* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atomic Structure [PowerPoint]
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
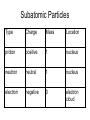
Atomic Structure Atom • The smallest part of an element with all the properties of the element. • Also called the building blocks of matter • Composed of protons, neutrons, & electrons. • * Subatomic Particles Type Charge Mass Location proton positive 1 nucleus neutron neutral 1 nucleus electron negative 0 electron cloud Protons • The protons determine the element. • The number of protons is equal to the atomic number. • Any atom with the same number of protons is the same element. • * Mass Number • The mass number is equal to the total number of protons plus the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. • Atoms of the same element may have different number of neutrons, thus varying mass numbers. • * Isotopes • Atoms of the same element with different number of neutrons. • Atoms of the same element with different mass numbers. • * Nucleus • What holds the protons together within the nucleus? • A force called the strong nuclear force overcomes the electromagnetic force that repels the positively charged protons. • * Electrons • The number of electrons in a neutral atom is equal to the number of protons. • Electrons are located in the electron cloud. • * Electron Cloud • Electrons are separated within the electron cloud because of their like charge repels them. • They are divided into energy levels and further divided into orbitals. • Orbitals can overlap.