Chapter 5
... o Atoms of the same element are identical o Atoms of different elements can physically mix or chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds o Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged, but they are never changed into another element - The radii of ...
... o Atoms of the same element are identical o Atoms of different elements can physically mix or chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds o Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged, but they are never changed into another element - The radii of ...
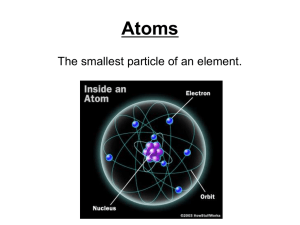
Atoms and Molecules
... and real magic tricks is that in a science magic trick we tell you how we did it • It looks like magic at first, but then you realize there really is no trick. Once you know how it’s done, you can do it too ...
... and real magic tricks is that in a science magic trick we tell you how we did it • It looks like magic at first, but then you realize there really is no trick. Once you know how it’s done, you can do it too ...
8th Grade Science Notes Chapter 2
... atoms have 6 protons each, oxygen atoms have 8 protons each, etc. Neutral Atoms - most atoms contain the same number of electrons as protons making them electrically neutral. Isotopes - atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. ...
... atoms have 6 protons each, oxygen atoms have 8 protons each, etc. Neutral Atoms - most atoms contain the same number of electrons as protons making them electrically neutral. Isotopes - atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. ...
Vocabulary for Periodic Table
... 6) Atomic mass number: the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus. 7) Isotope: atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons. 8) Ion: when an atom loses or gains electrons. 9) Atomic mass: the average mass of the atoms in an element. 10) Periodic Table: a tabl ...
... 6) Atomic mass number: the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus. 7) Isotope: atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons. 8) Ion: when an atom loses or gains electrons. 9) Atomic mass: the average mass of the atoms in an element. 10) Periodic Table: a tabl ...
Radioactivity - Science 9
... NUCLEAR FISSION: The splitting of an atomic nucleus into two smaller nuclei of approximately equal mass. This does not happen spontaneously, but usually happens in a chain reaction where the splitting of one nucleus triggers several others around it to do the same. Although the energy from one spl ...
... NUCLEAR FISSION: The splitting of an atomic nucleus into two smaller nuclei of approximately equal mass. This does not happen spontaneously, but usually happens in a chain reaction where the splitting of one nucleus triggers several others around it to do the same. Although the energy from one spl ...
Chapter 4 The structure of the Atom
... Atoms with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons 17. How do you identify an isotope? By the mass number 18. What is the mass number? The sum of the atomic number and the neutrons in the nucleus 19. Write some characteristics of isotopes Same chemical behavior Their abundance is ...
... Atoms with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons 17. How do you identify an isotope? By the mass number 18. What is the mass number? The sum of the atomic number and the neutrons in the nucleus 19. Write some characteristics of isotopes Same chemical behavior Their abundance is ...
Nuclear Chemistry I: Radioactivity Reading: Moore chapter 20
... particles by unstable atomic nuclei. It may refer to the energy or particles emitted. Note: The basic building blocks of the nucleus, neutrons and protons, are referred to as nucleons; forms of an element with the same atomic number and different mass numbers are isotopes. Some isotopes are stable; ...
... particles by unstable atomic nuclei. It may refer to the energy or particles emitted. Note: The basic building blocks of the nucleus, neutrons and protons, are referred to as nucleons; forms of an element with the same atomic number and different mass numbers are isotopes. Some isotopes are stable; ...
Document
... Atomic Mass (the decimal #’s) Atomic mass = ___________________________________________________. Representing Isotopes Isotopes are written using standard atomic notation. – Chemical symbol + atomic number + mass number. – Potassium has three isotopes, ...
... Atomic Mass (the decimal #’s) Atomic mass = ___________________________________________________. Representing Isotopes Isotopes are written using standard atomic notation. – Chemical symbol + atomic number + mass number. – Potassium has three isotopes, ...
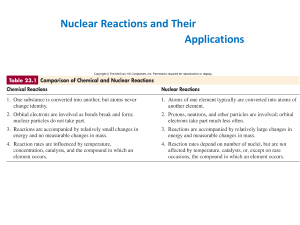
Nuclear Reactions and Their Applications
... Nuclides with 84 or more protons are unstable. Light nuclides are stable when Z equals A – Z (neutron/proton ratio is 1). For heavier elements the neutron/proton ratio required for stability is greater than 1 and increases with Z. Certain combinations of protons and neutrons seem to confer special s ...
