ps-5-1-and-5-2-ws
... Introduction to Atoms 5.1 & 5.2 1. What three particles are found in an atom? 2. Which two particles are found in an atom’s nucleus? 3. Explain why scientists use models to study atoms. ...
... Introduction to Atoms 5.1 & 5.2 1. What three particles are found in an atom? 2. Which two particles are found in an atom’s nucleus? 3. Explain why scientists use models to study atoms. ...
electron
... mass 10.012 amu and a relative abundance of 19.91%. The isotope with mass 11.009 amu has a relative abundance of 80.09%. 1. Calculate the atomic mass of this element (show all work) and then name this element. ...
... mass 10.012 amu and a relative abundance of 19.91%. The isotope with mass 11.009 amu has a relative abundance of 80.09%. 1. Calculate the atomic mass of this element (show all work) and then name this element. ...
Review 2 key - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]
... 7 Explain what the strong force is and the purpose of it. The strong force is the force that keeps the protons and neutrons in the nucleus. It holds them together even though all of the protons are positively charged and should be repel. 8 What is an isotope? Atoms of the same element that have di ...
... 7 Explain what the strong force is and the purpose of it. The strong force is the force that keeps the protons and neutrons in the nucleus. It holds them together even though all of the protons are positively charged and should be repel. 8 What is an isotope? Atoms of the same element that have di ...
Atomic Structure Past Paper Questions
... Explain why the difference between the 4th and 5th ionization energies is much greater than the difference between any two other successive values. (2) ...
... Explain why the difference between the 4th and 5th ionization energies is much greater than the difference between any two other successive values. (2) ...
File
... 19. What is the name of the process in which the nucleus of an atom of one element is changed into the nucleus of an atom of a different element? A) decomposition C) substitution ...
... 19. What is the name of the process in which the nucleus of an atom of one element is changed into the nucleus of an atom of a different element? A) decomposition C) substitution ...
Atoms - RPDP
... The electrons in an atom are not all the same distance from the nucleus. Those farthest away from the nucleus are called valence electrons. Valence electrons are involved in chemical ...
... The electrons in an atom are not all the same distance from the nucleus. Those farthest away from the nucleus are called valence electrons. Valence electrons are involved in chemical ...
Nuclear Fusion
... Fission- splitting of nuclei into smaller nuclei Radioactive Decay or radioactivity Reactions begin with unstable isotopes called radioisotopes that undergo change to become stable ...
... Fission- splitting of nuclei into smaller nuclei Radioactive Decay or radioactivity Reactions begin with unstable isotopes called radioisotopes that undergo change to become stable ...
History of the Atom & Atomic Structure
... ▪ No experiments performed! Major Contribution: The Atom ▪ He proposed that everything was made of these atoms and they were all indivisible ...
... ▪ No experiments performed! Major Contribution: The Atom ▪ He proposed that everything was made of these atoms and they were all indivisible ...
Chemistry Worksheet: Atomic Structure and Isotopes
... 8. einsteinium 9. boron 10. oxygen 11. einsteinium ...
... 8. einsteinium 9. boron 10. oxygen 11. einsteinium ...
Atomic structure
... How do ions form? • The majority of atoms are not happy • In an attempt to become happy (& chemically stable) some atoms will give up something. • Looking at the atom, what is easier to give up, protons, neutrons, or electrons? • Electrons are the easiest, because they are on the outside! ...
... How do ions form? • The majority of atoms are not happy • In an attempt to become happy (& chemically stable) some atoms will give up something. • Looking at the atom, what is easier to give up, protons, neutrons, or electrons? • Electrons are the easiest, because they are on the outside! ...
AtomsHandout - mrsgaschoscience
... Protons are _____________ charged particles located in the _______________ or core of the atom. Each proton has a mass of ________________. Neutrons are _______________ particles also located in the ________________. Each neutron has a mass of ______________________. Electrons are __________________ ...
... Protons are _____________ charged particles located in the _______________ or core of the atom. Each proton has a mass of ________________. Neutrons are _______________ particles also located in the ________________. Each neutron has a mass of ______________________. Electrons are __________________ ...
Chp 3 notes Click Here
... specific number of protons, i.e. 8 protons are in an oxygen atom. Most commonly an oxygen atom has 8 neutrons. Sometimes the nucleus contains has a different number of neutrons. Isotope is the term for atoms of a single element that have different numbers of neutrons. ...
... specific number of protons, i.e. 8 protons are in an oxygen atom. Most commonly an oxygen atom has 8 neutrons. Sometimes the nucleus contains has a different number of neutrons. Isotope is the term for atoms of a single element that have different numbers of neutrons. ...
