Functional Groups and Preparations
... It was traditionally used as a solvent but was found to be carcinogenic so methyl benzene (toluene is now used instead) Would you predict it would be soluble in water or ...
... It was traditionally used as a solvent but was found to be carcinogenic so methyl benzene (toluene is now used instead) Would you predict it would be soluble in water or ...
Organic Chemistry - City University of New York
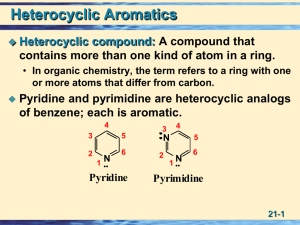
... compound: A compound that contains more than one kind of atom in a ring. • In organic chemistry, the term refers to a ring with one or more atoms that differ from carbon. ...
... compound: A compound that contains more than one kind of atom in a ring. • In organic chemistry, the term refers to a ring with one or more atoms that differ from carbon. ...
Plant Tissue Culture Media
... • Magnesium - Involved in photosynthetic and respiration systems. Active in uptake of phosphate and translocation of phosphate and starches. ...
... • Magnesium - Involved in photosynthetic and respiration systems. Active in uptake of phosphate and translocation of phosphate and starches. ...
Plant Tissue Culture Media - Horticultural Sciences at
... • Magnesium - Involved in photosynthetic and respiration systems. Active in uptake of phosphate and translocation of phosphate and starches. ...
... • Magnesium - Involved in photosynthetic and respiration systems. Active in uptake of phosphate and translocation of phosphate and starches. ...
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 03 JULY 2014 Lesson Description
... Grade 12 Question 3 (Adapted from DoE Exemplar Paper 1 – 2014) The flow diagram below shows the preparation of different organic compounds using CH3CH = CH2 as starting material. X, Y, Z and P represent different organic reactions. ...
... Grade 12 Question 3 (Adapted from DoE Exemplar Paper 1 – 2014) The flow diagram below shows the preparation of different organic compounds using CH3CH = CH2 as starting material. X, Y, Z and P represent different organic reactions. ...
Storage Pattern for Chemicals Where Space is Limited
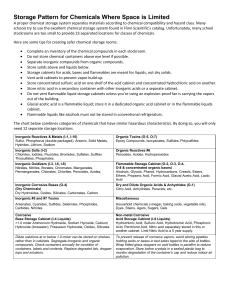
... Storage cabinets for acids, bases and flammables are meant for liquids, not dry solids. Vent acid cabinets to prevent vapor build-up. Store concentrated sulfuric acid on one shelf of the acid cabinet and concentrated hydrochloric acid on another. Store nitric acid in a secondary container with other ...
... Storage cabinets for acids, bases and flammables are meant for liquids, not dry solids. Vent acid cabinets to prevent vapor build-up. Store concentrated sulfuric acid on one shelf of the acid cabinet and concentrated hydrochloric acid on another. Store nitric acid in a secondary container with other ...
cycloalkanes
... Often written as: RCOOH or RCO2H IUPAC Nomenclature Carboxylic acids are named by replacing the -e of the alkane root name with -oic and adding the word acid. Substituents on the chain are named as usual. ...
... Often written as: RCOOH or RCO2H IUPAC Nomenclature Carboxylic acids are named by replacing the -e of the alkane root name with -oic and adding the word acid. Substituents on the chain are named as usual. ...
Alcohols, Phenols, Thiols, and Ethers
... reactions to produce ketones. • Tertiary alcohols do not undergo oxidation. ...
... reactions to produce ketones. • Tertiary alcohols do not undergo oxidation. ...
Carbon Chemistry
... • Hydrocarbon – an organic compound that contains only hydrogen and carbon. • Saturated hydrocarbon – all of the bonds are single bonds. ...
... • Hydrocarbon – an organic compound that contains only hydrogen and carbon. • Saturated hydrocarbon – all of the bonds are single bonds. ...
Chapter 11 Introduction to Organic Chemistry Part 2
... 5. Determine whether the following isomers are enantiomers or diastereomers. What characteristic feature of the molecule can be used to make the decision? ...