... Nuclides with 84 or more protons are unstable. Light nuclides are stable when Z equals A – Z (neutron/proton ratio is 1). For heavier elements the neutron/proton ratio required for stability is greater than 1 and increases with Z. Certain combinations of protons and neutrons seem to confer special s ...
Earth Chemistry
... Electrons dictate the many properties of a material including chemical reactivity and physical attributes, like taste, texture, appearance and color. ...
... Electrons dictate the many properties of a material including chemical reactivity and physical attributes, like taste, texture, appearance and color. ...
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions Chapter 2 Handout 1 The Atom Dalton`s
... In order to symbolically represent elements and isotopes chemists use the following notation: ...
... In order to symbolically represent elements and isotopes chemists use the following notation: ...
Atomic Structure [PowerPoint]
... • Atoms of the same element may have different number of neutrons, thus varying mass numbers. ...
... • Atoms of the same element may have different number of neutrons, thus varying mass numbers. ...
IPC Atoms and Periodic Table
... start with actinium (Ac) at atomic number 89 and finishing up with lawrencium (Lr) at number 103. • They are all radioactive and some are not found in nature. ...
... start with actinium (Ac) at atomic number 89 and finishing up with lawrencium (Lr) at number 103. • They are all radioactive and some are not found in nature. ...
Lecture
... the binding energy is(not) great enough to hold the nucleus together. Unstable atoms will lose neutrons or protons as they attempt to become stable. They are called radioactive atoms. What is a radioactive decay? o spontaneous breakdown of an atomic nucleus resulting in the release of nuclear radiat ...
... the binding energy is(not) great enough to hold the nucleus together. Unstable atoms will lose neutrons or protons as they attempt to become stable. They are called radioactive atoms. What is a radioactive decay? o spontaneous breakdown of an atomic nucleus resulting in the release of nuclear radiat ...
Learning Targets Chapter 4
... relative mass of protons (p+) , neutrons (n0) and electrons (e-) in an atom. I can calculate the number of protons (p+) , neutrons (n0) and electrons (e-) in an atom using the atomic number, mass number and overall charge of the atom or a periodic table provided. I can describe the similarity and di ...
... relative mass of protons (p+) , neutrons (n0) and electrons (e-) in an atom. I can calculate the number of protons (p+) , neutrons (n0) and electrons (e-) in an atom using the atomic number, mass number and overall charge of the atom or a periodic table provided. I can describe the similarity and di ...
Radioactivity Notes Day 1 and 2 Apr 23 and Apr 24
... Radioactivity and Its History • Radiation is everywhere, but can be difficult to detect. ...
... Radioactivity and Its History • Radiation is everywhere, but can be difficult to detect. ...
PowerPoint - Models of the Atom - A Historical Perspective
... Isotopes and Radioisotopes Isotopes: Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons – Due to isotopes, mass #s are not round #s. – E.g. Li (6.9) is made up of both 6Li and 7Li. – Often, at least one isotope is unstable.It breaks down, releasing radioactivity.These types of isotop ...
... Isotopes and Radioisotopes Isotopes: Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons – Due to isotopes, mass #s are not round #s. – E.g. Li (6.9) is made up of both 6Li and 7Li. – Often, at least one isotope is unstable.It breaks down, releasing radioactivity.These types of isotop ...
Isotope

Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, although all isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons in each atom. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos (ἴσος ""equal"") and topos (τόπος ""place""), meaning ""the same place""; thus, the meaning behind the name it is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic number identifies a specific element, but not the isotope; an atom of a given element may have a wide range in its number of neutrons. The number of nucleons (both protons and neutrons) in the nucleus is the atom's mass number, and each isotope of a given element has a different mass number.For example, carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are three isotopes of the element carbon with mass numbers 12, 13 and 14 respectively. The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that every carbon atom has 6 protons, so that the neutron numbers of these isotopes are 6, 7 and 8 respectively.











![Atomic Structure [PowerPoint]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000122096_1-1d100da6540d2f26db122fc51f672fe5-300x300.png)