Nuclear Power Date
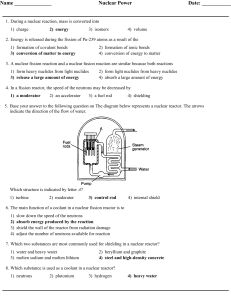
... 3. A nuclear fission reaction and a nuclear fusion reaction are similar because both reactions 1) form heavy nuclides from light nuclides 3) release a large amount of energy ...
... 3. A nuclear fission reaction and a nuclear fusion reaction are similar because both reactions 1) form heavy nuclides from light nuclides 3) release a large amount of energy ...
Chapter 9 - profpaz.com
... The first model of the atom (“soccer ball”) was introduced by John Dalton in early 1800. He thought of the atom as a featureless ball of uniform density. ...
... The first model of the atom (“soccer ball”) was introduced by John Dalton in early 1800. He thought of the atom as a featureless ball of uniform density. ...
Greek philosophers (300 BC)
... 1. All matter is made of atoms 2. Atoms are indestructible and can’t be divided 3. All atoms of one element are exactly alike, but different from atoms of other elements. 4. Atoms of diff elements combine in simple, whole-number ratios to make compounds 5. In reactions, atoms are combined, separated ...
... 1. All matter is made of atoms 2. Atoms are indestructible and can’t be divided 3. All atoms of one element are exactly alike, but different from atoms of other elements. 4. Atoms of diff elements combine in simple, whole-number ratios to make compounds 5. In reactions, atoms are combined, separated ...
3—3 Review and Reinforcement
... 7. The average mass of an element’s atoms is called the atomic number. 8. 1 atomic mass unit (amu) is equal to one twelfth of the mass of a carbon-12 atom. 9. Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of electrons are called isotopes. ...
... 7. The average mass of an element’s atoms is called the atomic number. 8. 1 atomic mass unit (amu) is equal to one twelfth of the mass of a carbon-12 atom. 9. Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of electrons are called isotopes. ...
Chapter 2: Matter is Made up of Atoms
... 1. All matter is made of atoms 2. Atoms are indestructible and can’t be divided 3. All atoms of one element are exactly alike, but different from atoms of other elements. 4. Atoms of diff elements combine in simple, whole-number ratios to make compounds 5. In reactions, atoms are combined, separated ...
... 1. All matter is made of atoms 2. Atoms are indestructible and can’t be divided 3. All atoms of one element are exactly alike, but different from atoms of other elements. 4. Atoms of diff elements combine in simple, whole-number ratios to make compounds 5. In reactions, atoms are combined, separated ...
Isotopes and Average Atomic Mass
... AVERAGE ATOMIC MASS • The average atomic mass on the periodic table = the weighted ...
... AVERAGE ATOMIC MASS • The average atomic mass on the periodic table = the weighted ...
The Atom
... - electrons move in orbits around the nucleus ( just like a solar system) - orbits or energy levels are located at certain levels from the nucleus Wave Model- electrons do not move in a perfect orbit, - only a prediction can be made where an electron will be Modern Atomic Theory- A small positively ...
... - electrons move in orbits around the nucleus ( just like a solar system) - orbits or energy levels are located at certain levels from the nucleus Wave Model- electrons do not move in a perfect orbit, - only a prediction can be made where an electron will be Modern Atomic Theory- A small positively ...
Chem 200 Dr. Saidane
... Historical Development of the Model of the Nuclear Atom. A series of discoveries were made that led to the modern model of the atom. 1. In the late 1700, scientists studied chemical reactions and their discoveries led to three basic laws: a) The Law of Conservation of Mass, which states that mass is ...
... Historical Development of the Model of the Nuclear Atom. A series of discoveries were made that led to the modern model of the atom. 1. In the late 1700, scientists studied chemical reactions and their discoveries led to three basic laws: a) The Law of Conservation of Mass, which states that mass is ...
Radioactivity
... A large nucleus (A 200 ) splits into two. The daughter fragments have higher binding energy than the parent. They are more stable. It was found (in 1939) that if uranium was bombarded with neutrons (these have no charge and are not repelled by the nuclei), that a uranium nucleus could be split into ...
... A large nucleus (A 200 ) splits into two. The daughter fragments have higher binding energy than the parent. They are more stable. It was found (in 1939) that if uranium was bombarded with neutrons (these have no charge and are not repelled by the nuclei), that a uranium nucleus could be split into ...
The Strong Nuclear Force and the Stability of the Nucleus
... The Strong Nuclear Force and the Stability of the Nucleus As nuclei get larger, more neutrons are required for stability. The neutrons act like glue without adding more repulsive force. The stable nuclides of the lighter elements have approximately equal numbers of protons and neutrons? However, as ...
... The Strong Nuclear Force and the Stability of the Nucleus As nuclei get larger, more neutrons are required for stability. The neutrons act like glue without adding more repulsive force. The stable nuclides of the lighter elements have approximately equal numbers of protons and neutrons? However, as ...
nuclear physics - review
... The Strong Nuclear Force and the Stability of the Nucleus As nuclei get larger, more neutrons are required for stability. The neutrons act like glue without adding more repulsive force. The stable nuclides of the lighter elements have approximately equal numbers of protons and neutrons? However, as ...
