Radioactivity2015
... B Nuclear energy is sometimes less expensive than other energy sources. C Uranium provides more energy than an equal amount of petroleum. D Nuclear fission produces less air pollution than burning fossil fuels. t (hr) Amount of ...
... B Nuclear energy is sometimes less expensive than other energy sources. C Uranium provides more energy than an equal amount of petroleum. D Nuclear fission produces less air pollution than burning fossil fuels. t (hr) Amount of ...
Practice Fall Final Exam Questions
... (d) It depends on the particular crystal. 32) Which particles may be gained, lost, or shared by an atom when it forms a chemical bond? (a) protons ...
... (d) It depends on the particular crystal. 32) Which particles may be gained, lost, or shared by an atom when it forms a chemical bond? (a) protons ...
Chapter 4 Worksheet 1
... F. What all things are made of; it occupies space G. An uncharged particle within the nucleus of an atom H. Tiny negative electrical charges that move around the nucleus of an atom I. An atom that has lost or gained electrons ...
... F. What all things are made of; it occupies space G. An uncharged particle within the nucleus of an atom H. Tiny negative electrical charges that move around the nucleus of an atom I. An atom that has lost or gained electrons ...
File - Ms M - EARL MARRIOTT SECONDARY
... The release of alpha particles is called alpha decay. Alpha particles are slow and penetrate materials much less than the other forms of radiation. A sheet of paper will stop an alpha particle. ...
... The release of alpha particles is called alpha decay. Alpha particles are slow and penetrate materials much less than the other forms of radiation. A sheet of paper will stop an alpha particle. ...
Ch 3 notes ppt
... electron has a very small mass compared with a proton or neutron * beta radiation is approx. 100 times more penetrating than alpha * it can penetrate clothing and harm skin ...
... electron has a very small mass compared with a proton or neutron * beta radiation is approx. 100 times more penetrating than alpha * it can penetrate clothing and harm skin ...
The Atom Notes
... What should a Model look like? Scientific models may not always look like the actual object. A model is an attempt to use familiar ideas to describe unfamiliar things in a visual way. Many of the models that you have seen may look like the one below. It shows the parts and structure of the atom. Eve ...
... What should a Model look like? Scientific models may not always look like the actual object. A model is an attempt to use familiar ideas to describe unfamiliar things in a visual way. Many of the models that you have seen may look like the one below. It shows the parts and structure of the atom. Eve ...
Basic Structure of the Atom
... Energy levels closest to nucleus have low energy Energy levels increase in energy with distance from the nucleus Electrons gain and lose energy by moving between energy levels (quantum) ...
... Energy levels closest to nucleus have low energy Energy levels increase in energy with distance from the nucleus Electrons gain and lose energy by moving between energy levels (quantum) ...
Nuclear Chemistry Worksheet
... The quantum mechanical model of the atom uses complex shapes of orbitals (sometimes called electron clouds), volumes of space in which there is likely to be an electron. So, this model is based on probability rather than certainty. Four numbers, called quantum numbers, were introduced to describe th ...
... The quantum mechanical model of the atom uses complex shapes of orbitals (sometimes called electron clouds), volumes of space in which there is likely to be an electron. So, this model is based on probability rather than certainty. Four numbers, called quantum numbers, were introduced to describe th ...
Review of Nuclear Chemistry
... During an alpha decay, a radioactive element's mass number decreases by 4 while its atomic number decreases by 2. During a beta decay, a radioactive element's mass number does not change while the number of protons increases by one. This is because beta particles are thought to form when a neutron b ...
... During an alpha decay, a radioactive element's mass number decreases by 4 while its atomic number decreases by 2. During a beta decay, a radioactive element's mass number does not change while the number of protons increases by one. This is because beta particles are thought to form when a neutron b ...
Chapter 16 Nuclear Chemistry - An Introduction to Chemistry
... our bodies, they pull electrons away from the tissue’s atoms. 34. Gamma photons are ionizing radiation, because they can excite electrons enough to actually remove them from atoms. 36. Because beta particles are smaller than alpha particles, and because they can move up to 90% the speed of light, th ...
... our bodies, they pull electrons away from the tissue’s atoms. 34. Gamma photons are ionizing radiation, because they can excite electrons enough to actually remove them from atoms. 36. Because beta particles are smaller than alpha particles, and because they can move up to 90% the speed of light, th ...
CH4 REVIEW
... 16. Analyzing Processes Particle accelerators, are devices that speed up charged particles in order to smash them together. Scientists use these devices to make atoms. How can scientists determine whether the atoms formed are a new element or a new isotope of a known element? ...
