Topic 7_1_Ext D__Nuclear structure and force
... FYI: A = Z + N, so that nuclear reactions do not generally include the N Topic 7.1 Extended values (since it can be calculated). ...
... FYI: A = Z + N, so that nuclear reactions do not generally include the N Topic 7.1 Extended values (since it can be calculated). ...
Atomic_Theory_and_Atomic_Structure__2011.php
... larger and heavier than electrons Protons have a positive charge (+) Located in the nucleus of the atom ...
... larger and heavier than electrons Protons have a positive charge (+) Located in the nucleus of the atom ...
Chapter 4: Atomic Structure
... 5. Problem: he found that if he set the mass of the proton at 1.00, then the protons that account for the positive charge do not account for the total mass – only part of it. 6. Therefore, the atom had more mass than the amount contributed by the protons. 7. Suggested tightly bound proton-electron p ...
... 5. Problem: he found that if he set the mass of the proton at 1.00, then the protons that account for the positive charge do not account for the total mass – only part of it. 6. Therefore, the atom had more mass than the amount contributed by the protons. 7. Suggested tightly bound proton-electron p ...
solutions
... Problem 3. Nobel laureate Richard Feynman once said that if two persons stood at arm’s length from each other and each person had p = 1% more electrons than protons, the force of repulsion between them would be enough to lift a “weight” equal to that of the entire Earth. Carry out an order of magnit ...
... Problem 3. Nobel laureate Richard Feynman once said that if two persons stood at arm’s length from each other and each person had p = 1% more electrons than protons, the force of repulsion between them would be enough to lift a “weight” equal to that of the entire Earth. Carry out an order of magnit ...
Topic 14 - Lloyd Crosby
... a. Up to Z = 20 this ratio of neutrons to protons ranges from 1 up to about 1.1 near Z = 20. b. At increasingly higher Z the band of stability falls in ratios of neutrons to protons which are continually increasing (up to 1.5 at the highest values of Z). 4. Example ...
... a. Up to Z = 20 this ratio of neutrons to protons ranges from 1 up to about 1.1 near Z = 20. b. At increasingly higher Z the band of stability falls in ratios of neutrons to protons which are continually increasing (up to 1.5 at the highest values of Z). 4. Example ...
Name: Date: ______ Period: Unit 3 – Atomic Structure Review
... 3. Where is most of the mass of the atom located? Nucleus 4. What subatomic particles have an electrical charge? Proton (+) and Electron (-) 5. ALL neutral atoms contain equal numbers of Protons and Electrons. 6. What do we call atoms that have gained or lost electrons? Ions 7. What do we call atoms ...
... 3. Where is most of the mass of the atom located? Nucleus 4. What subatomic particles have an electrical charge? Proton (+) and Electron (-) 5. ALL neutral atoms contain equal numbers of Protons and Electrons. 6. What do we call atoms that have gained or lost electrons? Ions 7. What do we call atoms ...
What do atoms look like?
... What do we know about atoms? *All elements are composed of atoms *The atoms of the same element are the same (and different from the atoms of any other element) *Atoms of different elements can mix together or can chemically combine in a whole number ratio to form compounds * Chemical reactions occ ...
... What do we know about atoms? *All elements are composed of atoms *The atoms of the same element are the same (and different from the atoms of any other element) *Atoms of different elements can mix together or can chemically combine in a whole number ratio to form compounds * Chemical reactions occ ...
atomic-models
... • Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. • Due to isotopes, mass #s are not round #s. • Li (6.9) is made up of both 6Li and 7Li. • Often, at least one isotope is unstable. • It breaks down, releasing radioactivity. • These types of isotopes are called ...
... • Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. • Due to isotopes, mass #s are not round #s. • Li (6.9) is made up of both 6Li and 7Li. • Often, at least one isotope is unstable. • It breaks down, releasing radioactivity. • These types of isotopes are called ...
Periodic Table ppt
... Compound: a substance made up of 2 or more DIFFERENT elements Molecule: a grouping of 2 or more atoms joined together ...
