____________ b. nitrogen____________ c. zinc__________ d. bromine_____________ ...
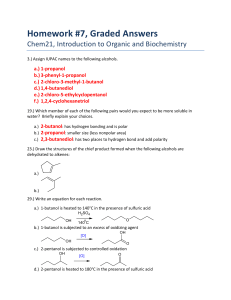
Homework #7, Graded Answers
... 29.) Write an equation for each reaction. a.) 1-butanol is heated to 140°C in the presence of sulfuric acid H2SO4 OH ...
... 29.) Write an equation for each reaction. a.) 1-butanol is heated to 140°C in the presence of sulfuric acid H2SO4 OH ...
Practice: Chapter 21
... 15.Yes; both compounds have the molecular formula C5H8, but they have different carbon chains. 16.The aromatic compounds are 1-methyl-4-propylbenzene and anthracene because these compounds contain benzene rings as part of their molecular structures. 17. Halocarbons are named by use of the prefixes f ...
... 15.Yes; both compounds have the molecular formula C5H8, but they have different carbon chains. 16.The aromatic compounds are 1-methyl-4-propylbenzene and anthracene because these compounds contain benzene rings as part of their molecular structures. 17. Halocarbons are named by use of the prefixes f ...
SNC2DExamChemistryreview
... 19. Predict if a reaction will happen using an activity series for the equation below. c) Li+HCl b) F2+MgCl2-> 20. The reaction of magnesium and oxygen produces a bright white light and heat. Mg(s) + O2 (g) 2MgO(g) a) What type of reaction is this? b) What are the reactants? What are the products ...
... 19. Predict if a reaction will happen using an activity series for the equation below. c) Li+HCl b) F2+MgCl2-> 20. The reaction of magnesium and oxygen produces a bright white light and heat. Mg(s) + O2 (g) 2MgO(g) a) What type of reaction is this? b) What are the reactants? What are the products ...
... Propionic acid , 2chloropropionic acid , 2 fluoropropionic acid. PART - B Answer any EIGHT questions (8 x 5 = 40) 11. Give a mechanism for the reaction of tert.butyl bromide with aqueous NaOH to form tert.butyl alcohol. 12. Explain Saytzeff rule and Hofmann rule with an example. 13. How is phenol pr ...
Spring 2017 - Ventura College Chemistry, Malia Rose-Seisa
... carboxylic acids, II. acid derivatives, amines, phenols, sugars, and proteins given reactant and target compounds, and propose alternate steps in reaction mechanisms for common reactions. C.) Examine, evaluate, and formulate appropriate multi-step synthetic pathways leading to target compounds invol ...
... carboxylic acids, II. acid derivatives, amines, phenols, sugars, and proteins given reactant and target compounds, and propose alternate steps in reaction mechanisms for common reactions. C.) Examine, evaluate, and formulate appropriate multi-step synthetic pathways leading to target compounds invol ...
Lecture 4 - Winthrop Chemistry, Physics, and Geology
... 1) Geometrical Isomers: The atoms on either side of a bond are arranged differently 2) Optical Isomers: The molecules are each other’s ...
... 1) Geometrical Isomers: The atoms on either side of a bond are arranged differently 2) Optical Isomers: The molecules are each other’s ...
Handout
... 23. List the different types of lipids and state each of their functions. 24. When a person goes on a diet, stored lipids begin to be digested. What happens chemically when the lipids are digested (broken down)? What is the name given to this process? 25. What type of compound is shown to the right? ...
... 23. List the different types of lipids and state each of their functions. 24. When a person goes on a diet, stored lipids begin to be digested. What happens chemically when the lipids are digested (broken down)? What is the name given to this process? 25. What type of compound is shown to the right? ...
Polyesters are condensation polymers.
... Note that sometimes other molecules (HCl for eg) are lost in other condensation reactions. It is the elimination of a molecule which makes it a condensation reaction, not the loss of water. ...
... Note that sometimes other molecules (HCl for eg) are lost in other condensation reactions. It is the elimination of a molecule which makes it a condensation reaction, not the loss of water. ...
Review Problems
... 3-ethyl-2-methylpentane 2,2-dichloropropane propylpental ether 2,2,3,3-tetramethylpentanal ...
... 3-ethyl-2-methylpentane 2,2-dichloropropane propylpental ether 2,2,3,3-tetramethylpentanal ...
