Homeostasis of glucose
... out of cells H+ Moves in • When Insulin is deficient there is a net efflux K+ from the cell. • Usually [Plasma K+] does not rise because excess K+ is lost in the urine (this occurs bc the glucose in the tubules that cannot be reabsorbed due to exceeding its Tm acts as a diuretic and pulls water and ...
... out of cells H+ Moves in • When Insulin is deficient there is a net efflux K+ from the cell. • Usually [Plasma K+] does not rise because excess K+ is lost in the urine (this occurs bc the glucose in the tubules that cannot be reabsorbed due to exceeding its Tm acts as a diuretic and pulls water and ...
Upgrading the Hemicellulosic Fraction of Biomass into Biofuel
... identified in both C. beijerinckii NCIMB8052 (Mitchell et al., 1991) and C. acetobutylicum ATCC824 (Tangney and Mitchell, 2007). However, PTS it is not usually involved in the uptake of pentoses. In E. coli for instance, two distinct transporters for xylose (XylFGH) and arabinose (AraFGH) have been ...
... identified in both C. beijerinckii NCIMB8052 (Mitchell et al., 1991) and C. acetobutylicum ATCC824 (Tangney and Mitchell, 2007). However, PTS it is not usually involved in the uptake of pentoses. In E. coli for instance, two distinct transporters for xylose (XylFGH) and arabinose (AraFGH) have been ...
... ii) What is the distribution of polar and non-polar residues along the polypeptide sequence and how does this distribution relate to the interaction of the protein with the membrane? iii) Residues that contact the lipid are generally large and nonpolar. Why are small non-polar seldom found? The diag ...
Ces locus embedded proteins control the non
... role of the genes adjacent to the structural genes cesA/cesB, coding for the nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS), gene inactivation- and overexpression mutants of the emetic strain F4810/72 were constructed and their impact on cereulide biosynthesis was assessed. The hydrolase CesH turned out to ...
... role of the genes adjacent to the structural genes cesA/cesB, coding for the nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS), gene inactivation- and overexpression mutants of the emetic strain F4810/72 were constructed and their impact on cereulide biosynthesis was assessed. The hydrolase CesH turned out to ...
Comparative genomic analysis of carbon and nitrogen assimilation
... The capability of microorganisms to fix atmospheric nitrogen plays an important role in recycling scarce nitrogen existing in nutrient-poor acidic conditions; however, the availability of nitrogen and the energy required for its fixation may limit bacterial growth and adversely affect the efficiency ...
... The capability of microorganisms to fix atmospheric nitrogen plays an important role in recycling scarce nitrogen existing in nutrient-poor acidic conditions; however, the availability of nitrogen and the energy required for its fixation may limit bacterial growth and adversely affect the efficiency ...
review on enhancement of glucose uptake and up
... adipocytes, and skeletal muscle cells. Medicinal plants or their active constituents that can up-regulate GLUT expression and translocation that helps in the treatment of insulin resistance and hyperglycemia. Evidence from insulin-resistant rodent models suggests that defective glucose transport in ...
... adipocytes, and skeletal muscle cells. Medicinal plants or their active constituents that can up-regulate GLUT expression and translocation that helps in the treatment of insulin resistance and hyperglycemia. Evidence from insulin-resistant rodent models suggests that defective glucose transport in ...
Genome-wide transcription profiling of aerobic and anaerobic
... cells grow rapidly when respiring oxygen. In the absence of oxygen and alternative electron acceptors, the cells switch to anaerobic respiration and fermentation (Partridge et al. 2006). However, it was shown that E. coli anaerobic biofilms could not be formed even when cultures were supplemented wi ...
... cells grow rapidly when respiring oxygen. In the absence of oxygen and alternative electron acceptors, the cells switch to anaerobic respiration and fermentation (Partridge et al. 2006). However, it was shown that E. coli anaerobic biofilms could not be formed even when cultures were supplemented wi ...
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase
... Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase increases in amount in most tissues, including skeletal muscle, via increased gene transcription. Under the same conditions, the amount of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Phosphatase decreases. The resulting inhibition of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase prevents muscle and other tiss ...
... Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase increases in amount in most tissues, including skeletal muscle, via increased gene transcription. Under the same conditions, the amount of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Phosphatase decreases. The resulting inhibition of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase prevents muscle and other tiss ...
intermediary metabolism
... Hormones are chemical menagers secreted by different endocrine glands and carried by blood to other tissues or organs, where they may stimulate or inhibit some specific metabolic activity. For e.g. the hormone adrenalin, secreted by the medulla of the adrenal gland, is carried by the blood to the li ...
... Hormones are chemical menagers secreted by different endocrine glands and carried by blood to other tissues or organs, where they may stimulate or inhibit some specific metabolic activity. For e.g. the hormone adrenalin, secreted by the medulla of the adrenal gland, is carried by the blood to the li ...