... Compound: a substance made up of 2 or more DIFFERENT elements Molecule: a grouping of 2 or more atoms joined together ...
A Proton is a positively charged particle found in the atom
... nucleus were the size of a Ping-Pong ball, the atom (with a single electron) would have a diameter of 2 kilometers (1.2 mile). Atomic Number and Isotopes The Neutron In 1932 Irene and Frederic Joliot-Curie discovered a type of radiation that had no charge but mass. This was identified as the neutron ...
... nucleus were the size of a Ping-Pong ball, the atom (with a single electron) would have a diameter of 2 kilometers (1.2 mile). Atomic Number and Isotopes The Neutron In 1932 Irene and Frederic Joliot-Curie discovered a type of radiation that had no charge but mass. This was identified as the neutron ...
The Atom
... • Chlorine has 2 isotopes. Chlorine-35 occurs at 75.53% and Chlorine-37 occurs at 24.47%. What’s the average atomic mass? • Avg Atomic Mass = (35)(75.53) + (37)(24.47) ...
... • Chlorine has 2 isotopes. Chlorine-35 occurs at 75.53% and Chlorine-37 occurs at 24.47%. What’s the average atomic mass? • Avg Atomic Mass = (35)(75.53) + (37)(24.47) ...
CH 4
... Bohr’s Model of the Atoms Electron cloud- In the 1926 model of the atom, the electrons move about in a cloud that surrounds the nucleus rather than welldefined orbits as Niels Bohr, a Danish scientist, depicted in 1913 that resembles a solar system of planets. (See pages 114-115) The electrons are s ...
... Bohr’s Model of the Atoms Electron cloud- In the 1926 model of the atom, the electrons move about in a cloud that surrounds the nucleus rather than welldefined orbits as Niels Bohr, a Danish scientist, depicted in 1913 that resembles a solar system of planets. (See pages 114-115) The electrons are s ...
on Nuclear Physics - Good Earth School
... Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay or radioactivity) is the process by which the nucleus of an unstable atom loses energy by emitting radiations ...
... Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay or radioactivity) is the process by which the nucleus of an unstable atom loses energy by emitting radiations ...
Page 1
... 1. The ancient Greek philosopher, Democritus, believed that all matter consisted of extremely small particles that could not be divided. 2. The Greek philosopher, mentioned in the previous question, thought that there were different types of atoms with specific sets of properties. (true, false) 3. A ...
... 1. The ancient Greek philosopher, Democritus, believed that all matter consisted of extremely small particles that could not be divided. 2. The Greek philosopher, mentioned in the previous question, thought that there were different types of atoms with specific sets of properties. (true, false) 3. A ...
Name Test Review Chemistry Unit 2: The Atom 1. Fill in the blank
... 7. What is the mass of 0.44 moles of carbon? 8. How many atoms does 43.25 g of iron contain? 9. If a student weighs out 2.01 g of silicon, how many moles is that? 10. How many moles are there in 2.4010 x 1025 particles of gold? 11. What is the mass of a block of aluminum that has a volume of 22.4 cm ...
... 7. What is the mass of 0.44 moles of carbon? 8. How many atoms does 43.25 g of iron contain? 9. If a student weighs out 2.01 g of silicon, how many moles is that? 10. How many moles are there in 2.4010 x 1025 particles of gold? 11. What is the mass of a block of aluminum that has a volume of 22.4 cm ...
nuclear fusion
... This led to the formation of H nuclei. • The H nuclei were pulled together by gravity into masses that would become the stars. The H nuclei fused into He nuclei, releasing enough energy that the star began to shine. • The fusion process continued for billions of years, releasing energy as heavier an ...
... This led to the formation of H nuclei. • The H nuclei were pulled together by gravity into masses that would become the stars. The H nuclei fused into He nuclei, releasing enough energy that the star began to shine. • The fusion process continued for billions of years, releasing energy as heavier an ...
Unit 2 Atomic structure review
... 8. What are atoms that have different numbers of protons? 9. How many protons, neutron, and electrons does U-234 have? 10. How many electrons would it take to equal the mass of one proton or one neutron? 11. What element has 21 protons and 24 neutrons? 12. An atom of potassium has 19 protons and 20 ...