... 16. Analyzing Processes Particle accelerators, are devices that speed up charged particles in order to smash them together. Scientists use these devices to make atoms. How can scientists determine whether the atoms formed are a new element or a new isotope of a known element? ...
1.1 Guided Reading
... Be sure to label the protons, neutrons, electrons, and the nucleus. (see page 13) ...
... Be sure to label the protons, neutrons, electrons, and the nucleus. (see page 13) ...
03.03a Atomic Number, Mass Number, and Isotopes
... ATOMS: All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons: the number of protons determines the identity of the atom. For example, a carbon atom always has six protons. If it has seven protons, it’s nitrogen, not carbon. The number of protons is called the atomic number (Z). ISOTOPES: Alt ...
... ATOMS: All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons: the number of protons determines the identity of the atom. For example, a carbon atom always has six protons. If it has seven protons, it’s nitrogen, not carbon. The number of protons is called the atomic number (Z). ISOTOPES: Alt ...
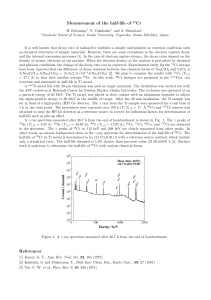
Measurement of the half-life of
... It is well known that decay rate of radioactive nuclides is usually independent on external conditions such as chemical structures of sample materials. However, there are some exceptions in the electron capture decay and the internal conversion processes [1]. In the case of electron capture decays, ...
... It is well known that decay rate of radioactive nuclides is usually independent on external conditions such as chemical structures of sample materials. However, there are some exceptions in the electron capture decay and the internal conversion processes [1]. In the case of electron capture decays, ...
Isotope PPT - MrsPage.com
... • You will be able to determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in different isotopes of the same element. • You will understand that atomic mass • You will understand what radioactivity is the average of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element. • You will be able to give examp ...
... • You will be able to determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in different isotopes of the same element. • You will understand that atomic mass • You will understand what radioactivity is the average of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element. • You will be able to give examp ...
1. Which of the following statements best describes the
... An atom must gain one or more electrons. ...
... An atom must gain one or more electrons. ...
Chapter 25
... See you in Unit 3 for Advanced. For Chemistry, we are finally DONE with new material, so let’s gets started reviewing EVERYTHING ELSE we learned for the SOL, which is coming up ...
... See you in Unit 3 for Advanced. For Chemistry, we are finally DONE with new material, so let’s gets started reviewing EVERYTHING ELSE we learned for the SOL, which is coming up ...
1 - kjpederson
... 6. Making Inferences: Does the term indivisible still describe the atom? Explain. No, the atom is not indivisible. It is made up of smaller parts such as the electron. ...
... 6. Making Inferences: Does the term indivisible still describe the atom? Explain. No, the atom is not indivisible. It is made up of smaller parts such as the electron. ...
Glossary of Technical Terms - Institute for Energy and Environmental
... food chain, or some combination of these pathways. nucleus The nucleus of an atom is the central core that comprises almost all the weight of the atom. All atomic nuclei (except H-1, which has a single proton) contain both protons and neutrons. neutron An elementary particle slightly heavier than a ...
... food chain, or some combination of these pathways. nucleus The nucleus of an atom is the central core that comprises almost all the weight of the atom. All atomic nuclei (except H-1, which has a single proton) contain both protons and neutrons. neutron An elementary particle slightly heavier than a ...
GRAMMAR: verb tenses
... appears in several nuclide forms which differ in their neutron number and hence in their mass number A. Nuclides with the same Z but different A are referred to as isotopes. For example, the isotopes of hydrogen are 11H, ziH, and 1/3H while heavy elements such as uranium may exhibit a number of isot ...
... appears in several nuclide forms which differ in their neutron number and hence in their mass number A. Nuclides with the same Z but different A are referred to as isotopes. For example, the isotopes of hydrogen are 11H, ziH, and 1/3H while heavy elements such as uranium may exhibit a number of isot ...
E = mc2 (Einstein)
... not found in nature, but it can be produced in nuclear reactions (see Chapter 14). What do we mean by stability? To answer this question, let us remind ourselves of the universal law of nature that we discussed in Chapter 3: we saw that there exists in nature a spontaneous tendency to maximize the e ...
... not found in nature, but it can be produced in nuclear reactions (see Chapter 14). What do we mean by stability? To answer this question, let us remind ourselves of the universal law of nature that we discussed in Chapter 3: we saw that there exists in nature a spontaneous tendency to maximize the e ...