atomic number - Net Start Class
... the same number of protons, but can have different numbers of neutrons. • An atom with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons are called isotopes. • Isotopes are chemically alike, because it is the protons which are responsible for the chemical behavior. ...
... the same number of protons, but can have different numbers of neutrons. • An atom with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons are called isotopes. • Isotopes are chemically alike, because it is the protons which are responsible for the chemical behavior. ...
Isotopes and Radioactive Decay
... GAMMA RADIATION: Radiation that is made up of ________________________ rays. A gamma ray is high-energy and contains no _____________ and is represented by the symbol __________. Gamma rays usually accompany ___________________ and ___________________ radiation. Gamma rays also account for _________ ...
... GAMMA RADIATION: Radiation that is made up of ________________________ rays. A gamma ray is high-energy and contains no _____________ and is represented by the symbol __________. Gamma rays usually accompany ___________________ and ___________________ radiation. Gamma rays also account for _________ ...
Chapter39
... EB = mDc2 where c2 = 931.5 MeV/u EB = (0.030377 u)(931.5 MeV/u) = 28.3 MeV A total of 28.3 MeV is required To tear apart the nucleons from the He-4 atom. ...
... EB = mDc2 where c2 = 931.5 MeV/u EB = (0.030377 u)(931.5 MeV/u) = 28.3 MeV A total of 28.3 MeV is required To tear apart the nucleons from the He-4 atom. ...
Chp 12 Lecture 2: The Atom!!! (stu copy)
... When this happens, these forms of an element are called _________. Chemical properties of isotopes are the same, although the physical properties of some isotopes may be different. Some isotopes are radioactive-meaning they "radiate" energy as they decay to a more stable form, perhaps another elemen ...
... When this happens, these forms of an element are called _________. Chemical properties of isotopes are the same, although the physical properties of some isotopes may be different. Some isotopes are radioactive-meaning they "radiate" energy as they decay to a more stable form, perhaps another elemen ...
Revision of Atomic Structure and Nuclide Notations Nuclide
... When an atom decays by losing a beta particle it gains a proton but its mass is unchanged. A neutron has been changed into a proton and an electron. Gamma emission often happens at the same time but has no effect on the mass number or atomic number. It is not included in nuclear equations. Balancing ...
... When an atom decays by losing a beta particle it gains a proton but its mass is unchanged. A neutron has been changed into a proton and an electron. Gamma emission often happens at the same time but has no effect on the mass number or atomic number. It is not included in nuclear equations. Balancing ...
T212 Atomic Structure Past Paper Questions
... Explain why the difference between the 4th and 5th ionization energies is much greater than the difference between any two other successive values. (2) ...
... Explain why the difference between the 4th and 5th ionization energies is much greater than the difference between any two other successive values. (2) ...
7.4 atomic theory 3
... Alpha helium particles are 8000 times more massive (bigger) than electrons, so Rutherford thought they would knock electrons out of the way, but they did not! ...
... Alpha helium particles are 8000 times more massive (bigger) than electrons, so Rutherford thought they would knock electrons out of the way, but they did not! ...
A or `Mass Number` - Uplift Pinnacle Prep
... The US mint estimates that of all the pennies currently in circulation 66.5% of them are “new” (post-1982) pennies and 33.5% are ‘old’ pennies. A ‘new’ penny weighs 2.5g and an old penny weighs 3.1 g. Use this information to determine the average mass of a penny. ...
... The US mint estimates that of all the pennies currently in circulation 66.5% of them are “new” (post-1982) pennies and 33.5% are ‘old’ pennies. A ‘new’ penny weighs 2.5g and an old penny weighs 3.1 g. Use this information to determine the average mass of a penny. ...
Atomic Structure * Learning Outcomes
... The location, charge, and atomic mass of sub-atomic particles are how they are distinguished. These masses and charges are so small (e.g. mass of proton = 0.000 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 001 67 kg), that we use new units more suitable. For mass, we use atomic mass units (u) and for charge, ...
... The location, charge, and atomic mass of sub-atomic particles are how they are distinguished. These masses and charges are so small (e.g. mass of proton = 0.000 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 001 67 kg), that we use new units more suitable. For mass, we use atomic mass units (u) and for charge, ...
Atomic Structure – Learning Outcomes
... Notice that the mass number on the periodic table comes with decimals. e.g. the mass number of hydrogen is given as 1.00794. Every hydrogen has 1 proton (that’s what makes it hydrogen), but some hydrogens have different numbers of neutrons in their nucleus. Hydrogen-1 has 1 proton, 0 neutron ...
... Notice that the mass number on the periodic table comes with decimals. e.g. the mass number of hydrogen is given as 1.00794. Every hydrogen has 1 proton (that’s what makes it hydrogen), but some hydrogens have different numbers of neutrons in their nucleus. Hydrogen-1 has 1 proton, 0 neutron ...
Introduction to Atoms
... 1. The nucleus is the center of the atom. 2. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus. 3. Protons have a positive charge. 4. Protons are very large (compared to electrons) a) A proton’s mass is about 1.00 amu (1840 times greater than the mass of an electron!) ...
... 1. The nucleus is the center of the atom. 2. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus. 3. Protons have a positive charge. 4. Protons are very large (compared to electrons) a) A proton’s mass is about 1.00 amu (1840 times greater than the mass of an electron!) ...
