Chapter 2, section 4 Formation of Elements
... When atoms decay by emitting a or b particles to form a new atom, the nuclei of the new atom formed may still have too much energy to be completely stable. This excess energy is emitted as gamma ...
... When atoms decay by emitting a or b particles to form a new atom, the nuclei of the new atom formed may still have too much energy to be completely stable. This excess energy is emitted as gamma ...
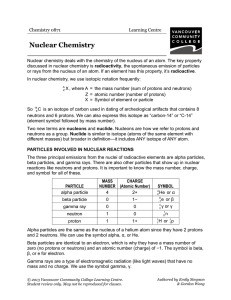
Nuclear Chemistry - VCC Library
... neutrons and 6 protons. We can also express this isotope as “carbon-14” or “C-14” (element symbol followed by mass number). Two new terms are nucleons and nuclide. Nucleons are how we refer to protons and neutrons as a group. Nuclide is similar to isotope (atoms of the same element with different ma ...
... neutrons and 6 protons. We can also express this isotope as “carbon-14” or “C-14” (element symbol followed by mass number). Two new terms are nucleons and nuclide. Nucleons are how we refer to protons and neutrons as a group. Nuclide is similar to isotope (atoms of the same element with different ma ...
03 Atoms – Nuclides
... Radioactivity is the ability of an unstable atomic nucleus to transform into a stable product or another unstable product while emitting radiation. This transformation and emission of energy is called radioactive decay. A transformation from one element to another is known as a transmutation. The ra ...
... Radioactivity is the ability of an unstable atomic nucleus to transform into a stable product or another unstable product while emitting radiation. This transformation and emission of energy is called radioactive decay. A transformation from one element to another is known as a transmutation. The ra ...
Life of a star
... In stars with masses comparable to the sun, the nucleus stops collapsing only when the inner temperature reaches above 100 million degrees, the threshold temperature necessary to start up nuclear fusions again. This time helium atoms fuse with carbon atoms releasing the necessary energy to regain th ...
... In stars with masses comparable to the sun, the nucleus stops collapsing only when the inner temperature reaches above 100 million degrees, the threshold temperature necessary to start up nuclear fusions again. This time helium atoms fuse with carbon atoms releasing the necessary energy to regain th ...
File
... All elements in order A unit of energy Positive or negative charge on an atom or group of atoms Atoms of the same element with different atomic mass A negatively charged particle A positively charged particle An atomic particle with no charge Used Boyle’s information to create the atomic theory The ...
... All elements in order A unit of energy Positive or negative charge on an atom or group of atoms Atoms of the same element with different atomic mass A negatively charged particle A positively charged particle An atomic particle with no charge Used Boyle’s information to create the atomic theory The ...
Chapter 7. Atomic Structure and Periodicity Part B. Definition and
... from left to right across a period, there are several exceptions to this rule in each period, which consider the change in electron repulsions as a function of electron configuration. ...
... from left to right across a period, there are several exceptions to this rule in each period, which consider the change in electron repulsions as a function of electron configuration. ...
Chem vocab quiz definitons
... the total mass of the reactants must equal the total mass of the products. Physical Change is a change in shape or form. Law of Conservation of Energy is the principle that the total amount energy stays the same during a chemical reaction. Ionic Bond is a chemical bond formed as a result of the attr ...
... the total mass of the reactants must equal the total mass of the products. Physical Change is a change in shape or form. Law of Conservation of Energy is the principle that the total amount energy stays the same during a chemical reaction. Ionic Bond is a chemical bond formed as a result of the attr ...
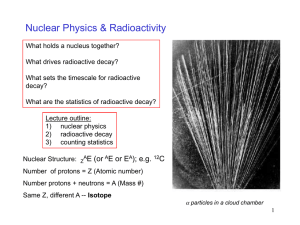
Radioactivity
... A large nucleus (A 200 ) splits into two. The daughter fragments have higher binding energy than the parent. They are more stable. It was found (in 1939) that if uranium was bombarded with neutrons (these have no charge and are not repelled by the nuclei), that a uranium nucleus could be split into ...