... 5. Determine whether the following isomers are enantiomers or diastereomers. What characteristic feature of the molecule can be used to make the decision? ...
Topic 10. Organic chemistry
... The starting compound has to be converted into the desired product using as few steps as possible and each step should have the highest possible yield. The reaction pathway describes this sequence of several steps between the starting material and the product. ...
... The starting compound has to be converted into the desired product using as few steps as possible and each step should have the highest possible yield. The reaction pathway describes this sequence of several steps between the starting material and the product. ...
Organic Chemistry - Unit 2
... aryl halide – this is a halocarbon in which there is a halogen substituent on an arene ring. (Substituted benzene) In all of these compounds, the halogen is considered to be the functional group. Very few halocarbons exist in nature but they are easily produced in substitution reactions. Alcohols Al ...
... aryl halide – this is a halocarbon in which there is a halogen substituent on an arene ring. (Substituted benzene) In all of these compounds, the halogen is considered to be the functional group. Very few halocarbons exist in nature but they are easily produced in substitution reactions. Alcohols Al ...
Phosphorus and sulfur cycles
... This is oxidised in water droplets in clouds to form sulfuric acid, H2SO4. Sulfuric acid is washed into the soil by rain. Sulfate ions form which can be absorbed and utilised by plants. Sulfuric acid can also be formed from DMSP (dimethyl sulfonioproprionate) which is formed by plankton species and ...
... This is oxidised in water droplets in clouds to form sulfuric acid, H2SO4. Sulfuric acid is washed into the soil by rain. Sulfate ions form which can be absorbed and utilised by plants. Sulfuric acid can also be formed from DMSP (dimethyl sulfonioproprionate) which is formed by plankton species and ...
carbon compound
... There are 4 main classes of organic compounds which are essential to the life processes of all living things. Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic Acids ...
... There are 4 main classes of organic compounds which are essential to the life processes of all living things. Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic Acids ...
Organic compounds
... Polymers are molecules made of many monomers (monomer + monomer = polymer) “poly” = many (Ex. a sentence) ...
... Polymers are molecules made of many monomers (monomer + monomer = polymer) “poly” = many (Ex. a sentence) ...
Uses and Sources of some Organic Molecules C11-5-14
... Esters Most esters have pleasant odors. Esters are responsible for the fragrances of many flowers and the pleasant tastes of ripened fruits. Bananas contain the ester amyl acetate, and oranges the ester octyl acetate. Beeswax and other waxes are composed of esters, as are animal and vegetable fats ...
... Esters Most esters have pleasant odors. Esters are responsible for the fragrances of many flowers and the pleasant tastes of ripened fruits. Bananas contain the ester amyl acetate, and oranges the ester octyl acetate. Beeswax and other waxes are composed of esters, as are animal and vegetable fats ...
Pre Ch15 HW
... 3. Structures and names of alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes (§15.2) 4. The distinctions among constitutional, optical, and geometric isomers (§15.2) 5. The importance of optical isomerism in organisms (§15.2) 6. The effect of restricted rotation around a π bond on the structures and properties of alken ...
... 3. Structures and names of alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes (§15.2) 4. The distinctions among constitutional, optical, and geometric isomers (§15.2) 5. The importance of optical isomerism in organisms (§15.2) 6. The effect of restricted rotation around a π bond on the structures and properties of alken ...
The Infinite Variety of Carbon Compounds
... All alcohols are toxic. Methanol for instance is oxidized to formaldehyde by liver enzymes. It can lead to blindness and death. Even ethanol is toxic. The effects of drinking ethanol are due to its toxicity. Drunk driving, alcoholism, and fetal alcohol syndrome are all effects due to the toxicity of ...
... All alcohols are toxic. Methanol for instance is oxidized to formaldehyde by liver enzymes. It can lead to blindness and death. Even ethanol is toxic. The effects of drinking ethanol are due to its toxicity. Drunk driving, alcoholism, and fetal alcohol syndrome are all effects due to the toxicity of ...