Corn Syrups: Clearing up the Confusion
... syrups range from a low of 20 to above 73 DE. Spray or vacuum drum driers are used to make dried corn syrups (corn syrup solids), which function the same as liquid products when rehydrated. HFCS contains both fructose and glucose (a key distinguishing feature from regular corn syrups), and are not c ...
... syrups range from a low of 20 to above 73 DE. Spray or vacuum drum driers are used to make dried corn syrups (corn syrup solids), which function the same as liquid products when rehydrated. HFCS contains both fructose and glucose (a key distinguishing feature from regular corn syrups), and are not c ...
Carbohydrates and the liver
... several hours after the meal, EGP rises slowly towards basal levels. These changes in EGP are controlled primarily by two pancreatic hormones, insulin and glucagon. Insulin is secreted by the pancreatic β cells directly into the portal circulation. The liver extracts and degrades between 50% and 80% ...
... several hours after the meal, EGP rises slowly towards basal levels. These changes in EGP are controlled primarily by two pancreatic hormones, insulin and glucagon. Insulin is secreted by the pancreatic β cells directly into the portal circulation. The liver extracts and degrades between 50% and 80% ...
(lip) that - Repositories
... regulatory elements. The transcriptional activity of the lip gene was monitored under a variety of growth conditions in an attempt to detect changes in lip expression. Several models of gene regulation were evaluated in this manner. Among these were catabolite repression, end-product repression, and ...
... regulatory elements. The transcriptional activity of the lip gene was monitored under a variety of growth conditions in an attempt to detect changes in lip expression. Several models of gene regulation were evaluated in this manner. Among these were catabolite repression, end-product repression, and ...
Regulation of nitrogen metabolism in gram
... nitrogen excess, GlnR functions as a repressor of the glnRA operon [5]. In contrast to GlnR, TnrA may repress as well as activate transcription. Under conditions of an excess of glutamine and glutamate in the cell, TnrA binds to glutamine synthase, forming an inactive complex. As a result, TnrA cann ...
... nitrogen excess, GlnR functions as a repressor of the glnRA operon [5]. In contrast to GlnR, TnrA may repress as well as activate transcription. Under conditions of an excess of glutamine and glutamate in the cell, TnrA binds to glutamine synthase, forming an inactive complex. As a result, TnrA cann ...
pDsRed-Monomer-C1 Vector Information
... DsRed-Monomer coding sequence and the SV40 polyadenylation signal (SV40 poly A). Genes cloned into the MCS will be expressed as fusions to the C-terminus of DsRed-Monomer if they are in the same reading frame as DsRed-Monomer and there are no intervening stop codons. A Kozak consensus translation in ...
... DsRed-Monomer coding sequence and the SV40 polyadenylation signal (SV40 poly A). Genes cloned into the MCS will be expressed as fusions to the C-terminus of DsRed-Monomer if they are in the same reading frame as DsRed-Monomer and there are no intervening stop codons. A Kozak consensus translation in ...
Electrone transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation
... pathway, the product of one reaction serves as the substrate of the subsequent reaction. These are collectively called metabolism, which is the sum of all the chemical changes occurring in a cell, a tissue, or the body. Most pathways can be classified as either catabolic (degradative) or ...
... pathway, the product of one reaction serves as the substrate of the subsequent reaction. These are collectively called metabolism, which is the sum of all the chemical changes occurring in a cell, a tissue, or the body. Most pathways can be classified as either catabolic (degradative) or ...
EPISTASIS & METABOLISM Presented by Chintan Joshi
... - Our method evaluates effects of intergenic mutations which affect the network properties. - Our method captures the effect of environmental factors on the network. We showed that difference in environmental conditions can change epistasis landscape. We are only capturing the long-term effects; i.e ...
... - Our method evaluates effects of intergenic mutations which affect the network properties. - Our method captures the effect of environmental factors on the network. We showed that difference in environmental conditions can change epistasis landscape. We are only capturing the long-term effects; i.e ...
Production of Poly Hydroxybutyric Acid with B megaterium
... carbohydrates, minerals, phenolic compounds, and amino acids, the maple syrup, when added to the minimal medium which already provided a small amount of a carbon source and amino acids, allowed the bacteria to sustain itself in the exponential growth phase for a longer period of time and become more ...
... carbohydrates, minerals, phenolic compounds, and amino acids, the maple syrup, when added to the minimal medium which already provided a small amount of a carbon source and amino acids, allowed the bacteria to sustain itself in the exponential growth phase for a longer period of time and become more ...
03-1 Metabolism of carbohydrate
... Both activities are on the same protein. It’s a bifunctional enzyme. ...
... Both activities are on the same protein. It’s a bifunctional enzyme. ...
