Due Date - Humble ISD
... 9. How many total chromosomes does this individual have? __46__________ 10. Does this individual have Klinefelter’s syndrome, Turner syndrome, or Down syndrome? _no, this individual has the correct number of chromosomes.________ 11. For chromosome #’s 1-22, why are there 2 of each chromosome? Each i ...
... 9. How many total chromosomes does this individual have? __46__________ 10. Does this individual have Klinefelter’s syndrome, Turner syndrome, or Down syndrome? _no, this individual has the correct number of chromosomes.________ 11. For chromosome #’s 1-22, why are there 2 of each chromosome? Each i ...
Eötvös Loránd Science University Faculty of Sciences Department of
... The course intends to introduce students to the principles and applications of gene technology, that is recombinant DNS techniques, based on background knowledge of biochemistry and molecular biology. Our important goal is that the students understand the controversial and often misinterpreted conce ...
... The course intends to introduce students to the principles and applications of gene technology, that is recombinant DNS techniques, based on background knowledge of biochemistry and molecular biology. Our important goal is that the students understand the controversial and often misinterpreted conce ...
Dictyostelium discoideum, an interesting model organism for
... proteins from the information in genes (in eukaryotes, genes are located on chromosomes in the nucleus). The RNAi pathway interacts with an intermediate in this process (messenger RNA) and hinders the production of functional proteins. This process is therefore very important in the regulation of pr ...
... proteins from the information in genes (in eukaryotes, genes are located on chromosomes in the nucleus). The RNAi pathway interacts with an intermediate in this process (messenger RNA) and hinders the production of functional proteins. This process is therefore very important in the regulation of pr ...
Chapter 9
... The following terms are freely used in your text book. Make sure you know what they mean, how they are used, and how to use them. When an example is given, make sure you can describe and recall it. If a picture is provided, know what the structure looks like and where it is located. If a diagram des ...
... The following terms are freely used in your text book. Make sure you know what they mean, how they are used, and how to use them. When an example is given, make sure you can describe and recall it. If a picture is provided, know what the structure looks like and where it is located. If a diagram des ...
Life science semester 2 final review
... ___________________________________________ 9. What separates the lizard from the salamander? ___________________________________________ 10. What do all of these animals have in common? ___________________________________________ 11. Which animals have lungs? _______________________________________ ...
... ___________________________________________ 9. What separates the lizard from the salamander? ___________________________________________ 10. What do all of these animals have in common? ___________________________________________ 11. Which animals have lungs? _______________________________________ ...
Biology STAAR Review
... Sex determination – controlled by sex chromosomes X & Y Autosomes – non-sex chromosomes. (44 in humans +2 sex chromosomes) Sex-linked traits – genes located on the sex chromosomes Sex-linked Traits: In humans, the Y chromosome contains the determinant for maleness, the X contains many genes. If a ma ...
... Sex determination – controlled by sex chromosomes X & Y Autosomes – non-sex chromosomes. (44 in humans +2 sex chromosomes) Sex-linked traits – genes located on the sex chromosomes Sex-linked Traits: In humans, the Y chromosome contains the determinant for maleness, the X contains many genes. If a ma ...
View the Accelerated Biology Syllabus
... 13 Days Big Ideas #8 & 9 Variations in Genetics 3 Quizzes Human Genetics/Genetic Testing/Counseling ...
... 13 Days Big Ideas #8 & 9 Variations in Genetics 3 Quizzes Human Genetics/Genetic Testing/Counseling ...
EOC_CUMMULATIVE_REVIEW
... because 13 countries worked on it. 4. The objective of the Human Genome Project was to understand the ____________________. 5. Scientists wanted to determine the sequence of bases to ultimately find the ____________________ responsible for certain diseases. VI. Genetics A. Vocabulary (terms: phenoty ...
... because 13 countries worked on it. 4. The objective of the Human Genome Project was to understand the ____________________. 5. Scientists wanted to determine the sequence of bases to ultimately find the ____________________ responsible for certain diseases. VI. Genetics A. Vocabulary (terms: phenoty ...
biology second semester study guide
... Transfer RNA genetic code frameshift mutation Transcription codon mutagent RNA polymerase translation polyploidy Promoter anticodon operon operator ...
... Transfer RNA genetic code frameshift mutation Transcription codon mutagent RNA polymerase translation polyploidy Promoter anticodon operon operator ...
