Section 2A
... Atomic Number - tells the number of protons in an atom. In a neutral atom, the number of protons must equal the number of electrons. Atomic Mass - tells the total mass of the atom (protons and neutrons). A complete chemical symbol not only tells the symbol for an element, but also the information ab ...
... Atomic Number - tells the number of protons in an atom. In a neutral atom, the number of protons must equal the number of electrons. Atomic Mass - tells the total mass of the atom (protons and neutrons). A complete chemical symbol not only tells the symbol for an element, but also the information ab ...
Ch. 2 note packet
... John Dalton (1808) “Father of Atomic Theory” Essentials of his theory. . . 1. An element is composed of tiny particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element show the same chemical properties. 2. Atoms of different elements have different properties. In an ordinary chemical reaction, no atom of ...
... John Dalton (1808) “Father of Atomic Theory” Essentials of his theory. . . 1. An element is composed of tiny particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element show the same chemical properties. 2. Atoms of different elements have different properties. In an ordinary chemical reaction, no atom of ...
Document
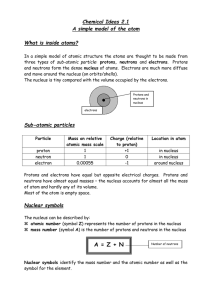
... Chemical Ideas 2.2 Nuclear reactions Emissions from radioactive substances Some isotopes of some elements are unstable, so their nuclei break down spontaneously and emit rays and particles called emissions. They are radioactive. This breakdown or RADIOACTIVE DECAY occurs without any need to be trig ...
... Chemical Ideas 2.2 Nuclear reactions Emissions from radioactive substances Some isotopes of some elements are unstable, so their nuclei break down spontaneously and emit rays and particles called emissions. They are radioactive. This breakdown or RADIOACTIVE DECAY occurs without any need to be trig ...
Chapter 3
... Developed a new diagram of the atom Electrons can only be at certain energies Electrons must gain a specific amount of energy to move to a higher level, called a quantum ...
... Developed a new diagram of the atom Electrons can only be at certain energies Electrons must gain a specific amount of energy to move to a higher level, called a quantum ...
NOTES: 2.1 - Intro to Chemistry
... ATOM: smallest unit of matter that retains the physical and chemical properties of its element ● three subatomic particles: ...
... ATOM: smallest unit of matter that retains the physical and chemical properties of its element ● three subatomic particles: ...
04-Atoms_ molecules_ ions_etc
... all the isotopes of an element • average of relative abundance x mass number for each isotope ...
... all the isotopes of an element • average of relative abundance x mass number for each isotope ...
Atomic Theory - Chemistry
... Atoms of the same element have the same properties. (mass, size, etc.) In a chemical reaction, matter cannot be created or destroyed – Law of Conservation of Mass ...
... Atoms of the same element have the same properties. (mass, size, etc.) In a chemical reaction, matter cannot be created or destroyed – Law of Conservation of Mass ...
Atomic Structure and Periodic Table Quick Notes
... (making it Neutrally Charged) Two types of Atoms: Ions- these are atoms that have LOST or GAINED an ELECTRON during a chemical reaction If an atom loses an electron, it becomes a Positive Ion If an atom gains an electron, it becomes a Negative Ion Ex: when Na reacts with Cl to form NaCl, the Na ...
... (making it Neutrally Charged) Two types of Atoms: Ions- these are atoms that have LOST or GAINED an ELECTRON during a chemical reaction If an atom loses an electron, it becomes a Positive Ion If an atom gains an electron, it becomes a Negative Ion Ex: when Na reacts with Cl to form NaCl, the Na ...
Atomic Notation
... ie. Lithium (refer to reference Periodic Table) Mass Number (A) :7 Atomic Number (Z): 3 Element Name (X): Li Number of Protons: 3 Number of Neutrons: 7 – 3 = 4 Number of Electrons: 3 (so that there will be a neutral charge) But why is the mass number rounded? -because there are different forms of an ...
... ie. Lithium (refer to reference Periodic Table) Mass Number (A) :7 Atomic Number (Z): 3 Element Name (X): Li Number of Protons: 3 Number of Neutrons: 7 – 3 = 4 Number of Electrons: 3 (so that there will be a neutral charge) But why is the mass number rounded? -because there are different forms of an ...
