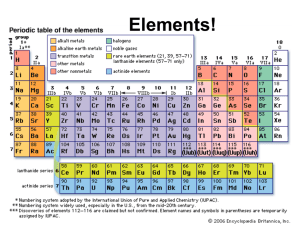
Atomic number
... 10-3 Masses of Atoms Isotopes - atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons (same # of protons); less common than the main element. The existence of isotopes accounts for the average atomic mass. Average atomic mass - the average mass of the mixture of an element & its isotope ...
... 10-3 Masses of Atoms Isotopes - atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons (same # of protons); less common than the main element. The existence of isotopes accounts for the average atomic mass. Average atomic mass - the average mass of the mixture of an element & its isotope ...
The parts of Dalton`s theory Matter is composed of small, chemically
... - ISOTOPES: are atoms of the same element with different mass numbers. In other words, they have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. ...
... - ISOTOPES: are atoms of the same element with different mass numbers. In other words, they have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. ...
1 - My eCoach
... c. Radioactive decay b. Individual elements d. Copper 30. The primary force that prevents the nucleus of an atom from flying apart is: a. Gravity c. The strong nuclear force b. The electrostatic force d. The weak nuclear force 32. Radioactive elements change into different elements as time goes by. ...
... c. Radioactive decay b. Individual elements d. Copper 30. The primary force that prevents the nucleus of an atom from flying apart is: a. Gravity c. The strong nuclear force b. The electrostatic force d. The weak nuclear force 32. Radioactive elements change into different elements as time goes by. ...
Atomic Structure
... following: Protons, neutrons, electrons, nucleus, electron cloud, any and all shells Write down the name, atomic number, atomic mass, and symbol ...
... following: Protons, neutrons, electrons, nucleus, electron cloud, any and all shells Write down the name, atomic number, atomic mass, and symbol ...
Unit 3 Review Worksheet
... ________9. Incorrectly believed, and wrote in his theory, that the atom was indivisible ________10. Credited with calculating the charge of a single electron ________11. The first to propose atomic theory based on scientific evidence ________12. Hypothesized that the model of the atom was like “Plum ...
... ________9. Incorrectly believed, and wrote in his theory, that the atom was indivisible ________10. Credited with calculating the charge of a single electron ________11. The first to propose atomic theory based on scientific evidence ________12. Hypothesized that the model of the atom was like “Plum ...
Unit 1 – Atomic Structure
... 2. Atoms are identified by their atomic number 3. Because atoms are neutral, # protons = # electrons 4. Periodic Table is in order of increasing atomic number B. Mass Number 1. The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an isotope C. Isotopes 1. Atoms of the same element that have di ...
... 2. Atoms are identified by their atomic number 3. Because atoms are neutral, # protons = # electrons 4. Periodic Table is in order of increasing atomic number B. Mass Number 1. The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an isotope C. Isotopes 1. Atoms of the same element that have di ...
PowerPoint - Models of the Atom
... • Electrons can be bumped up to a higher shell if hit by an electron or a photon of light. ...
... • Electrons can be bumped up to a higher shell if hit by an electron or a photon of light. ...
atomic models
... • Electrons can be bumped up to a higher shell if hit by an electron or a photon of light. ...
... • Electrons can be bumped up to a higher shell if hit by an electron or a photon of light. ...
Radioactive Isotopes and Nuclear Equations
... Radioactive Decay, Nuclear Equations, and Half-Lives I. View the “Nuclear Energy” video II. Radioactive Isotopes and Nuclear Equations Atoms are composed of three subatomic particles: protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of an atom. The total number of proto ...
... Radioactive Decay, Nuclear Equations, and Half-Lives I. View the “Nuclear Energy” video II. Radioactive Isotopes and Nuclear Equations Atoms are composed of three subatomic particles: protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of an atom. The total number of proto ...
Chapter 10 Power Point - Biloxi Public Schools
... 10-3 Masses of Atoms Isotopes - atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons (same # of protons); less common than the main element. The existence of isotopes accounts for the average atomic mass. Average atomic mass - the average mass of the mixture of an element & its isotope ...
... 10-3 Masses of Atoms Isotopes - atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons (same # of protons); less common than the main element. The existence of isotopes accounts for the average atomic mass. Average atomic mass - the average mass of the mixture of an element & its isotope ...
Element: a pure, simple substance that can`t be broken down into
... What do we call a horizontal row on the periodic table? What do we call the vertical columns on the periodic table? The number of protons in an atom is called the atomic ________? ...
... What do we call a horizontal row on the periodic table? What do we call the vertical columns on the periodic table? The number of protons in an atom is called the atomic ________? ...
Test 1
... Different isotopes of an element contain different numbers of neutrons. The three primary sub-atomic particles all have different charges. ...
... Different isotopes of an element contain different numbers of neutrons. The three primary sub-atomic particles all have different charges. ...
Structure of the Atom Cornell Notes (pg
... What are the 3 main subatomic particles? (p. 172) What is the nucleus of an atom? (p. 172 Fig. 1) How does the diameter of the nucleus compare to the diameter of the atom?(p. 172 Fig. 1) What are protons? What is their charge? Where are they located? (see Fig. 1) What are neutrons? What is their cha ...
... What are the 3 main subatomic particles? (p. 172) What is the nucleus of an atom? (p. 172 Fig. 1) How does the diameter of the nucleus compare to the diameter of the atom?(p. 172 Fig. 1) What are protons? What is their charge? Where are they located? (see Fig. 1) What are neutrons? What is their cha ...
bohrmodelofatomclassnote0
... and neutrons make up most of the mass of an atom. If the atom is neutral, the protons = electrons. An ion gains or loses electrons to get a full valence (outer) shell. ...
... and neutrons make up most of the mass of an atom. If the atom is neutral, the protons = electrons. An ion gains or loses electrons to get a full valence (outer) shell. ...
Radioactivity - Mrs. Sjuts` Science Site
... Small nuclei have few protons, so the repulsive force on a proton due to other protons is small In a large nuclei, the attractive strong force is exerted only by the nearest neighbors. All the protons exert repulsive forces making the repulsive force large. ...
... Small nuclei have few protons, so the repulsive force on a proton due to other protons is small In a large nuclei, the attractive strong force is exerted only by the nearest neighbors. All the protons exert repulsive forces making the repulsive force large. ...
Atomic Structure
... atoms Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties ...
... atoms Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties ...
atom - Images
... nucleus, the attraction due to the strong force is greater than the repulsion due to electrostatic force. As elements get heavier, they become more unstable. Extra neutrons must be present to the nucleus (like glue) to increase stability by increasing the strong force. Nuclear reactions are DIFFER ...
... nucleus, the attraction due to the strong force is greater than the repulsion due to electrostatic force. As elements get heavier, they become more unstable. Extra neutrons must be present to the nucleus (like glue) to increase stability by increasing the strong force. Nuclear reactions are DIFFER ...
Isotope

Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, although all isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons in each atom. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos (ἴσος ""equal"") and topos (τόπος ""place""), meaning ""the same place""; thus, the meaning behind the name it is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic number identifies a specific element, but not the isotope; an atom of a given element may have a wide range in its number of neutrons. The number of nucleons (both protons and neutrons) in the nucleus is the atom's mass number, and each isotope of a given element has a different mass number.For example, carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are three isotopes of the element carbon with mass numbers 12, 13 and 14 respectively. The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that every carbon atom has 6 protons, so that the neutron numbers of these isotopes are 6, 7 and 8 respectively.