Characteristics of Life Notes Packet
... b. cells may group into tissues, organs, organ systems in more complex organisms examples: plants, animals, most fungi, some protists. ...
... b. cells may group into tissues, organs, organ systems in more complex organisms examples: plants, animals, most fungi, some protists. ...
STAAR Biology EOC Practice Test #1
... A I must be complementary to an mRNA codon. B This process occurs in the nucleus of a cell. C III shows the first two amino acids of a growing polypeptide chain. D The process shown is translation. 21 Bacterial species’ genomes are arranged somewhat differently than those of eukaryotes. Their circul ...
... A I must be complementary to an mRNA codon. B This process occurs in the nucleus of a cell. C III shows the first two amino acids of a growing polypeptide chain. D The process shown is translation. 21 Bacterial species’ genomes are arranged somewhat differently than those of eukaryotes. Their circul ...
BIO EXAM NOTES
... zygote: a cell formed by the fusion of two gametes fertilization: in humans, the joining of male and female gametes haploid: a cell that contains half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell diploid: a cell that contains pairs of homologous chromosomes synapsis: the aligning of homologous chrom ...
... zygote: a cell formed by the fusion of two gametes fertilization: in humans, the joining of male and female gametes haploid: a cell that contains half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell diploid: a cell that contains pairs of homologous chromosomes synapsis: the aligning of homologous chrom ...
Chapters 4 and 5 Cell Structures, Functions and Transport
... • The Struggle for Existence-members of each species have to compete for food, shelter, other life necessities • Survival of the Fittest-Some individuals better suited for the environment • Over time, natural selection results in changes in inherited characteristics of a ...
... • The Struggle for Existence-members of each species have to compete for food, shelter, other life necessities • Survival of the Fittest-Some individuals better suited for the environment • Over time, natural selection results in changes in inherited characteristics of a ...
Life Science Review MCAS
... • The Struggle for Existence-members of each species have to compete for food, shelter, other life necessities • Survival of the Fittest-Some individuals better suited for the environment • Over time, natural selection results in changes in inherited characteristics of a ...
... • The Struggle for Existence-members of each species have to compete for food, shelter, other life necessities • Survival of the Fittest-Some individuals better suited for the environment • Over time, natural selection results in changes in inherited characteristics of a ...
Questions - National Biology Competition
... 23. You are asked to generate, within two weeks, a collection of recombinant plasmid clones that contain pieces of a large proportion of all human genes. What would be the fastest strategy? a. Digest human DNA with a restriction enzyme; digest the plasmid with two further restriction enzymes. Ligate ...
... 23. You are asked to generate, within two weeks, a collection of recombinant plasmid clones that contain pieces of a large proportion of all human genes. What would be the fastest strategy? a. Digest human DNA with a restriction enzyme; digest the plasmid with two further restriction enzymes. Ligate ...
Cell Membrane
... Meiosis – Reproduction of gametes (sex cells) o Each cell goes through 2 cell divisions producing 4 HAPLOID gametes. These cells have the number found in body cells so that when fertilization occurs, the original number is returned. Example: 23 + 23 = 46 o Allows variety! Prokaryotes such as bacteri ...
... Meiosis – Reproduction of gametes (sex cells) o Each cell goes through 2 cell divisions producing 4 HAPLOID gametes. These cells have the number found in body cells so that when fertilization occurs, the original number is returned. Example: 23 + 23 = 46 o Allows variety! Prokaryotes such as bacteri ...
Test Review Sheet: Biology Final – 09 Know the steps of the
... 20. Be able to complete a two trait cross using a punnet square? 21. What does cell respiration take place in the cell? What is the end result of cell respiration? 22. What is the equation for cell respiration? 23. What is cancer? 24. Be able to complete a one trait cross using a punnet square. 25. ...
... 20. Be able to complete a two trait cross using a punnet square? 21. What does cell respiration take place in the cell? What is the end result of cell respiration? 22. What is the equation for cell respiration? 23. What is cancer? 24. Be able to complete a one trait cross using a punnet square. 25. ...
Ch 12.DNA and RNA.Biology.Landis
... 25. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about transcription. a. During transcription, DNA polymerase binds to RNA and separates the DNA strands. b. RNA polymerase uses one strand of DNA as a template to assemble nucleotides into a strand of RNA. c. RNA polymerase binds only to DNA promot ...