Insulin and Glucagon
... adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL) at the fat droplet-cytosol border*. Diglycerides are thereafter converted to monoglycerides by hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL). The monoglycerides are hydrolyzed by a cytosolic monoglyceride lipase. These three enzymes and their control elements (also proteins, esp ...
... adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL) at the fat droplet-cytosol border*. Diglycerides are thereafter converted to monoglycerides by hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL). The monoglycerides are hydrolyzed by a cytosolic monoglyceride lipase. These three enzymes and their control elements (also proteins, esp ...
Principles of Metabolic Regulation
... Under resting conditions, [ATP] is high and [AMP] low because the total adenine nucleotide pool is constant. [Citrate] and [acetyl-CoA] are intermediate because O2 is not limiting and the citric acid cycle is functioning. Under conditions of active exertion (running), O2 becomes limiting and ATP syn ...
... Under resting conditions, [ATP] is high and [AMP] low because the total adenine nucleotide pool is constant. [Citrate] and [acetyl-CoA] are intermediate because O2 is not limiting and the citric acid cycle is functioning. Under conditions of active exertion (running), O2 becomes limiting and ATP syn ...
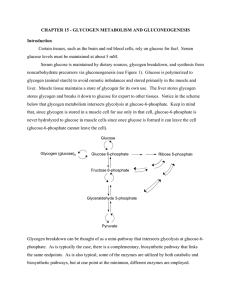
CHAPTER 15 - GLYCOGEN METABOLISM AND
... Not shown in this figure is the effect of cAMP dependent protein kinase on glycogen synthase whose activity, if you’ll recall, is also sensitive to phosphorlation. In this case, however, phosphorylation inactivates glycogen synthase. The phosphorylation, thus inactivation, of glycogen synthase is c ...
... Not shown in this figure is the effect of cAMP dependent protein kinase on glycogen synthase whose activity, if you’ll recall, is also sensitive to phosphorlation. In this case, however, phosphorylation inactivates glycogen synthase. The phosphorylation, thus inactivation, of glycogen synthase is c ...
Genetic Engineering for Improved Xylose Fermentation by Yeasts
... assimilative enzymes do not, By 1945, various fusaria had been used to ferment sulfite waste liquors and hydrolysates [12]. Karczewska reported in 1959 that Candida tropicalis would directly convert D-xylose and L-arabinose to ethanol under low aeration conditions [13] and that C. tropicalis and Can ...
... assimilative enzymes do not, By 1945, various fusaria had been used to ferment sulfite waste liquors and hydrolysates [12]. Karczewska reported in 1959 that Candida tropicalis would directly convert D-xylose and L-arabinose to ethanol under low aeration conditions [13] and that C. tropicalis and Can ...
as a PDF
... The B. subtilis trpEDCFBA operon contains six of the seven genes that are required for the biosynthesis of tryptophan from chorismic acid, the common aromatic amino acid precursor (Fig. 1). The trp operon is present within a histidine and aromatic amino acid supraoperon. In addition to the trp opero ...
... The B. subtilis trpEDCFBA operon contains six of the seven genes that are required for the biosynthesis of tryptophan from chorismic acid, the common aromatic amino acid precursor (Fig. 1). The trp operon is present within a histidine and aromatic amino acid supraoperon. In addition to the trp opero ...
Lac operon

lac operon (lactose operon) is an operon required for the transport and metabolism of lactose in Escherichia coli and many other enteric bacteria. Although glucose is the preferred carbon source for most bacteria, the lac operon allows for the effective digestion of lactose when glucose is not available. Gene regulation of the lac operon was the first genetic regulatory mechanism to be understood clearly, so it has become a foremost example of prokaryotic gene regulation. It is often discussed in introductory molecular and cellular biology classes at universities for this reason.Bacterial operons are polycistronic transcripts that are able to produce multiple proteins from one mRNA transcript. In this case, when lactose is required as a sugar source for the bacterium, the three genes of the lac operon can be expressed and their subsequent proteins translated: lacZ, lacY, and lacA. The gene product of lacZ is β-galactosidase which cleaves lactose, a disaccharide, into glucose and galactose. LacY encodes lactose permease, a protein which becomes embedded in the cytoplasmic membrane to enable transport of lactose into the cell. Finally, lacA encodes galactoside O-acetyltransferase. Layout of the lac operon.It would be wasteful to produce the enzymes when there is no lactose available or if there is a more preferable energy source available, such as glucose. The lac operon uses a two-part control mechanism to ensure that the cell expends energy producing the enzymes encoded by the lac operon only when necessary. In the absence of lactose, the lac repressor halts production of the enzymes encoded by the lac operon. In the presence of glucose, the catabolite activator protein (CAP), required for production of the enzymes, remains inactive, and EIIAGlc shuts down lactose permease to prevent transport of lactose into the cell. This dual control mechanism causes the sequential utilization of glucose and lactose in two distinct growth phases, known as diauxie.