Biology 2011-2012
... Mitosis = division of 1 cell to get 2 IDENTICAL daughter cells. (Diploid to diploid) Meiosis = sex cells (gametes). 1 cell divides to get 4 daughter cells that are haploid. Human diploid number = 46. Haploid number = 23. Mitosis = PMAT (Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase) Interphase occurs dur ...
... Mitosis = division of 1 cell to get 2 IDENTICAL daughter cells. (Diploid to diploid) Meiosis = sex cells (gametes). 1 cell divides to get 4 daughter cells that are haploid. Human diploid number = 46. Haploid number = 23. Mitosis = PMAT (Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase) Interphase occurs dur ...
7th Grade Fall Semester Review 2011
... 1. Organisms vary and these variations (genes) are inherited by their offspring. 2. Organisms produce more offspring than can possibly survive in nature. ...
... 1. Organisms vary and these variations (genes) are inherited by their offspring. 2. Organisms produce more offspring than can possibly survive in nature. ...
Evolution`s Greatest Mistakes
... During recent human evolution, by contrast, there may have been strong selection for longer lifespans. The "grandmother hypothesis" proposes that individuals with long-lived grandparents to support them and pass down knowledge have more children who survive (New Scientist, 10 July 2004, p 14). Verdi ...
... During recent human evolution, by contrast, there may have been strong selection for longer lifespans. The "grandmother hypothesis" proposes that individuals with long-lived grandparents to support them and pass down knowledge have more children who survive (New Scientist, 10 July 2004, p 14). Verdi ...
Grade 7 - Humble ISD
... Radiant energy is transformed by plants into chemical energy in the form of glucose, in a process called photosynthesis. • Photosynthesis is a chemical reaction that uses carbon dioxide, water, and solar energy to produce glucose and oxygen. • Catastrophic events lead to disruptions in the natural e ...
... Radiant energy is transformed by plants into chemical energy in the form of glucose, in a process called photosynthesis. • Photosynthesis is a chemical reaction that uses carbon dioxide, water, and solar energy to produce glucose and oxygen. • Catastrophic events lead to disruptions in the natural e ...
EJU Syllabus for Biology for printing
... (2) Segregation of genetic information Segregation of genetic information by somatic cell division Cell cycle and DNA replication Mechanism of DNA replication (3) Expression of genetic information Mechanism of gene expression [Example] transcription, translation, splicing, Changes in genetic informa ...
... (2) Segregation of genetic information Segregation of genetic information by somatic cell division Cell cycle and DNA replication Mechanism of DNA replication (3) Expression of genetic information Mechanism of gene expression [Example] transcription, translation, splicing, Changes in genetic informa ...
Biology II – Chapter 1 Study Guide
... 12. A ________________________________________ is a general explanation of natural phenomena based on extensive and repeated observable evidence. 13. An organism that eats other organisms is a(n) __________________________________. 14. A _______________________________ is all the organisms and their ...
... 12. A ________________________________________ is a general explanation of natural phenomena based on extensive and repeated observable evidence. 13. An organism that eats other organisms is a(n) __________________________________. 14. A _______________________________ is all the organisms and their ...
AB Biology Summer Assignment (Word)
... b) Name a fifth group of organic molecules. 16) What is an enzyme? a) What group of macromolecules are enzymes in? b) What is the job of an enzyme? c) List 2 ways to increase an enzyme’s activity. d) What two things can cause enzymes to malfunction? 17) An acid is a substance with a pH of __________ ...
... b) Name a fifth group of organic molecules. 16) What is an enzyme? a) What group of macromolecules are enzymes in? b) What is the job of an enzyme? c) List 2 ways to increase an enzyme’s activity. d) What two things can cause enzymes to malfunction? 17) An acid is a substance with a pH of __________ ...
Mutation The primary source of variation for all life forms.
... 39. What the millions of different species on our plant compete for. Down 1. Like a family tree this shows how all living things are related. 2. The selection that has a goal in mind; to preserve a specific trait. Usually controlled by humans. 3. The second source of variation that shuffles our gene ...
... 39. What the millions of different species on our plant compete for. Down 1. Like a family tree this shows how all living things are related. 2. The selection that has a goal in mind; to preserve a specific trait. Usually controlled by humans. 3. The second source of variation that shuffles our gene ...
Epigenetics - Creighton Chemistry Webserver
... complexes recognize the modified histones through specific domains ...
... complexes recognize the modified histones through specific domains ...