... 25. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about transcription. a. During transcription, DNA polymerase binds to RNA and separates the DNA strands. b. RNA polymerase uses one strand of DNA as a template to assemble nucleotides into a strand of RNA. c. RNA polymerase binds only to DNA promot ...
Semester I exam study guide
... Homozygous: when two alleles of a gene in an individual are the same. XX or PP Heterozygous: when two alleles of a gene in an individual are different. Xx or Pp Phenotype: the physical appearance of a character. Genotype: the set of alleles that an individual has for its character (basically, chara ...
... Homozygous: when two alleles of a gene in an individual are the same. XX or PP Heterozygous: when two alleles of a gene in an individual are different. Xx or Pp Phenotype: the physical appearance of a character. Genotype: the set of alleles that an individual has for its character (basically, chara ...
File
... Gametes-meiosis Autosomes- mitosis Some plants send out runners to reproduce-asexual • Sexual reproduction must have a sperm and egg • Virus must use the invaded host ...
... Gametes-meiosis Autosomes- mitosis Some plants send out runners to reproduce-asexual • Sexual reproduction must have a sperm and egg • Virus must use the invaded host ...
Cell Membrane
... Meiosis – Reproduction of gametes (sex cells) o Each cell goes through 2 cell divisions producing 4 HAPLOID gametes. These cells have the number found in body cells so that when fertilization occurs, the original number is returned. Example: 23 + 23 = 46 o Allows variety! Prokaryotes such as bacteri ...
... Meiosis – Reproduction of gametes (sex cells) o Each cell goes through 2 cell divisions producing 4 HAPLOID gametes. These cells have the number found in body cells so that when fertilization occurs, the original number is returned. Example: 23 + 23 = 46 o Allows variety! Prokaryotes such as bacteri ...
12C Analyze the flow of matter and energy through trophic levels
... Autosome - chromosome that is not a sex chromosome P generation- individuals for initial cross F1 generation - offspring from initial cross F2 generation - offspring that results from cross of F1 individuals Dominant allele - masks recessive allele; expressed in homozygous dominant and heterozygous ...
... Autosome - chromosome that is not a sex chromosome P generation- individuals for initial cross F1 generation - offspring from initial cross F2 generation - offspring that results from cross of F1 individuals Dominant allele - masks recessive allele; expressed in homozygous dominant and heterozygous ...
Name Date ______ Hour ______ Living Things Study Guide 1
... grain from another flower of the same species lands on the stigma (cross-pollination) 25. Describe how fertilization takes place in a flower. Sperm is found in the pollen. After the pollen lands on the stigma, a tube grows from the pollen grain. The tube grows through the style to the ovule. The pol ...
... grain from another flower of the same species lands on the stigma (cross-pollination) 25. Describe how fertilization takes place in a flower. Sperm is found in the pollen. After the pollen lands on the stigma, a tube grows from the pollen grain. The tube grows through the style to the ovule. The pol ...
Development and Apoptosis
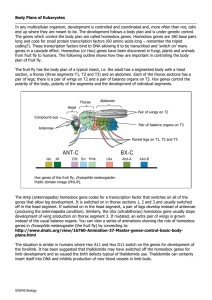
... In any multicellular organism, development is controlled and coordinated and, more often than not, cells end up where they are meant to be. The development follows a body plan and is under genetic control. The genes which control the body plan are called homeobox genes. Homeobox genes are 180 base p ...
... In any multicellular organism, development is controlled and coordinated and, more often than not, cells end up where they are meant to be. The development follows a body plan and is under genetic control. The genes which control the body plan are called homeobox genes. Homeobox genes are 180 base p ...
100 Important Facts you need to know to pass the
... 28. CANCER : certain genetic mutations in a cell can result in uncontrolled cell division. 29 CIRCULATORY system is the body's primary defense against diseasecausing pathogens. (IMMUNITY) 30. SURFACE RECEPTOR PROTEIN- a molecule found on the outer surfaces if cells that the immune system recognizes ...
... 28. CANCER : certain genetic mutations in a cell can result in uncontrolled cell division. 29 CIRCULATORY system is the body's primary defense against diseasecausing pathogens. (IMMUNITY) 30. SURFACE RECEPTOR PROTEIN- a molecule found on the outer surfaces if cells that the immune system recognizes ...