Chemical Basis of Life
... Composed of atoms 2+ of same atoms is a molecule (O2) 2+ of different atoms is a compound (NaCl, H2O) ...
... Composed of atoms 2+ of same atoms is a molecule (O2) 2+ of different atoms is a compound (NaCl, H2O) ...
Chapter 4 Study Guide-Atomic Structure Define the following terms
... Atomic Mass Unit (amu)-unit of mass of a proton or neutron (1 amu each) Atomic number-number of protons, periodic table Dalton’s Atomic Theory-first theory to relate chemical changes to events at the atomic level Electron-negatively charged subatomic particle, lives outside of the nucleus Group-vert ...
... Atomic Mass Unit (amu)-unit of mass of a proton or neutron (1 amu each) Atomic number-number of protons, periodic table Dalton’s Atomic Theory-first theory to relate chemical changes to events at the atomic level Electron-negatively charged subatomic particle, lives outside of the nucleus Group-vert ...
Physics
... Describe how general relativity theory pictures Newton’s gravitational force as a distortion of space and time. Explain that Marie and Pierre Curie made radium available to researchers all over the world, increasing the study of radioactivity and leading to the realization that one kind of atom may ...
... Describe how general relativity theory pictures Newton’s gravitational force as a distortion of space and time. Explain that Marie and Pierre Curie made radium available to researchers all over the world, increasing the study of radioactivity and leading to the realization that one kind of atom may ...
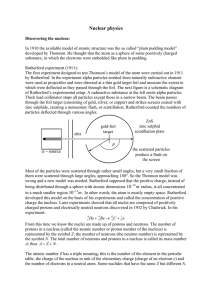
Nuclear physics α −
... number of nucleons. The nuclear interaction goes into saturation. The curve has a minimum at ...
... number of nucleons. The nuclear interaction goes into saturation. The curve has a minimum at ...
Section G23: Atoms and Radioactivity
... 7.2 describe the structure of an atom in terms of protons, neutrons and electrons and use symbols such as C 14 6 to describe particular nuclei 7.3 understand the terms atomic (proton) number, mass (nucleon) number and isotope 7.4 understand that alpha and beta particles and gamma rays are ionising r ...
... 7.2 describe the structure of an atom in terms of protons, neutrons and electrons and use symbols such as C 14 6 to describe particular nuclei 7.3 understand the terms atomic (proton) number, mass (nucleon) number and isotope 7.4 understand that alpha and beta particles and gamma rays are ionising r ...
Nuclear Fission and Nuclear Fusion
... nucleus with a particle. Split the atom releasing high energy, more high energy neutrons, and two daughter nuclides. Fission occurs only rarely in nature. Alpha decay is much more common. ...
... nucleus with a particle. Split the atom releasing high energy, more high energy neutrons, and two daughter nuclides. Fission occurs only rarely in nature. Alpha decay is much more common. ...
A2_Unit5_Nuclear_13_Binding_Energy
... getting less. The explanation for this observation lies in that the strong nuclear force that binds the nucleus together has a very limited range, and there is a limit to the number of nucleons that can be crammed into a particular space. ...
... getting less. The explanation for this observation lies in that the strong nuclear force that binds the nucleus together has a very limited range, and there is a limit to the number of nucleons that can be crammed into a particular space. ...
Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity2
... fundamental forces, gravitational, strong nuclear, weak nuclear, and electromagnetic, were originally one force at the universe's beginning. The electromagnetic and the weak nuclear forces were unified into the electroweak force in the 1970's. Nuclear Energy In 1934, Enrico Fermi and Emilio Segré bo ...
... fundamental forces, gravitational, strong nuclear, weak nuclear, and electromagnetic, were originally one force at the universe's beginning. The electromagnetic and the weak nuclear forces were unified into the electroweak force in the 1970's. Nuclear Energy In 1934, Enrico Fermi and Emilio Segré bo ...
biol 1406 chapter 3: water
... Determine if the statement is true. If it is not, rewrite the italicized part to make it true. 1. An element is a substance that can be broken down into simpler substances. ______________________ 2. On Earth, 90 elements occur naturally. ________________________________________ 3. Only four elements ...
... Determine if the statement is true. If it is not, rewrite the italicized part to make it true. 1. An element is a substance that can be broken down into simpler substances. ______________________ 2. On Earth, 90 elements occur naturally. ________________________________________ 3. Only four elements ...
Nuclear Chemistry powerpoint
... ) and no charge ( ). Thus, it causes change in or numbers. Gamma rays almost accompany alpha and beta radiation. However, since there is effect on mass number or atomic number, they are usually from nuclear equations. ...
... ) and no charge ( ). Thus, it causes change in or numbers. Gamma rays almost accompany alpha and beta radiation. However, since there is effect on mass number or atomic number, they are usually from nuclear equations. ...
Alpha Decay
... The alpha particle is a helium nucleus (2protons, 2 neutrons) produced from the radioactive decay of heavy metals and some nuclear reaction. The high positive charge (2+) of an alpha particle causes electrical excitation and ionization of surrounding atoms. Alpha particles are the least penetr ...
... The alpha particle is a helium nucleus (2protons, 2 neutrons) produced from the radioactive decay of heavy metals and some nuclear reaction. The high positive charge (2+) of an alpha particle causes electrical excitation and ionization of surrounding atoms. Alpha particles are the least penetr ...