... 8. What are atoms that have different numbers of protons? 9. How many protons, neutron, and electrons does U-234 have? 10. How many electrons would it take to equal the mass of one proton or one neutron? 11. What element has 21 protons and 24 neutrons? 12. An atom of potassium has 19 protons and 20 ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... decays by alpha emission. Write the balanced nuclear equation for the decay of 212Po. ...
... decays by alpha emission. Write the balanced nuclear equation for the decay of 212Po. ...
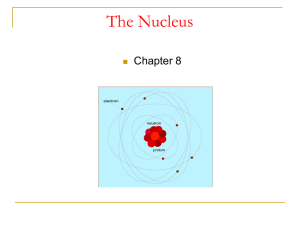
CH_8_nucleus_new
... Rutherford found that the only way to explain the deflections was to picture an atom with a tiny nucleus in which positive charge existed and nearly all the mass existed; And the electrons were some distance away from the nucleus. In other words, AN ATOM IS MOSTLY EMPTY SPACE. ...
... Rutherford found that the only way to explain the deflections was to picture an atom with a tiny nucleus in which positive charge existed and nearly all the mass existed; And the electrons were some distance away from the nucleus. In other words, AN ATOM IS MOSTLY EMPTY SPACE. ...
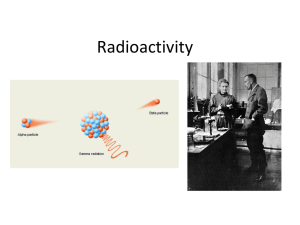
Radioactivity
... • Radioisotopes decay from one element to another until they are transformed into stable, non-radioactive isotopes. • For example, 238U decays 11 times, shedding mass and energy each time, eventually becoming 206Pb, a stable isotope. • Radioactive decay is spontaneous – it does not require an input ...
... • Radioisotopes decay from one element to another until they are transformed into stable, non-radioactive isotopes. • For example, 238U decays 11 times, shedding mass and energy each time, eventually becoming 206Pb, a stable isotope. • Radioactive decay is spontaneous – it does not require an input ...
Atomic and Nuclear Terms
... ► Nuclear Reactions – A reaction that occurs whenever the number of protons or neutrons changes. • Nuclear reactions include natural and artificial transmutation, fission, and fusion. ► Transmutation – Nuclear change of one element into another. • In natural transmutations the nucleus decays spontan ...
... ► Nuclear Reactions – A reaction that occurs whenever the number of protons or neutrons changes. • Nuclear reactions include natural and artificial transmutation, fission, and fusion. ► Transmutation – Nuclear change of one element into another. • In natural transmutations the nucleus decays spontan ...
Elements and Atoms
... The Periodic Table of the Elements gives information about each element. We can use the information in the Periodic Table to figure out the number of protons, neutrons and electrons that are in each element. Here is how: a. Find the atomic number. This is the number that identifies each element. It ...
... The Periodic Table of the Elements gives information about each element. We can use the information in the Periodic Table to figure out the number of protons, neutrons and electrons that are in each element. Here is how: a. Find the atomic number. This is the number that identifies each element. It ...
Name Test Review Chapters 4 and 25 Honors Chemistry 1. Fill in
... 11. What is the mass of a block of aluminum that has a volume of 22.4 cm3? (Density of Al = 2.70 g/cm3) 12. If a metal cylinder of copper (density = 8.9 g/cm3) has a mass of 45.4 grams, what is the volume of the cylinder? What is the cylinder’s diameter if it is 1.2 cm in height? 13. Convert 2950 m ...
... 11. What is the mass of a block of aluminum that has a volume of 22.4 cm3? (Density of Al = 2.70 g/cm3) 12. If a metal cylinder of copper (density = 8.9 g/cm3) has a mass of 45.4 grams, what is the volume of the cylinder? What is the cylinder’s diameter if it is 1.2 cm in height? 13. Convert 2950 m ...