Lipids
... Sphingolipids are amino alcohols – note the amide in R2 and vinyl group in R3 • Named in the 1920s, when Egyptology was all the rage (“Sphinx” = mysterious) and these compounds were discovered and their function not known at the time • Now known to have many functions, including nerve cell sheaths ...
... Sphingolipids are amino alcohols – note the amide in R2 and vinyl group in R3 • Named in the 1920s, when Egyptology was all the rage (“Sphinx” = mysterious) and these compounds were discovered and their function not known at the time • Now known to have many functions, including nerve cell sheaths ...
F.example
... N.B. this reaction changes only the –OH group of the reaction. Dimethyl ether that is the structural isomer of ethyl alcohol cannot give the same reaction with sodium. Thus the functional group in dimethyl ether is not the same as that in ethyl alcohol. Another important organic family is that of th ...
... N.B. this reaction changes only the –OH group of the reaction. Dimethyl ether that is the structural isomer of ethyl alcohol cannot give the same reaction with sodium. Thus the functional group in dimethyl ether is not the same as that in ethyl alcohol. Another important organic family is that of th ...
슬라이드 1
... coupling is that the nickel reaction can be more readily applied to saturated alkyl groups because of a reduced tendency for b-elimination. ...
... coupling is that the nickel reaction can be more readily applied to saturated alkyl groups because of a reduced tendency for b-elimination. ...
Olive oil presentation of Italia
... Studies (human, animal, in vivo and in vitro) have shown that olive oil phenolics, for example, hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein, that are responsible for its peculiar taste and for its high stability, are powerful antioxidants and have positive effects on certain physiological parameters, such as ...
... Studies (human, animal, in vivo and in vitro) have shown that olive oil phenolics, for example, hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein, that are responsible for its peculiar taste and for its high stability, are powerful antioxidants and have positive effects on certain physiological parameters, such as ...
Chemistry 131
... The second half of the course is dedicated to how those compounds function in living systems (biochemistry). Course Mechanics: ...
... The second half of the course is dedicated to how those compounds function in living systems (biochemistry). Course Mechanics: ...
Exam 2 Study Guide
... Exam 2, on Tuesday May 8th, will cover chapters 13 and 14.1 to 14.3. The exam is an open lecture and lab note but closed textbook exam. You will be provided a copy of the periodic table, electronegativity values and trends and a table of the functional groups that we study in this course, and thus y ...
... Exam 2, on Tuesday May 8th, will cover chapters 13 and 14.1 to 14.3. The exam is an open lecture and lab note but closed textbook exam. You will be provided a copy of the periodic table, electronegativity values and trends and a table of the functional groups that we study in this course, and thus y ...
Phenols

In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest of the class is phenol, which is also called carbolic acid C6H5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule.Synonyms are arenols or aryl alcohols.Phenolic compounds are synthesized industrially; they also are produced by plants and microorganisms, with variation between and within species.Although similar to alcohols, phenols have unique properties and are not classified as alcohols (since the hydroxyl group is not bonded to a saturated carbon atom). They have higher acidities due to the aromatic ring's tight coupling with the oxygen and a relatively loose bond between the oxygen and hydrogen. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids (their pKa is usually between 10 and 12).Loss of a positive hydrogen ion (H+) from the hydroxyl group of a phenol forms a corresponding negative phenolate ion or phenoxide ion, and the corresponding salts are called phenolates or phenoxides, although the term aryloxides is preferred according to the IUPAC Gold Book. Phenols can have two or more hydroxy groups bonded to the aromatic ring(s) in the same molecule. The simplest examples are the three benzenediols, each having two hydroxy groups on a benzene ring.Organisms that synthesize phenolic compounds do so in response to ecological pressures such as pathogen and insect attack, UV radiation and wounding. As they are present in food consumed in human diets and in plants used in traditional medicine of several cultures, their role in human health and disease is a subject of research.ref name=Klepacka Some phenols are germicidal and are used in formulating disinfectants. Others possess estrogenic or endocrine disrupting activity.