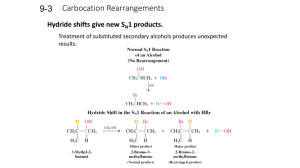
Carbocation Rearrangements
... Treatment of substituted secondary alcohols produces unexpected results: ...
... Treatment of substituted secondary alcohols produces unexpected results: ...
Workshop 5
... using either light or heat. Alternatively, tetramethyl lead ((CH3)4Pb) can be added to initiate this same reaction at a lower temperature. The Pb-C bond energy in (CH3)4Pb is 49 kcal/mol. a. Show the initiation and propagation steps for the chlorination of CH4 using (CH3)4Pb with CH4 and Cl2. Explai ...
... using either light or heat. Alternatively, tetramethyl lead ((CH3)4Pb) can be added to initiate this same reaction at a lower temperature. The Pb-C bond energy in (CH3)4Pb is 49 kcal/mol. a. Show the initiation and propagation steps for the chlorination of CH4 using (CH3)4Pb with CH4 and Cl2. Explai ...
Exam 1
... As mentioned in the text, diethyl ether, pentane, and 1-butanol have similar molar masses, but different physical properties. Boiling points are 35oC, 36oC, and 117oC, respectively. Their respective solubilities in water are 7.5g/100mL, insoluble, and 9g/100mL. (i) Draw structures for each of these ...
... As mentioned in the text, diethyl ether, pentane, and 1-butanol have similar molar masses, but different physical properties. Boiling points are 35oC, 36oC, and 117oC, respectively. Their respective solubilities in water are 7.5g/100mL, insoluble, and 9g/100mL. (i) Draw structures for each of these ...
Chemistry 218, Winter 2007 Exam 2 Name: 1.
... 5. Draw an energy diagram of the molecular orbitals of oxazole (you do not need to draw the molecular orbitals, just their relative energies). From your diagram, determine if the molecule is aromatic or anti-aromatic. (8 pts.) O N ...
... 5. Draw an energy diagram of the molecular orbitals of oxazole (you do not need to draw the molecular orbitals, just their relative energies). From your diagram, determine if the molecule is aromatic or anti-aromatic. (8 pts.) O N ...
Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction
... In above mechanism the overall rate is limited to that of the slower second stage which depends only on the concentration of the conjugate base of the reactant. This mechanism is called as E1cB which means elimination, unimolecular, conjugate base. The distinction between E2 and E1cB mechanism can b ...
... In above mechanism the overall rate is limited to that of the slower second stage which depends only on the concentration of the conjugate base of the reactant. This mechanism is called as E1cB which means elimination, unimolecular, conjugate base. The distinction between E2 and E1cB mechanism can b ...
Slide 1
... Two viable reaction mechanisms exist for this reaction. In the first mechanism 2-amino substituted carbonyl compound 1 and carbonyl compound 2 react in a rate-limiting step to aldol adduct 3. This intermediate loses water in an elimination reaction to unsaturated carbonyl compound 4 and then loses w ...
... Two viable reaction mechanisms exist for this reaction. In the first mechanism 2-amino substituted carbonyl compound 1 and carbonyl compound 2 react in a rate-limiting step to aldol adduct 3. This intermediate loses water in an elimination reaction to unsaturated carbonyl compound 4 and then loses w ...
E2 reactions
... Decide whether the following substrates could react by E1 or E2 (and by SN1 or SN2). Br ...
... Decide whether the following substrates could react by E1 or E2 (and by SN1 or SN2). Br ...
06 MC /08 MC /08 NMR
... only trans-l-4-dimethylcyclohexane. onlycrs-1-4-dimethylcyclohexane. both trans and cis-l -4-dimethylcyclohexane. It's impossible to tell. --'i ...
... only trans-l-4-dimethylcyclohexane. onlycrs-1-4-dimethylcyclohexane. both trans and cis-l -4-dimethylcyclohexane. It's impossible to tell. --'i ...
+ Y
... has an electron-poor atom (e.g H+, CH3+ ) and can form a bond by accepting a pair of electrons from a nucleophile ...
... has an electron-poor atom (e.g H+, CH3+ ) and can form a bond by accepting a pair of electrons from a nucleophile ...
CHE 322
... conditions, to make the indicated large compound? In each case show the reaction that makes the C-C or C-O bond that links the pieces. All three must be different kinds of reactions. [Caution: parts of some reaction partners are missing in the given products due to replacement or subsequent reaction ...
... conditions, to make the indicated large compound? In each case show the reaction that makes the C-C or C-O bond that links the pieces. All three must be different kinds of reactions. [Caution: parts of some reaction partners are missing in the given products due to replacement or subsequent reaction ...
CHAPTER 9 Further Reactions of Alcohols and the Chemistry of
... • Primary alcohols rearrange, so this is not a good reaction for converting 1° alcohols into alkenes. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • Primary alcohols rearrange, so this is not a good reaction for converting 1° alcohols into alkenes. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Slides for Chapter 1-4 - Department of Chemistry and Physics
... many alkyl halides(reaction as Lewis base) Nucleophiles that are Brønsted bases produce elimination ...
... many alkyl halides(reaction as Lewis base) Nucleophiles that are Brønsted bases produce elimination ...
Chapter 11: Reactions at an sp3 Hybridized Carbon III
... • TBS will replace H of an alcohol to act as a protecting group for the alcohol • Polarize H(+) and RO(-) in the alcohol and TBS(+) and Cl(-) in TBSCl • Si loves F even more than O and will grab F– and spit out RO– when you need to break off the TBS protecting group ...