05: Atoms and Molecules
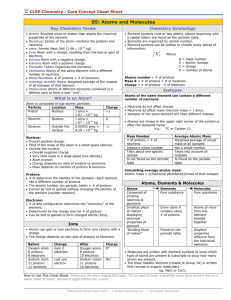
... Atoms of the same element can contain a different number of neutrons. • Neutrons do not affect charge. • Neutrons do affect mass (neutron mass = 1 amu). • Isotopes of the same element will have different masses. • Masses are shown in the upper right corner of the symbol or after the elements name: e ...
... Atoms of the same element can contain a different number of neutrons. • Neutrons do not affect charge. • Neutrons do affect mass (neutron mass = 1 amu). • Isotopes of the same element will have different masses. • Masses are shown in the upper right corner of the symbol or after the elements name: e ...
1.1 to 1.4
... that contains two or more kinds of atoms in fixed proportions. Ex. H2O • can be broken down • can be either ionic (made up of a metal and a nonmetal) or molecular (made up of two or more non- ...
... that contains two or more kinds of atoms in fixed proportions. Ex. H2O • can be broken down • can be either ionic (made up of a metal and a nonmetal) or molecular (made up of two or more non- ...
chap7_nucleus
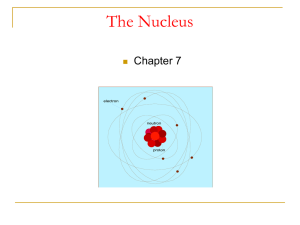
... Rutherford found that the only way to explain the deflections was to picture an atom with a tiny nucleus in which positive charge existed and nearly all the mass existed; And the electrons were some distance away from the nucleus. In other words, AN ATOM IS MOSTLY EMPTY SPACE. ...
... Rutherford found that the only way to explain the deflections was to picture an atom with a tiny nucleus in which positive charge existed and nearly all the mass existed; And the electrons were some distance away from the nucleus. In other words, AN ATOM IS MOSTLY EMPTY SPACE. ...
Isotopes
... left of the chemical symbol, For iron (Fe) we have, for example: 54Fe, 56Fe, 57Fe, and 58Fe. Since the iron has the atomic number zFe = 26, we have 54 - 26 = 28 neutrons in 54Fe, and 30, 31, and 32 neutrons, respectively, in the other three isotopes given. Isotopes come in two basic variants: 1. Rad ...
... left of the chemical symbol, For iron (Fe) we have, for example: 54Fe, 56Fe, 57Fe, and 58Fe. Since the iron has the atomic number zFe = 26, we have 54 - 26 = 28 neutrons in 54Fe, and 30, 31, and 32 neutrons, respectively, in the other three isotopes given. Isotopes come in two basic variants: 1. Rad ...
Atoms, Elements, and Ions
... • The atom is extremely small. One teaspoon of water has 3 times as many atoms as the Atlantic Ocean has teaspoons of water. • If a large sports stadium were an atom, a marble would represent the nucleus. ...
... • The atom is extremely small. One teaspoon of water has 3 times as many atoms as the Atlantic Ocean has teaspoons of water. • If a large sports stadium were an atom, a marble would represent the nucleus. ...
Section 12.1 - CPO Science
... 12.1 How atoms of various elements are different Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. The mass number of an isotope tells you the number of protons plus the number of neutrons. How are these carbon isotopes different? ...
... 12.1 How atoms of various elements are different Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. The mass number of an isotope tells you the number of protons plus the number of neutrons. How are these carbon isotopes different? ...
“Plum Pudding” model
... – Fixed electrons do not emit radiation – Angular momentum is quantized – Can’ Can’t explain how electrons move from one energy state to the next ...
... – Fixed electrons do not emit radiation – Angular momentum is quantized – Can’ Can’t explain how electrons move from one energy state to the next ...
12.1 Structure of the Atom - appleg8
... 12.1 How atoms of various elements are different Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. The mass number of an isotope tells you the number of protons plus the number of neutrons. How are these carbon isotopes different? ...
... 12.1 How atoms of various elements are different Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. The mass number of an isotope tells you the number of protons plus the number of neutrons. How are these carbon isotopes different? ...
ATOMS
... All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed Atoms of different elements combine i ...
... All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed Atoms of different elements combine i ...
protons and neutrons
... • Location: Where it is on the atom • Charge: Electric charge (positive, negative or neutral) • Mass: how big or small it is ...
... • Location: Where it is on the atom • Charge: Electric charge (positive, negative or neutral) • Mass: how big or small it is ...
The Structure of the Atom- Chapter 4, 3
... Nuclear chemistry is the study of the changes of the NUCLEUS of an atom. Nuclear Reactions involve changes within the nucleus where as chemical reactions involve the loss, gain or sharing of electrons. ...
... Nuclear chemistry is the study of the changes of the NUCLEUS of an atom. Nuclear Reactions involve changes within the nucleus where as chemical reactions involve the loss, gain or sharing of electrons. ...
File - Biochemistry
... Calculate the atomic mass of magnesium. The three magnesium isotopes have atomic masses and relative abundances as follows: 23.985 amu (78.99%) 24.986 amu (10.00%) 25.982 amu (11.01%) ...
... Calculate the atomic mass of magnesium. The three magnesium isotopes have atomic masses and relative abundances as follows: 23.985 amu (78.99%) 24.986 amu (10.00%) 25.982 amu (11.01%) ...