How to write up a practical: General review
... electrons and neutrons and some of their properties TO BE ABLE draw the basic structure of the atom. TO UNDERSTAND how these particles are physically arranged in relation to each other. ...
... electrons and neutrons and some of their properties TO BE ABLE draw the basic structure of the atom. TO UNDERSTAND how these particles are physically arranged in relation to each other. ...
Atoms pg. 102
... atoms that cannot be divided. 2. All atoms of the same element are exactly alike. 3. Atoms cannot be created or destroyed, only rearranged. 4. Every compound is composed of atoms of different elements combined in a specific ratio. ...
... atoms that cannot be divided. 2. All atoms of the same element are exactly alike. 3. Atoms cannot be created or destroyed, only rearranged. 4. Every compound is composed of atoms of different elements combined in a specific ratio. ...
Ch. 2-1 Nature of Matter
... by Miller and Levine, © 2007. These images have been produced from the originals by permission of the publisher. These illustrations may not be reproduced in any format for any purpose without express written permission from the publisher. ...
... by Miller and Levine, © 2007. These images have been produced from the originals by permission of the publisher. These illustrations may not be reproduced in any format for any purpose without express written permission from the publisher. ...
Candidate 2 - Elgin Academy
... The following is an extract from the SQA course Support Notes for National 5 Chemistry: Task 2 Assessment Standards 2.2 and 2.3 can be achieved using one or two pieces of evidence covering work done on different occasions. Assessors should record evidence of achievement of Outcomes and Assessment St ...
... The following is an extract from the SQA course Support Notes for National 5 Chemistry: Task 2 Assessment Standards 2.2 and 2.3 can be achieved using one or two pieces of evidence covering work done on different occasions. Assessors should record evidence of achievement of Outcomes and Assessment St ...
1.2 Atomic Theory
... The average atomic mass for magnesium found on the periodic table is a weighted average of the three isotopes: 24.31 g of Mg Radioactivity: spontaneous decay of nuclei, releasing energy and subatomic particles Radioisotopes: an unstable isotope of an element, which undergoes radioactive decay ...
... The average atomic mass for magnesium found on the periodic table is a weighted average of the three isotopes: 24.31 g of Mg Radioactivity: spontaneous decay of nuclei, releasing energy and subatomic particles Radioisotopes: an unstable isotope of an element, which undergoes radioactive decay ...
Chapter 18 Notes
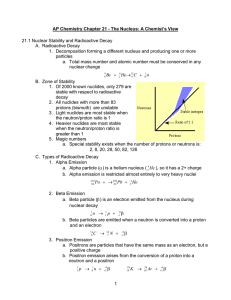
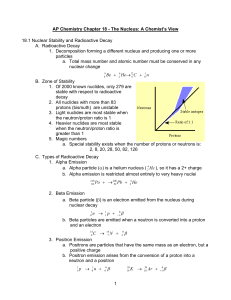
... AP Chemistry Chapter 18 - The Nucleus: A Chemist’s View 18.1 Nuclear Stability and Radioactive Decay A. Radioactive Decay 1. Decomposition forming a different nucleus and producing one or more particles a. Total mass number and atomic number must be conserved in any nuclear change ...
... AP Chemistry Chapter 18 - The Nucleus: A Chemist’s View 18.1 Nuclear Stability and Radioactive Decay A. Radioactive Decay 1. Decomposition forming a different nucleus and producing one or more particles a. Total mass number and atomic number must be conserved in any nuclear change ...
Flashback 2
... At the facility, uranium-235 is used to produce molybdenum, Mo, as well as other products. One of the isotopes of molybdenum produced at Chalk River is Mo-99. Possible isotopes of the element are: ...
... At the facility, uranium-235 is used to produce molybdenum, Mo, as well as other products. One of the isotopes of molybdenum produced at Chalk River is Mo-99. Possible isotopes of the element are: ...
Isotope

Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, although all isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons in each atom. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos (ἴσος ""equal"") and topos (τόπος ""place""), meaning ""the same place""; thus, the meaning behind the name it is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic number identifies a specific element, but not the isotope; an atom of a given element may have a wide range in its number of neutrons. The number of nucleons (both protons and neutrons) in the nucleus is the atom's mass number, and each isotope of a given element has a different mass number.For example, carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are three isotopes of the element carbon with mass numbers 12, 13 and 14 respectively. The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that every carbon atom has 6 protons, so that the neutron numbers of these isotopes are 6, 7 and 8 respectively.