Carbon Compounds
... • Are compounds that contain only the elements carbon and hydrogen. • Properties of Hydrocarbons: 1. Hydrocarbons mix poorly with water 2. Hydrocarbons are flammable. Chemical Formulas of Hydrocarbons: ...
... • Are compounds that contain only the elements carbon and hydrogen. • Properties of Hydrocarbons: 1. Hydrocarbons mix poorly with water 2. Hydrocarbons are flammable. Chemical Formulas of Hydrocarbons: ...
Organic Chemistry
... polysaccharides - polymers (long chains of repeating units) of monosaccharides, starch and glycogen ...
... polysaccharides - polymers (long chains of repeating units) of monosaccharides, starch and glycogen ...
Experiment #8 – properties of Alcohols and Phenols
... In each of the following cases you will attempt to make an approximately 10% (by weight) solution of the alcohol or phenol in water (very polar) and in hexane (nonpolar) to see if the compound is soluble to at least that extent. 1. Label clean dry test tubes as follows: 1-propanol, 1-butanol, 1-pent ...
... In each of the following cases you will attempt to make an approximately 10% (by weight) solution of the alcohol or phenol in water (very polar) and in hexane (nonpolar) to see if the compound is soluble to at least that extent. 1. Label clean dry test tubes as follows: 1-propanol, 1-butanol, 1-pent ...
Lecture Review of Organic Chemistry and Herbicide Chemistry
... tend to be degraded readily by microbes e.g. Roundup (glyphosate), Liberty/Ignite/Finale (glufosinate), and several thiocarbamate herbicides ...
... tend to be degraded readily by microbes e.g. Roundup (glyphosate), Liberty/Ignite/Finale (glufosinate), and several thiocarbamate herbicides ...
The Chemistry of Biology Student carbon compounds
... From the smallest single-celled organism to the tallest tree, all life depends on the properties and reactions of four classes of organic (carbon-based) compounds—carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. These organic molecules are the building blocks of all living things, and are respons ...
... From the smallest single-celled organism to the tallest tree, all life depends on the properties and reactions of four classes of organic (carbon-based) compounds—carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. These organic molecules are the building blocks of all living things, and are respons ...
Macromolecules Notes - Liberty Union High School District
... A few examples of dietary fats: (don’t copy this slide) Unsaturated fats are found in many plant products, such as olive and canola oils, nuts, avocadoes, and also found in fish. ...
... A few examples of dietary fats: (don’t copy this slide) Unsaturated fats are found in many plant products, such as olive and canola oils, nuts, avocadoes, and also found in fish. ...
Macromolecules Notes - Summit School District
... Amino acids and they combine in long chains to form… • Hair, Blood, Muscle, Skin, Bones, Antibodies, Enzymes, and Hormones. • One example is Tryptophan which is found in Turkey, cheese, chicken and pork and has a calming effect. ...
... Amino acids and they combine in long chains to form… • Hair, Blood, Muscle, Skin, Bones, Antibodies, Enzymes, and Hormones. • One example is Tryptophan which is found in Turkey, cheese, chicken and pork and has a calming effect. ...
Phenols

In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest of the class is phenol, which is also called carbolic acid C6H5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule.Synonyms are arenols or aryl alcohols.Phenolic compounds are synthesized industrially; they also are produced by plants and microorganisms, with variation between and within species.Although similar to alcohols, phenols have unique properties and are not classified as alcohols (since the hydroxyl group is not bonded to a saturated carbon atom). They have higher acidities due to the aromatic ring's tight coupling with the oxygen and a relatively loose bond between the oxygen and hydrogen. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids (their pKa is usually between 10 and 12).Loss of a positive hydrogen ion (H+) from the hydroxyl group of a phenol forms a corresponding negative phenolate ion or phenoxide ion, and the corresponding salts are called phenolates or phenoxides, although the term aryloxides is preferred according to the IUPAC Gold Book. Phenols can have two or more hydroxy groups bonded to the aromatic ring(s) in the same molecule. The simplest examples are the three benzenediols, each having two hydroxy groups on a benzene ring.Organisms that synthesize phenolic compounds do so in response to ecological pressures such as pathogen and insect attack, UV radiation and wounding. As they are present in food consumed in human diets and in plants used in traditional medicine of several cultures, their role in human health and disease is a subject of research.ref name=Klepacka Some phenols are germicidal and are used in formulating disinfectants. Others possess estrogenic or endocrine disrupting activity.