... The Strong Nuclear Force and the Stability of the Nucleus As nuclei get larger, more neutrons are required for stability. The neutrons act like glue without adding more repulsive force. The stable nuclides of the lighter elements have approximately equal numbers of protons and neutrons? However, as ...
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 2 of 12
... becomes filled with electrons. The highest occupied energy level contains just one electron on the left-‐hand side of the table. It is filled by the time you get to the right-‐hand side. Moving do ...
... becomes filled with electrons. The highest occupied energy level contains just one electron on the left-‐hand side of the table. It is filled by the time you get to the right-‐hand side. Moving do ...
Atomic Structure Scientists
... • Atomos: The point at which matter can no longer be subdivided. ...
... • Atomos: The point at which matter can no longer be subdivided. ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure Notes
... A. Dimitri Mendeleev (1869) (Russian) – publishing the 1st periodic table based on increasing atomic mass no. 1. The elements fell into 7 columns based on chemical & physical properties 2. He left spaces for undiscovered elements B. Henry Mosely (1913) (British) publishes the “modern” periodic table ...
... A. Dimitri Mendeleev (1869) (Russian) – publishing the 1st periodic table based on increasing atomic mass no. 1. The elements fell into 7 columns based on chemical & physical properties 2. He left spaces for undiscovered elements B. Henry Mosely (1913) (British) publishes the “modern” periodic table ...
chapter 21 blm answer key
... When the fission process is critical, one neutron from each fission event causes one more fission event. At the critical level, the reaction is sustained at a constant rate. When the process is subcritical, fewer than one neutron from each fission event causes a further fission event. The reaction s ...
... When the fission process is critical, one neutron from each fission event causes one more fission event. At the critical level, the reaction is sustained at a constant rate. When the process is subcritical, fewer than one neutron from each fission event causes a further fission event. The reaction s ...
Introduction to the Atom PPT - all things chemistry with dr. cody
... atoms. The atom is the smallest unit of an element that has all the properties of that element. An element is composed entirely of one type of atom. The chemical properties of all atoms of any element are the same. A compound contains atoms of two or more different elements. The relative number of a ...
... atoms. The atom is the smallest unit of an element that has all the properties of that element. An element is composed entirely of one type of atom. The chemical properties of all atoms of any element are the same. A compound contains atoms of two or more different elements. The relative number of a ...
NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY REVIEW SHEET
... a. electron b. neutron c. alpha particle d. Hydrogen _____23. When a heavy nucleus splits to form nuclei of intermediate mass, it undergoes a. nuclear disintegration b. fusion c. radioactive decay d. fission _____24. For the nuclear reaction 40 K 40 Ar + X, what is the identity of the species indi ...
... a. electron b. neutron c. alpha particle d. Hydrogen _____23. When a heavy nucleus splits to form nuclei of intermediate mass, it undergoes a. nuclear disintegration b. fusion c. radioactive decay d. fission _____24. For the nuclear reaction 40 K 40 Ar + X, what is the identity of the species indi ...
File
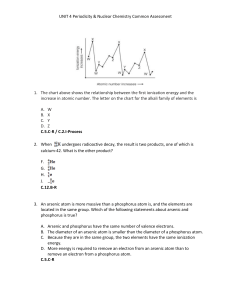
... UNIT 4 Periodicity & Nuclear Chemistry Common Assessment 16. In the figure below, what type of nuclear activity is represented? ...
... UNIT 4 Periodicity & Nuclear Chemistry Common Assessment 16. In the figure below, what type of nuclear activity is represented? ...
Name: Period:______ Date: CHEMISTRY Chapter 3 AND Nuclear
... reached a basic particle that could no longer be cut in half and still be gold; he called the smallest particle atomos; Greek philosopher. 2. The positive particle in the nucleus of an atom. 3. The dense, tiny, positively charged core of an atom; contains protons and neutrons. 4. Proposed an atomic ...
... reached a basic particle that could no longer be cut in half and still be gold; he called the smallest particle atomos; Greek philosopher. 2. The positive particle in the nucleus of an atom. 3. The dense, tiny, positively charged core of an atom; contains protons and neutrons. 4. Proposed an atomic ...
Quarter 1 Unit 3 Radioactivitypptx
... Alpha, beta and gamma 2. Alpha- gives off alpha particle which is 2 protons and 2 neutrons. It reduces the atomic number by 2 and the mass by 4 so becomes a new element Beta- a neutron becomes a proton and an electron and gives off the electron, it adds 1 to the atomic number but leaves the mass nu ...
... Alpha, beta and gamma 2. Alpha- gives off alpha particle which is 2 protons and 2 neutrons. It reduces the atomic number by 2 and the mass by 4 so becomes a new element Beta- a neutron becomes a proton and an electron and gives off the electron, it adds 1 to the atomic number but leaves the mass nu ...
Radioactive Decay
... ________________: the difference between the mass of an atom and the sum of the masses of its protons, neutrons and electrons. ...
... ________________: the difference between the mass of an atom and the sum of the masses of its protons, neutrons and electrons. ...