... • TBS will replace H of an alcohol to act as a protecting group for the alcohol • Polarize H(+) and RO(-) in the alcohol and TBS(+) and Cl(-) in TBSCl • Si loves F even more than O and will grab F– and spit out RO– when you need to break off the TBS protecting group ...
Preface - Wiley Online Library
... Nitrogen is everywhere! Molecular nitrogen is the largest single component of the Earth’s atmosphere (78%); it constitutes 4% of the dry weight of plant matter and 3% by weight of the human body and is absolutely essential for life. In addition, over 90% of pharmaceutical substances contain at least ...
... Nitrogen is everywhere! Molecular nitrogen is the largest single component of the Earth’s atmosphere (78%); it constitutes 4% of the dry weight of plant matter and 3% by weight of the human body and is absolutely essential for life. In addition, over 90% of pharmaceutical substances contain at least ...
Unit 3: Reactions of Alkenes. Thermodynamics and Kinetics
... This symbol indicates that the reaction takes place under standard conditions --all species at 1 M, 25 OC, and 1 atm. ...
... This symbol indicates that the reaction takes place under standard conditions --all species at 1 M, 25 OC, and 1 atm. ...
Exam 2 Review A
... You should be able to predict the products of a given reaction, based upon an understanding of the reaction mechanisms (i.e., SN1 or SN2 or E1 or E2) operative for a given electrophile, nucleophile, and reaction conditions (solvent and temperature). [table 6.7] You should be able to work in the reve ...
... You should be able to predict the products of a given reaction, based upon an understanding of the reaction mechanisms (i.e., SN1 or SN2 or E1 or E2) operative for a given electrophile, nucleophile, and reaction conditions (solvent and temperature). [table 6.7] You should be able to work in the reve ...
Exam 2 Review A
... You should be able to predict the products of a given reaction, based upon an understanding of the reaction mechanisms (i.e., SN1 or SN2 or E1 or E2) operative for a given electrophile, nucleophile, and reaction conditions (solvent and temperature). [table 6.7] You should be able to work in the reve ...
... You should be able to predict the products of a given reaction, based upon an understanding of the reaction mechanisms (i.e., SN1 or SN2 or E1 or E2) operative for a given electrophile, nucleophile, and reaction conditions (solvent and temperature). [table 6.7] You should be able to work in the reve ...
Exam 2 Review A
... You should be able to predict the products of a given reaction, based upon an understanding of the reaction mechanisms (i.e., SN1 or SN2 or E1 or E2) operative for a given electrophile, nucleophile, and reaction conditions (solvent and temperature). [table 6.7] You should be able to work in the reve ...
... You should be able to predict the products of a given reaction, based upon an understanding of the reaction mechanisms (i.e., SN1 or SN2 or E1 or E2) operative for a given electrophile, nucleophile, and reaction conditions (solvent and temperature). [table 6.7] You should be able to work in the reve ...
Unit 3 Goals - kimscience.com
... o complete and balance combustion reactions of organic molecules containing carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, and explain the reaction in terms of bonds breaking and forming, enthalpy, and entropy change. o distinguish between complete and incomplete combustion in terms of reaction conditions, resulting ...
... o complete and balance combustion reactions of organic molecules containing carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, and explain the reaction in terms of bonds breaking and forming, enthalpy, and entropy change. o distinguish between complete and incomplete combustion in terms of reaction conditions, resulting ...
CHMY_271_practice_exam_3
... 11. (6 pt) If the following alkyl halide were to undergo elimination, predict the major product in each case, and explain your answer. You do not need to draw out the mechanism, but knowing the mechanism will help you to predict reasonable products. ...
... 11. (6 pt) If the following alkyl halide were to undergo elimination, predict the major product in each case, and explain your answer. You do not need to draw out the mechanism, but knowing the mechanism will help you to predict reasonable products. ...
- professional publication
... Electrophilic Aromatic Substitutions Effect of Substituent Groups, Determination of Orientation, Determination of Relative Reactivity, Classification of Substituent Groups, Mechanism of Nitration, Sulphonation, Halogenation, Friedel Craft’s Alkylation and Friedel Craft’s Acylation, Reactivity and Or ...
... Electrophilic Aromatic Substitutions Effect of Substituent Groups, Determination of Orientation, Determination of Relative Reactivity, Classification of Substituent Groups, Mechanism of Nitration, Sulphonation, Halogenation, Friedel Craft’s Alkylation and Friedel Craft’s Acylation, Reactivity and Or ...
Oxacyclopropane (Epoxide) Synthesis: Epoxidation by
... Catalytic amounts of osmium tetroxide in the presence of an oxidizing agent (H2O2) to regenerate the spent osmium tetroxide are often used, due to the expense and toxicity of OsO4. ...
... Catalytic amounts of osmium tetroxide in the presence of an oxidizing agent (H2O2) to regenerate the spent osmium tetroxide are often used, due to the expense and toxicity of OsO4. ...
Vinylcyclopropane rearrangement

The vinylcyclopropane rearrangement or vinylcyclopropane-cyclopentene rearrangement is a ring expansion reaction, converting a vinyl-substituted cyclopropane ring into a cyclopentene ring.Intense experimental as well as computational investigations have revealed that mechanistically, the vinylcyclopropane rearrangement can be thought of as either a diradical-mediated two-step and/or orbital-symmetry-controlled pericyclic process. The amount by which each of the two mechanisms is operative is highly dependent on the substrate.Due to its ability to form cyclopentene rings the vinylcyclopropane rearrangement has served several times as a key reaction in complex natural product synthesis.