Atoms and Their Parts (Subatomic Particles)
... would mean you have a different element. Electrons are negatively charged and are located in shells or orbits spinning around the nucleus. The number of protons and electrons can be equal. This equality is important so that the atom is neither positively nor negatively charged. It is said to be ne ...
... would mean you have a different element. Electrons are negatively charged and are located in shells or orbits spinning around the nucleus. The number of protons and electrons can be equal. This equality is important so that the atom is neither positively nor negatively charged. It is said to be ne ...
ch-7 [Basic Chemistry]
... • The mass number (A), also called atomic mass number or nucleon number, is the total number of protons and neutrons (together known as nucleons) in an atomic nucleus. • All atoms have a mass number which is derived as follows. ...
... • The mass number (A), also called atomic mass number or nucleon number, is the total number of protons and neutrons (together known as nucleons) in an atomic nucleus. • All atoms have a mass number which is derived as follows. ...
Atomic Structure study guide # 1
... 16. Look at the calcium and aluminum examples above. Notice the mass of calcium from the periodic table is 40.08 amu (40 amu rounded), and the mass of aluminum from the table is 26.982 amu (27 amu rounded). Based on the information in the picture, how was this mass determined? ...
... 16. Look at the calcium and aluminum examples above. Notice the mass of calcium from the periodic table is 40.08 amu (40 amu rounded), and the mass of aluminum from the table is 26.982 amu (27 amu rounded). Based on the information in the picture, how was this mass determined? ...
ppt - Physics
... The physical quantity responsible of physical and chemical changes in an irradiated material is the energy absorbed from the radiation field. Dosimetry provides a way to determine the amount of energy that has been absorbed by the irradiated material from the radiation. The dose D, is the amount of ...
... The physical quantity responsible of physical and chemical changes in an irradiated material is the energy absorbed from the radiation field. Dosimetry provides a way to determine the amount of energy that has been absorbed by the irradiated material from the radiation. The dose D, is the amount of ...
File 15-16unit 6
... • occurs when a beta particle is emitted from the nucleus • Parent daughter: equal mass but atomic number increases by 1. • a neutron becomes a proton. Example: Carbon-14 undergoes beta decay. Write the decay reaction. ...
... • occurs when a beta particle is emitted from the nucleus • Parent daughter: equal mass but atomic number increases by 1. • a neutron becomes a proton. Example: Carbon-14 undergoes beta decay. Write the decay reaction. ...
Atomic Mass and Isotopes
... How to do a Average Atomic Mass If the head wizard of the Land of Ooo had a chunk of Derpium Ore and didn’t feel like explaining to the King that 25% of The Derpium had less mass than the rest of the 75% of the Derpium, he could create a weighted average 25% of the ore is 19 amu: ...
... How to do a Average Atomic Mass If the head wizard of the Land of Ooo had a chunk of Derpium Ore and didn’t feel like explaining to the King that 25% of The Derpium had less mass than the rest of the 75% of the Derpium, he could create a weighted average 25% of the ore is 19 amu: ...
Name
... 27. _____________________ is the particles or energy emitted from an atomic nucleus when it is unstable due to stronger ________________ repulsive forces than ______________ attractive forces. ...
... 27. _____________________ is the particles or energy emitted from an atomic nucleus when it is unstable due to stronger ________________ repulsive forces than ______________ attractive forces. ...
Unit 2 * Chapter 11 - Dr. Wall`s Science
... Isotopes • Mass number: Total of protons + neutrons • To calculate, add protons plus neutrons • To name an isotope: – Write name of element, followed by mass number – C-12 – O-18 ...
... Isotopes • Mass number: Total of protons + neutrons • To calculate, add protons plus neutrons • To name an isotope: – Write name of element, followed by mass number – C-12 – O-18 ...
Chapter 4 - Mr. Fischer.com
... An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains its identity in a chemical reaction. A. Early philosophers believed that atoms were indivisible and indestructible. B. Dalton’s Atomic theory. Dalton used experimental methods, to transform Democritus’s ideas on atoms into scientific theory ...
... An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains its identity in a chemical reaction. A. Early philosophers believed that atoms were indivisible and indestructible. B. Dalton’s Atomic theory. Dalton used experimental methods, to transform Democritus’s ideas on atoms into scientific theory ...
Physics 102, Class 25 The Atomic Nucleus and Radioactivity
... – If + charges are emitted, the atomic number goes down by the number of + charges – If – charges are emitted, the atomic number goes up by the number of – charges – If neutrons are emitted, the atomic mass goes down by the number of neutrons – If gamma rays are emitted, atomic number and atomic mas ...
... – If + charges are emitted, the atomic number goes down by the number of + charges – If – charges are emitted, the atomic number goes up by the number of – charges – If neutrons are emitted, the atomic mass goes down by the number of neutrons – If gamma rays are emitted, atomic number and atomic mas ...
Elements, Isotopes and Ions
... 1. Any atom of Calcium can have 20, 22, or 24 neutrons. These different versions of Calcium are called ...
... 1. Any atom of Calcium can have 20, 22, or 24 neutrons. These different versions of Calcium are called ...
are made up of
... that grouped elements accordingto their properties. They found that these properties repeated in a regular or periodic manner. This fact was used to predict properties of undiscovered elements. Reviewelectron arrangement from your textbook.In Table I, write.the maximum number of electrons that can f ...
... that grouped elements accordingto their properties. They found that these properties repeated in a regular or periodic manner. This fact was used to predict properties of undiscovered elements. Reviewelectron arrangement from your textbook.In Table I, write.the maximum number of electrons that can f ...