HERE
... repair cells, organs, and repairing limbs. Discuss the steps in Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection: 1) Beneficial traits help organisms survive are passes from parents to offspring. 2) Resources limit carrying capacity with limits the number of offspring. 3) Traits that help in surviv ...
... repair cells, organs, and repairing limbs. Discuss the steps in Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection: 1) Beneficial traits help organisms survive are passes from parents to offspring. 2) Resources limit carrying capacity with limits the number of offspring. 3) Traits that help in surviv ...
Spring Semester Biology Review
... • Meiosis occurs only in sexually reproducing organisms. Depending on the organism, it may produce haploid gametes, which do not divide further but instead fuse to produce a diploid zygote; or it may produce haploid spores, which divide by mitotic cell cycles and produce unicellular or multicellular ...
... • Meiosis occurs only in sexually reproducing organisms. Depending on the organism, it may produce haploid gametes, which do not divide further but instead fuse to produce a diploid zygote; or it may produce haploid spores, which divide by mitotic cell cycles and produce unicellular or multicellular ...
EIGHTH GRADE CRT FIRST QUARTER 2003 (COURSE #40208)
... Transcription is the process by which genetic information encoded in DNA is transferred to what type of molecule? What are the portions of DNA molecules that actually code for the production of proteins called? What are the enzymes that unwind DNA called? Guanine typically occurs in the same amount ...
... Transcription is the process by which genetic information encoded in DNA is transferred to what type of molecule? What are the portions of DNA molecules that actually code for the production of proteins called? What are the enzymes that unwind DNA called? Guanine typically occurs in the same amount ...
Biology 1406 - HCC Learning Web
... topic – the most important concept in biology, because it explains how living things that are so different can show so much similarity between them. The term diversity refers to the millions of different species that exist – cows and pea plants, mosquitoes and oak trees. In all this diversity, there ...
... topic – the most important concept in biology, because it explains how living things that are so different can show so much similarity between them. The term diversity refers to the millions of different species that exist – cows and pea plants, mosquitoes and oak trees. In all this diversity, there ...
Final Exam Review Packet (Scary, Isn`t It?) Date: Time: Room
... solution it _________gains water____________. If in an isotonic solution it __________remains the same. 34. How is facilitated diffusion different from regular diffusion? _____________movement of molecules through a protein channel_____________________ 35. What three substances may pass through the ...
... solution it _________gains water____________. If in an isotonic solution it __________remains the same. 34. How is facilitated diffusion different from regular diffusion? _____________movement of molecules through a protein channel_____________________ 35. What three substances may pass through the ...
Protists
... • “creates more variation” Is this valid or necessary? • allows more individuals to survive a disease (mutant survival vs recessives • Allows, through crossover, combination of bad genes and elimination. (bad genes often do bad things, not just inoperative) • Bigger cells, smaller population, mutati ...
... • “creates more variation” Is this valid or necessary? • allows more individuals to survive a disease (mutant survival vs recessives • Allows, through crossover, combination of bad genes and elimination. (bad genes often do bad things, not just inoperative) • Bigger cells, smaller population, mutati ...
biology vocabulary eoc review - GastonCountyScienceResources
... _______ 1. cellular structure with analogous function to the human skeleton; maintains cell shape _______ 2. protein that changes the rate of a chemical reaction and is involved in nearly all metabolic processes _______ 3. disease-causing, non-living particle composed of an inner core of nucleic aci ...
... _______ 1. cellular structure with analogous function to the human skeleton; maintains cell shape _______ 2. protein that changes the rate of a chemical reaction and is involved in nearly all metabolic processes _______ 3. disease-causing, non-living particle composed of an inner core of nucleic aci ...
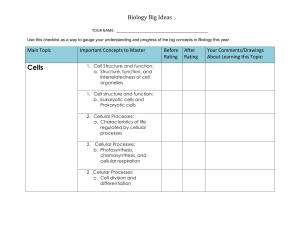
Biology Standards Checklist
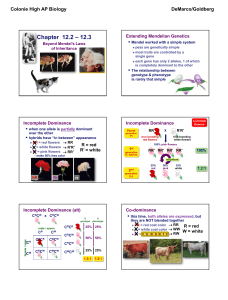
... 1. Cellular genetics: protein synthesis, replication, transcription, translation 2. Structure and function of DNA in cells 3. Genetic mechanisms and inheritance: incomplete dominance, sex-linked traits, pleiotropy, epistasis, dihybrid crosses, polygenic inheritance 4. Mutations: DNA alterations 5. M ...
