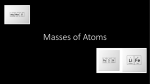* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atomic Structure, Isotopes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Diagram of Atom Atomic Structure, Isotopes STM Chapter 5 Pages 88-108 Humphry Davy Michael Faraday • Davy’s assistant • 1791-1829 • Coined terms we use today for electrical circuits • c. 1840 • 1778-1829 • British chemist—1807 found metals Electrolysis of Salts • Anode + • Cathode – • Opposites attract – particlesÆ + + particles Æ – • – particle: ANION • + particle: CATION Joseph John Thomson • • • • • 1856-1940 1897 discovered nature of ‘cathode rays’ Actually particles ELECTRONS Calculated mass to charge ratio of electrons Link to history of electron discovery http://www.aip.org/history/electron/ http://e3.uci.edu/clients/bjbecker/SpinningWeb/lecture19.html 1 Cathode Ray Tube Cathode ray deflection diagram Cathode ray deflection photo Perforated cathode Robert A. Millikan Static on oil drops • 1868-1953 • Discovered charge of an electron by oil-drop experiment • Calculated mass from Thomson’s mass to charge ratio • 1923 Nobel prize in physics http://www.physik.uni-frankfurt.de/~jr/gif/phys/millikan.jpg 2 Antoine-Henri Becquerel Marie Curie • 1852-1908 • Discovered spontaneous radioactivity • 1867-1934 • Named radioactivity • Discovered polonium, radium • 1903 and 1911 Nobel prize in physics http://www.anlamak.com/tanimak/yabanci/Curie-Marie.htm http://www.chemistryexplained.com/Ar-Bo/Becquerel-Antoine-Henri.html Radioactive emissions and their charge Ernest Rutherford • 1871-1937 • Named types of radiation • Proposed nucleus of atom as explanation for alpha particle behavior in 1911 http://www.physics.northwestern.edu/Phyx103/web/nuc-timeline.html Gold foil deflects a few alpha particles Model to explain alpha particle deflection 3 Analogy of atom--cont Atomic model analogy http://www.joesentell.com/panther/panther.htm http://web.ics.purdue.edu/~drhodes/hort410/vgsd13.htm http://www.skynet.ie/~ceason/cormac/stuff/housefly_anim.gif http://www.sportslighting.com/feature/ls.html Hydrogen ion James Chadwick • • • • • Protons and Neutrons in Nucleus 1891-1974 Discovered neutron Same mass as proton Accounts for isotopes 1935 Nobel prize in physics http://news.sina.com.cn/cl/2001-12-07/414701.html Atomic Structure • Protons • Neutrons • Electrons 4 Atomic Structure Atomic Structure • Neutrons • Protons Electrical charge 0 Mass = 1 atomic unit Electrical charge +1 Mass = 1 atomic mass unit (u) Atomic Structure Atomic Structure • Electrons • Protons • Neutrons Make up the NUCLEUS NEW KLEE US Nucleons—have mass NEW KLEE ONS • Electrons—minimal mass Electrical charge -1 Mass = almost nothing (1/1837 of a proton) Analogy of atom--cont Protons and Neutrons in Nucleus http://www.joesentell.com/panther/panther.htm http://web.ics.purdue.edu/~drhodes/hort410/vgsd13.htm http://www.skynet.ie/~ceason/cormac/stuff/housefly_anim.gif 5 Atomic Structure Atomic Structure • Protons • Neutrons • Electrons • Protons Atomic Structure Isotope notation Atomic Number Controls properties of elements Constant number for all atoms of the same element • Neutrons – Atoms may have different numbers of neutrons – Different atomic masses of atoms of the same element – ISOTOPES of the same element In-class Activity #1 Stable Isotope of Sodium In-class activity #2 • Write the atomic number in this isotope notation. In-class activity #2 • How many protons? • How many neutrons? 6 In-class activity #2 Electrons • • • • Positioned in energy levels First_level 2 Second_level 8 Higher_levels temporarily_fill_with_8 • How many nucleons? • What is the atomic mass number Neils Bohr’s electron energy level diagram Periodic Table In Class Activity # 3 • • • • Groups of the Periodic Table Alkali Metals—first column Alkaline Earth Metals—second column Halogens—next to last column Noble Gases—last column 7