Phys 282 EXP 8
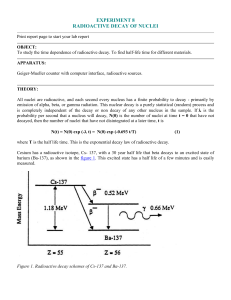
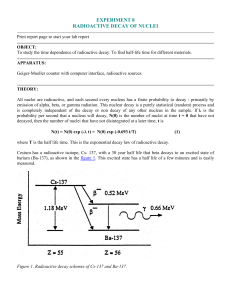
... All nuclei are radioactive, and each second every nucleus has a finite probability to decay - primarily by emission of alpha, beta, or gamma radiation. This nuclear decay is a purely statistical (random) process and is completely independent of the decay or non decay of any other nucleus in the samp ...
... All nuclei are radioactive, and each second every nucleus has a finite probability to decay - primarily by emission of alpha, beta, or gamma radiation. This nuclear decay is a purely statistical (random) process and is completely independent of the decay or non decay of any other nucleus in the samp ...
experiment 8 radioactive decay of nuclei
... All nuclei are radioactive, and each second every nucleus has a finite probability to decay - primarily by emission of alpha, beta, or gamma radiation. This nuclear decay is a purely statistical (random) process and is completely independent of the decay or non decay of any other nucleus in the samp ...
... All nuclei are radioactive, and each second every nucleus has a finite probability to decay - primarily by emission of alpha, beta, or gamma radiation. This nuclear decay is a purely statistical (random) process and is completely independent of the decay or non decay of any other nucleus in the samp ...
Questions About Atoms and Elements
... d.) Name the element. ____________________ e.) Name another element with the same number of outer-shell electrons in its atoms. _______________________________ ...
... d.) Name the element. ____________________ e.) Name another element with the same number of outer-shell electrons in its atoms. _______________________________ ...
Atoms of different elements are
... Understand the inverse relationship between wavelength and frequency, and the direct relationship between energy and frequency Analyze diagrams related to the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom in terms of allowed, discrete energy levels in the emission spectrum Describe the electron cloud of the atom ...
... Understand the inverse relationship between wavelength and frequency, and the direct relationship between energy and frequency Analyze diagrams related to the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom in terms of allowed, discrete energy levels in the emission spectrum Describe the electron cloud of the atom ...
Atomic Structure Test – Study Guide
... What is the electrical charge and position in the atom for each of the subatomic particles? 1. Electron - negative charge; located in a “cloud” rotating around the nucleus 2. Proton – positive charge; located in the center or nucleus of the atom 3. Neutron - no charge; located in the center or nucle ...
... What is the electrical charge and position in the atom for each of the subatomic particles? 1. Electron - negative charge; located in a “cloud” rotating around the nucleus 2. Proton – positive charge; located in the center or nucleus of the atom 3. Neutron - no charge; located in the center or nucle ...
Topic 7. 1 Atomic Structure
... This is where atomic mass comes from. It’s the weighted average mass of all the different isotopes. Nuclei of different atoms are known as nuclides. Ex. C – 12, C – 14 Both are carbon but different isotopes Their nuclei have different numbers of neutrons. These are different nuclides. 7. ...
... This is where atomic mass comes from. It’s the weighted average mass of all the different isotopes. Nuclei of different atoms are known as nuclides. Ex. C – 12, C – 14 Both are carbon but different isotopes Their nuclei have different numbers of neutrons. These are different nuclides. 7. ...
Chapter 5
... Chapter 5 The ATOM • Democritus (400 BC) reasoned that all things were made up of indivisible particles: ATOMS • Dalton (1766-1844) performed experiments – Atomic Theory • All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called ATOMS • Atoms of the same element are identical, but different fr ...
... Chapter 5 The ATOM • Democritus (400 BC) reasoned that all things were made up of indivisible particles: ATOMS • Dalton (1766-1844) performed experiments – Atomic Theory • All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called ATOMS • Atoms of the same element are identical, but different fr ...
Analysis of Experimental Results on Excess Heat Power Production, Impurity Nuclides... Cathode Material and Penetrating Radiation in Experiments with High-Current Glow Discharge International Conference on Cold Fusion
... of a big number of primary phonons with energies of 0.07 - 1.5 keV a small number of high energy phonons (up to tens and hundreds keV) is formed. The primary phonons energy spectrum is displaced in the direction of bigger values. As this takes place the Pd crystal lattice is “cold” (300-400°) K, Pd ...
... of a big number of primary phonons with energies of 0.07 - 1.5 keV a small number of high energy phonons (up to tens and hundreds keV) is formed. The primary phonons energy spectrum is displaced in the direction of bigger values. As this takes place the Pd crystal lattice is “cold” (300-400°) K, Pd ...
Chemistry - Spokane Public Schools
... portion of their electron clouds. This is called a covalent bond. The combined atoms form what is called a molecule. 12. Compound - When the atoms of different elements combine to form a substance that has different properties from the original elements this is called a compound. Example: When two a ...
... portion of their electron clouds. This is called a covalent bond. The combined atoms form what is called a molecule. 12. Compound - When the atoms of different elements combine to form a substance that has different properties from the original elements this is called a compound. Example: When two a ...
Atomic Structure File
... charge: electrical charges can be positive or negative. Opposite cancel each other out, so the charge of an atom is the difference between how many positive charges (protons) it has, and how many negative charges (electrons) it has. For example, a chlorine atom with 17 protons (+17) and 18 electrons ...
... charge: electrical charges can be positive or negative. Opposite cancel each other out, so the charge of an atom is the difference between how many positive charges (protons) it has, and how many negative charges (electrons) it has. For example, a chlorine atom with 17 protons (+17) and 18 electrons ...
![ch-7 [Basic Chemistry]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002135636_1-6e0da68ae8ae81ce33d9eac4143328a5-300x300.png)