... 1. Cellular genetics: protein synthesis, replication, transcription, translation 2. Structure and function of DNA in cells 3. Genetic mechanisms and inheritance: incomplete dominance, sex-linked traits, pleiotropy, epistasis, dihybrid crosses, polygenic inheritance 4. Mutations: DNA alterations 5. M ...
SCIENCE
... 1. Follow all safety rules. 2. Handle all equipment carefully. 3. Do not visit other lab tables or workstations. 4. Talk quietly with your lab partner. 5. CLEAN UP after yourself. 6. Be sure your results are accurate and lab questions complete. ASSIGNMENTS: 1. Late assignments may be turned in for h ...
... 1. Follow all safety rules. 2. Handle all equipment carefully. 3. Do not visit other lab tables or workstations. 4. Talk quietly with your lab partner. 5. CLEAN UP after yourself. 6. Be sure your results are accurate and lab questions complete. ASSIGNMENTS: 1. Late assignments may be turned in for h ...
Bacterial Transformation
... exist outside the main bacterial chromosome and carry their own genes for specialized functions. In genetic engineering, plasmids are one means used to introduce foreign genes into a bacterial cell. Some plasmids have the ampR gene, which confers resistance to the antibiotic ampicillin. E. coli ce ...
... exist outside the main bacterial chromosome and carry their own genes for specialized functions. In genetic engineering, plasmids are one means used to introduce foreign genes into a bacterial cell. Some plasmids have the ampR gene, which confers resistance to the antibiotic ampicillin. E. coli ce ...
Unit 7: DNA –Part 2—Protein synthesis
... thousands of different genes. One or many genes can determine an inherited trait of an individual, and a single gene can influence more than one trait. Before a cell divides, this genetic information must be copied and apportioned evenly into the daughter cells. ...
... thousands of different genes. One or many genes can determine an inherited trait of an individual, and a single gene can influence more than one trait. Before a cell divides, this genetic information must be copied and apportioned evenly into the daughter cells. ...
EOC review packet answers Biology EOC
... a. Sickle cell anemia – point mutation – substitution of one letter in the DNA codes for the wrong amino acid. Blood cells are sickle shaped. b. Colorblindness – X linked trait, recessive c. Cystic fibrosis – recessive, somatic trait. d. Hemophilia – X linked trait, recessive e. Down syndrome – non ...
... a. Sickle cell anemia – point mutation – substitution of one letter in the DNA codes for the wrong amino acid. Blood cells are sickle shaped. b. Colorblindness – X linked trait, recessive c. Cystic fibrosis – recessive, somatic trait. d. Hemophilia – X linked trait, recessive e. Down syndrome – non ...
Test Review Sheet: Biology Final – 09 The Answer are under each
... Plants- large vacuole, starch as food storage, larger size, regular shape, cell wall Animals – small vacuole, glycogen as food storage, small size, irregular shape, no cell wall 11. What is changed during a controlled experiment? Variable 12. What are the three laws of Gregor Mendel? Law of dominanc ...
... Plants- large vacuole, starch as food storage, larger size, regular shape, cell wall Animals – small vacuole, glycogen as food storage, small size, irregular shape, no cell wall 11. What is changed during a controlled experiment? Variable 12. What are the three laws of Gregor Mendel? Law of dominanc ...
Cells - SchoolRack
... from the mRNA by tRNA to make a protein. This happens at the ribosomes on the endoplasmic reticulum. A tRNA carries the specific amino acid. A codon is a sequence of 3 bases on an mRNA molecule. For example… guanine - uracil - cytosine is a codon for a specific amino acid (valine). ...
... from the mRNA by tRNA to make a protein. This happens at the ribosomes on the endoplasmic reticulum. A tRNA carries the specific amino acid. A codon is a sequence of 3 bases on an mRNA molecule. For example… guanine - uracil - cytosine is a codon for a specific amino acid (valine). ...
Test Review Sheet: Biology Final – 09 The Answer are under each
... Plants- large vacuole, starch as food storage, larger size, regular shape, cell wall Animals – small vacuole, glycogen as food storage, small size, irregular shape, no cell wall 11. What is changed during a controlled experiment? Variable 12. What are the three laws of Gregor Mendel? Law of dominanc ...
... Plants- large vacuole, starch as food storage, larger size, regular shape, cell wall Animals – small vacuole, glycogen as food storage, small size, irregular shape, no cell wall 11. What is changed during a controlled experiment? Variable 12. What are the three laws of Gregor Mendel? Law of dominanc ...