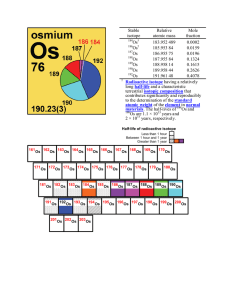
Stable isotope Relative atomic mass Mole fraction Os 183.952 489
... and an equal but opposite (positive) charge. proton – an elementary particle having a rest mass of about 1.673 × 10–27 kg, slightly less than that of a neutron, and a positive electric charge equal and opposite to that of the electron. The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is the atomic nu ...
... and an equal but opposite (positive) charge. proton – an elementary particle having a rest mass of about 1.673 × 10–27 kg, slightly less than that of a neutron, and a positive electric charge equal and opposite to that of the electron. The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is the atomic nu ...
Textbook Unit 4 Review Solutions
... fundamental particle: a particle that cannot be divided into smaller particles; an elementary particle fusion: reaction in which two low-mass nuclei combine to form a single nucleus with A < 60, resulting in a nucleus that is more tightly bound; the energy given off equals the difference between the ...
... fundamental particle: a particle that cannot be divided into smaller particles; an elementary particle fusion: reaction in which two low-mass nuclei combine to form a single nucleus with A < 60, resulting in a nucleus that is more tightly bound; the energy given off equals the difference between the ...
atomic number
... electrons The electrons move around in the empty space of the atom surrounding the nucleus Rutherford proposed that the nucleus had a particle that had the same amount of charge as an electron but opposite sign - based on measurements of the nuclear charge of the elements These particles are called ...
... electrons The electrons move around in the empty space of the atom surrounding the nucleus Rutherford proposed that the nucleus had a particle that had the same amount of charge as an electron but opposite sign - based on measurements of the nuclear charge of the elements These particles are called ...
Matter – Properties and Changes
... Alkali Metals and Alkaline Earth Metals are Groups 1A and 2A, respectively. Alkali Metals form ions with +1 charge, and Alkaline Earth Metals for ions with +2 charge. ...
... Alkali Metals and Alkaline Earth Metals are Groups 1A and 2A, respectively. Alkali Metals form ions with +1 charge, and Alkaline Earth Metals for ions with +2 charge. ...
1 - Groupfusion.net
... experiments. Usually taken as “fact” by most scientists. Theory: An explanation supported by many experiments, but is still subject to new experimental data, and can be modified C. What is the difference between a hypothesis and a theory? ...
... experiments. Usually taken as “fact” by most scientists. Theory: An explanation supported by many experiments, but is still subject to new experimental data, and can be modified C. What is the difference between a hypothesis and a theory? ...
`background radiation`.
... ionization? Only Alpha and Beta. 3.What is an isotope? Atoms of the same element with a different Mass number (i.e. different numbers of neutrons). 4.What is a radioisotope? An isotope/s of an element which emits nuclear radiation ...
... ionization? Only Alpha and Beta. 3.What is an isotope? Atoms of the same element with a different Mass number (i.e. different numbers of neutrons). 4.What is a radioisotope? An isotope/s of an element which emits nuclear radiation ...
Unit 2 Spiraling
... (You must know everything in Unit 1 and add to it the following information) Essential Knowledge Atoms are made of three types of subatomic particles: protons, neutrons and electrons. Each atom has a nucleus in the center, made of protons and neutrons packed tightly together. An electron cloud surro ...
... (You must know everything in Unit 1 and add to it the following information) Essential Knowledge Atoms are made of three types of subatomic particles: protons, neutrons and electrons. Each atom has a nucleus in the center, made of protons and neutrons packed tightly together. An electron cloud surro ...
File first semester final study guide key
... particles with no charge. ____Electrons____ are negatively charged particles that are found outside the nucleus. Atoms can become charged when they gain or lose electrons. A __anion_______ is a negatively charged ion and a ____cation______ is a positively charged ion. When an atom has a different nu ...
... particles with no charge. ____Electrons____ are negatively charged particles that are found outside the nucleus. Atoms can become charged when they gain or lose electrons. A __anion_______ is a negatively charged ion and a ____cation______ is a positively charged ion. When an atom has a different nu ...
NOTES Atomic Structure Number Mass.docx
... measure – atomic mass. Atomic mass is the relative average mass of an atom of the element. There are no mass units for atomic mass. They are simply a ratio. Carbon has an atomic mass of 12, so it is 12 times heavier than hydrogen, which is 1. Oxygen atoms have 16 times more mass than hydrogen. John ...
... measure – atomic mass. Atomic mass is the relative average mass of an atom of the element. There are no mass units for atomic mass. They are simply a ratio. Carbon has an atomic mass of 12, so it is 12 times heavier than hydrogen, which is 1. Oxygen atoms have 16 times more mass than hydrogen. John ...
Solutions - Dynamic Science
... The smallest particle of matter. The smallest possible sugar crystal. The smallest particle of water. The energy given off during a chemical reaction. ...
... The smallest particle of matter. The smallest possible sugar crystal. The smallest particle of water. The energy given off during a chemical reaction. ...
Episode 534 - Teaching Advanced Physics
... that were being discovered. It was possible to identify elements from the spectrum of the light they gave out when heated. It should be possible to do much the same for radioactive sources using these newer emissions. What they were beginning to realise at this time was that a good emitter like radi ...
... that were being discovered. It was possible to identify elements from the spectrum of the light they gave out when heated. It should be possible to do much the same for radioactive sources using these newer emissions. What they were beginning to realise at this time was that a good emitter like radi ...