Atom - Britannica
... nucleus. No other element has an atomic number of 1. Another property of atoms is their atomic weight. This is roughly equal to the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom. Atoms that have the same atomic number but different atomic weights are called isotopes. Carbon-12, the ordinary form o ...
... nucleus. No other element has an atomic number of 1. Another property of atoms is their atomic weight. This is roughly equal to the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom. Atoms that have the same atomic number but different atomic weights are called isotopes. Carbon-12, the ordinary form o ...
Structure - Britannica Encyclopedia Online
... nucleus. No other element has an atomic number of 1. Another property of atoms is their atomic weight. This is roughly equal to the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom. Atoms that have the same atomic number but different atomic weights are called isotopes. Carbon-12, the ordinary form o ...
... nucleus. No other element has an atomic number of 1. Another property of atoms is their atomic weight. This is roughly equal to the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom. Atoms that have the same atomic number but different atomic weights are called isotopes. Carbon-12, the ordinary form o ...
atomic number
... distinguished by their different masses – Compounds are combinations of atoms of different elements and possess properties different from those of their component elements – In chemical reactions, atoms are neither created nor destroyed but only exchanged between ...
... distinguished by their different masses – Compounds are combinations of atoms of different elements and possess properties different from those of their component elements – In chemical reactions, atoms are neither created nor destroyed but only exchanged between ...
No Slide Title
... distinguished by their different masses – Compounds are combinations of atoms of different elements and possess properties different from those of their component elements – In chemical reactions, atoms are neither created nor destroyed but only exchanged between ...
... distinguished by their different masses – Compounds are combinations of atoms of different elements and possess properties different from those of their component elements – In chemical reactions, atoms are neither created nor destroyed but only exchanged between ...
11/13 atoms powerpoint
... Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged ...
... Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged ...
Atomic Structure - Peoria Public Schools
... J.J. Thomson: discovery of the electron Henri Becquerel: Discovery of radioactivity 1900's Robert Millikan: Charge and mass of the electron Ernest Rutherford: Existence of the nucleus, and its relative size Meitner & Fermi: Sustained nuclear fission Ernest Lawrence: The cyclotron and tra ...
... J.J. Thomson: discovery of the electron Henri Becquerel: Discovery of radioactivity 1900's Robert Millikan: Charge and mass of the electron Ernest Rutherford: Existence of the nucleus, and its relative size Meitner & Fermi: Sustained nuclear fission Ernest Lawrence: The cyclotron and tra ...
Atomic nuclei: radioactivity and types of radiation
... 1.2 Beta (β ) particles and beta decay In nuclear physics, β decay is a type of radioactive decay in which a β particle (an electron or a positron) is emitted. In the case of electron emission, it is referred to as beta minus (β -), while in the case of a positron emission as beta plus (β +). An ele ...
... 1.2 Beta (β ) particles and beta decay In nuclear physics, β decay is a type of radioactive decay in which a β particle (an electron or a positron) is emitted. In the case of electron emission, it is referred to as beta minus (β -), while in the case of a positron emission as beta plus (β +). An ele ...
Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom
... 5. Why do you think that Rutherford said an atom is composed mostly of empty space? ...
... 5. Why do you think that Rutherford said an atom is composed mostly of empty space? ...
Chapter 10 PowerPoint
... slightest bit more mass. Protons and electrons may differ in size but their charges cancel each other out. If charges are unequal then you will have an ion. -1 electron then positive ion. +1 electron then negative ion. The diameter of the nucleus is 1/100,000 the diameter of the atom. ...
... slightest bit more mass. Protons and electrons may differ in size but their charges cancel each other out. If charges are unequal then you will have an ion. -1 electron then positive ion. +1 electron then negative ion. The diameter of the nucleus is 1/100,000 the diameter of the atom. ...
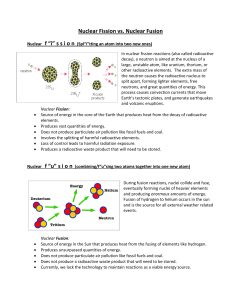
Nuclear Fission vs. Nuclear Fusion
... Nuclear Fusion: Source of energy in the Sun that produces heat from the fusing of elements like hydrogen. Produces unsurpassed quantities of energy. Does not produce particulate air pollution like fossil fuels and coal. Does not produce a radioactive waste product that will need to be stored. Curren ...
... Nuclear Fusion: Source of energy in the Sun that produces heat from the fusing of elements like hydrogen. Produces unsurpassed quantities of energy. Does not produce particulate air pollution like fossil fuels and coal. Does not produce a radioactive waste product that will need to be stored. Curren ...

![Review 2 key - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000860497_1-e3bea510ba504d09bc42d6f5e4936390-300x300.png)