Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
... resonance” when it is irradiated with RF photons having energy equal to the energy difference between the spin states. ¾ A photon with the right amount of energy can be absorbed and cause the spinning proton to flip. ...
... resonance” when it is irradiated with RF photons having energy equal to the energy difference between the spin states. ¾ A photon with the right amount of energy can be absorbed and cause the spinning proton to flip. ...
Matter—anything that has mass and occupies space Weight—pull of
... Atomic number, mass number, atomic weight Give “picture” of each element Allow identification ...
... Atomic number, mass number, atomic weight Give “picture” of each element Allow identification ...
Chemistry Test Study Guide
... 21. A mixture is created when two pure substances are combined so that each of the pure substances retains its own properties. 22. Where is the majority of the mass of an atom located? In the nucleus.(Protons and Neutrons) 23. If an atom loses electron’s, will it have a positive or negative charge? ...
... 21. A mixture is created when two pure substances are combined so that each of the pure substances retains its own properties. 22. Where is the majority of the mass of an atom located? In the nucleus.(Protons and Neutrons) 23. If an atom loses electron’s, will it have a positive or negative charge? ...
Practice problems for chapter 1, 2 and 3 1) A small amount of salt
... 31) Elements in Group 7A are known as the __________. A) chalcogens B) alkali metals C) alkaline earth metals D) halogens E) noble gases 32) When a metal and a nonmetal react, the __________ tends to lose electrons and the __________ tends to gain electrons. A) metal, metal B) nonmetal, nonmetal C) ...
... 31) Elements in Group 7A are known as the __________. A) chalcogens B) alkali metals C) alkaline earth metals D) halogens E) noble gases 32) When a metal and a nonmetal react, the __________ tends to lose electrons and the __________ tends to gain electrons. A) metal, metal B) nonmetal, nonmetal C) ...
25.3 Fission and Fusion of Atomic Nuclei
... A fusionist might bring together different factions into one cohesive group. ...
... A fusionist might bring together different factions into one cohesive group. ...
Effective Nuclear charge
... •Effective nuclear charge (Zeff): actual charge _________________________ •Main concept of Ch. 7 ...
... •Effective nuclear charge (Zeff): actual charge _________________________ •Main concept of Ch. 7 ...
Chemistry: Matter and Change
... • Marie Curie and her husband Pierre isolated the first radioactive materials. ...
... • Marie Curie and her husband Pierre isolated the first radioactive materials. ...
Physics Sample Questions
... 2. Alpha particles move in air in straight lines, because of their high momentum 3. Typically an alpha particle shot in air produces about 105 ion pairs per cm 4. Alpha particles are emitted by nuclei with mass numbers greater than 200 5. Alpha particles are not deflected as they pass through a magn ...
... 2. Alpha particles move in air in straight lines, because of their high momentum 3. Typically an alpha particle shot in air produces about 105 ion pairs per cm 4. Alpha particles are emitted by nuclei with mass numbers greater than 200 5. Alpha particles are not deflected as they pass through a magn ...
Nuclear and Thermal Physics
... characteristic of nuclei having a large proportion of neutrons (neutron changes to proton). + emission is characteristic of nuclei having a large proportion of protons. The ejected electrons come from the nucleus rather than from the electron cloud, and yet do not exist as electrons while in the n ...
... characteristic of nuclei having a large proportion of neutrons (neutron changes to proton). + emission is characteristic of nuclei having a large proportion of protons. The ejected electrons come from the nucleus rather than from the electron cloud, and yet do not exist as electrons while in the n ...
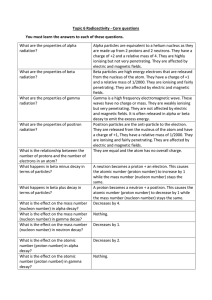
Topic 6 Radioactivity Core Questions
... particles are repelled by positive charge. It was detected that most of the alpha particles (7999/8000) went straight through the foil but a small number (1/8000) of the alpha particles were deflected through anything from 1 ͦ to 180 ͦ (straight back at them). Rutherford explained the results and sa ...
... particles are repelled by positive charge. It was detected that most of the alpha particles (7999/8000) went straight through the foil but a small number (1/8000) of the alpha particles were deflected through anything from 1 ͦ to 180 ͦ (straight back at them). Rutherford explained the results and sa ...
atoms
... Alpha (a): a-particles carry two fundamental units of positive charge and the same mass as helium atoms. This particle are identical to He2+ions Beta (b): b-particles are negatively charged and have the same properties as electrons Gamma (g) rays: is not effected by electric or magnetic field. ...
... Alpha (a): a-particles carry two fundamental units of positive charge and the same mass as helium atoms. This particle are identical to He2+ions Beta (b): b-particles are negatively charged and have the same properties as electrons Gamma (g) rays: is not effected by electric or magnetic field. ...
Quarter 1 Unit 3 Radioactivitypptx
... Radioactive decay has provided scientists with a technique for determining the age of fossils, geological formations and human artifacts. ...
... Radioactive decay has provided scientists with a technique for determining the age of fossils, geological formations and human artifacts. ...
atoms
... develop on the comb and causes bits of paper to be attracted to the comb (b) Both objects on the left carry negative charge repel each other The objects in the center lack any electrical charge and exert no force on each other ...
... develop on the comb and causes bits of paper to be attracted to the comb (b) Both objects on the left carry negative charge repel each other The objects in the center lack any electrical charge and exert no force on each other ...