... A large nucleus (A 200 ) splits into two. The daughter fragments have higher binding energy than the parent. They are more stable. It was found (in 1939) that if uranium was bombarded with neutrons (these have no charge and are not repelled by the nuclei), that a uranium nucleus could be split into ...
05 shell model
... already seen that the Shell Model does not predict magnetic dipole moments or the spectra of excited states very well. One further failing of the Shell Model are the predictions of electric quadrupole moments, which in the Shell Model are predicted to be very small. However, heavier nuclei with A in ...
... already seen that the Shell Model does not predict magnetic dipole moments or the spectra of excited states very well. One further failing of the Shell Model are the predictions of electric quadrupole moments, which in the Shell Model are predicted to be very small. However, heavier nuclei with A in ...
Chemistry
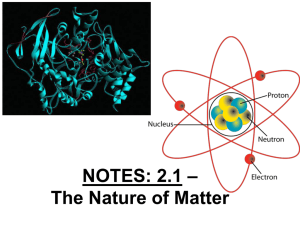
... Electrons, protons, and neutrons are parts of the atom and have measurable properties, including mass and, in the case of protons and electrons, charge. The nuclei of atoms are composed of protons and neutrons. A kind of force that is only evident at nuclear distances holds the particles of the nucl ...
... Electrons, protons, and neutrons are parts of the atom and have measurable properties, including mass and, in the case of protons and electrons, charge. The nuclei of atoms are composed of protons and neutrons. A kind of force that is only evident at nuclear distances holds the particles of the nucl ...
Document
... • Binding energy due to fact that nucleons are in potential well, ie. have –ve potential energy – energy needs to be supplied to remove nucleons ...
... • Binding energy due to fact that nucleons are in potential well, ie. have –ve potential energy – energy needs to be supplied to remove nucleons ...
ppt
... Remember that, after a radioactive isotope has decayed, the new isotopes may also be radioactive. ...
... Remember that, after a radioactive isotope has decayed, the new isotopes may also be radioactive. ...
Chapter #20 Nuclear Chemistry
... Light elements are stable if the neutrons and protons are equal, i.e. 1:1 ration, heavier nuclides require a ratio of 1:1.5 Magic numbers of protons and neutrons seem to exist, much like 8 electrons to make elements and ions Nobel. ...
... Light elements are stable if the neutrons and protons are equal, i.e. 1:1 ration, heavier nuclides require a ratio of 1:1.5 Magic numbers of protons and neutrons seem to exist, much like 8 electrons to make elements and ions Nobel. ...
1 - M*W
... 49) Magnesium dissolves in hydrochloric acid to produce magnesium chloride and hydrogen gas. Which of the following represents the reactants in this reaction? a) Magnesium and magnesium chloride b) Hydrochloric acid and hydrogen gas c) Magnesium and hydrochloric acid d) Magnesium chloride and hydrog ...
... 49) Magnesium dissolves in hydrochloric acid to produce magnesium chloride and hydrogen gas. Which of the following represents the reactants in this reaction? a) Magnesium and magnesium chloride b) Hydrochloric acid and hydrogen gas c) Magnesium and hydrochloric acid d) Magnesium chloride and hydrog ...
So where did all the matter on Earth come from - Bennatti
... Each element has a unique number of protons. The number of protons is its atomic number. For example, hydrogen has the atomic number 1 meaning each hydrogen atom has one proton in its nucleus. No other atom has one proton in its nucleus. Hydrogen is the simplest element. The atomic number of helium ...
... Each element has a unique number of protons. The number of protons is its atomic number. For example, hydrogen has the atomic number 1 meaning each hydrogen atom has one proton in its nucleus. No other atom has one proton in its nucleus. Hydrogen is the simplest element. The atomic number of helium ...