Chapter 5 Endocrine Regulation of Glucose - Rose
... Insulin is a peptide hormone. It is synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum as part of an 11.5 kDa precursor protein called pre-proinsulin. The endoplasmic reticulum-targeting sequence is cleaved during peptide synthesis to release proinsulin. Proinsulin is packaged into secretory vesicles, w ...
... Insulin is a peptide hormone. It is synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum as part of an 11.5 kDa precursor protein called pre-proinsulin. The endoplasmic reticulum-targeting sequence is cleaved during peptide synthesis to release proinsulin. Proinsulin is packaged into secretory vesicles, w ...
Channel-mediated lactic acid transport: a novel function for
... of water channels. LpGlpF1 and LpGlpF4 clustered together in the second group (named GlpF1/F4) as expected, since their protein sequences were 92 % identical. The glpF1 gene of Lb. plantarum is part of the lar operon, consisting of larA, larB, larC, larD (glpF1) and larE (Figure 1B). Since glpF1 is ...
... of water channels. LpGlpF1 and LpGlpF4 clustered together in the second group (named GlpF1/F4) as expected, since their protein sequences were 92 % identical. The glpF1 gene of Lb. plantarum is part of the lar operon, consisting of larA, larB, larC, larD (glpF1) and larE (Figure 1B). Since glpF1 is ...
PPT
... Extremely High Rates of +1 Frameshifting Occur in Euplotes Species Euplotes species use UAA and UAG as stop codons, and have recoded UGA as a cysteine codon. Most organisms have an extremely low incidence of programmed translational frameshifting (e.g., frameshifting occurs in only 3 out of 600 ...
... Extremely High Rates of +1 Frameshifting Occur in Euplotes Species Euplotes species use UAA and UAG as stop codons, and have recoded UGA as a cysteine codon. Most organisms have an extremely low incidence of programmed translational frameshifting (e.g., frameshifting occurs in only 3 out of 600 ...
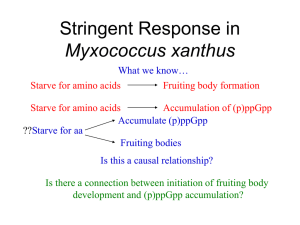
Stringent Response in Myxococcus xanthus
... How do we test to see if DK527is really a relA- mutant? ...
... How do we test to see if DK527is really a relA- mutant? ...
G. M. Tielens Hellemond, Fred R. Opperdoes and Aloysius Susanne
... long slender bloodstream form has the simplest pathway for the degradation of glucose, viz. glycolysis, and excretes pyruvate as the sole end product (2– 4). However, the glycosomal and mitochondrial metabolism of T. brucei changes significantly upon transformation from the long slender bloodstream ...
... long slender bloodstream form has the simplest pathway for the degradation of glucose, viz. glycolysis, and excretes pyruvate as the sole end product (2– 4). However, the glycosomal and mitochondrial metabolism of T. brucei changes significantly upon transformation from the long slender bloodstream ...
CHAPTER 1 1.1 Introduction In many developing countries, herbal
... (Kamboj, 2000). This is supported by literature in behavioural and pharmacological sciences with animals and people using a number of different plants for the control of disease symptoms and related illnesses in their environment (Hart, 2004; Cousins and Huffman, 2002). One of such disorder is diabe ...
... (Kamboj, 2000). This is supported by literature in behavioural and pharmacological sciences with animals and people using a number of different plants for the control of disease symptoms and related illnesses in their environment (Hart, 2004; Cousins and Huffman, 2002). One of such disorder is diabe ...
Physiology Ch 78 p939-954 [4-25
... -in high concentrations, it enhances strength of heart, increases blood flow to tissues, enhances bile secretion, and inhibits gastric acid secretion Regulation of Glucagon Secretion -Increased Blood Glucose Inhibits Glucagon Secretion – most potent factor controlling glucagon secretion, opposite to ...
... -in high concentrations, it enhances strength of heart, increases blood flow to tissues, enhances bile secretion, and inhibits gastric acid secretion Regulation of Glucagon Secretion -Increased Blood Glucose Inhibits Glucagon Secretion – most potent factor controlling glucagon secretion, opposite to ...
Gluconeogenesis
... Bypass of Pyruvate Kinase Pyruvate Kinase (Glycolysis) catalyzes: phosphoenolpyruvate + ADP pyruvate + ATP For bypass of the Pyruvate Kinase reaction, cleavage of 2 ~P bonds is required. DG for cleavage of one ~P bond of ATP is insufficient to drive synthesis of phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP). PEP has ...
... Bypass of Pyruvate Kinase Pyruvate Kinase (Glycolysis) catalyzes: phosphoenolpyruvate + ADP pyruvate + ATP For bypass of the Pyruvate Kinase reaction, cleavage of 2 ~P bonds is required. DG for cleavage of one ~P bond of ATP is insufficient to drive synthesis of phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP). PEP has ...
Time-Resolved Transcriptome Analysis of Bacillus subtilis
... availability have been performed by proteomics and transcriptomics [15]. In these studies, Casamino Acid (CAA), a mixture of amino acids and oligopeptides and constitutes a rich nitrogen source, were used. The products of CAA-regulated genes are involved in various metabolic pathways, including nitr ...
... availability have been performed by proteomics and transcriptomics [15]. In these studies, Casamino Acid (CAA), a mixture of amino acids and oligopeptides and constitutes a rich nitrogen source, were used. The products of CAA-regulated genes are involved in various metabolic pathways, including nitr ...
Glycerol is a major substrate for glucose, glycogen, and
... to glycogen, glucose, and nonessential AA (NEAA) synthesis on embryonic day (e) 14/15 and e19/20. Chicken embryos from small (56.6 ± 0.88 g) and large eggs (71.7 ± 1.09 g) were repeatedly dosed with either [13C3]glycerol (14 mg/d for 4 d) or [13C6]glucose (15 mg/d for 3 d) into the chorio-allantoic ...
... to glycogen, glucose, and nonessential AA (NEAA) synthesis on embryonic day (e) 14/15 and e19/20. Chicken embryos from small (56.6 ± 0.88 g) and large eggs (71.7 ± 1.09 g) were repeatedly dosed with either [13C3]glycerol (14 mg/d for 4 d) or [13C6]glucose (15 mg/d for 3 d) into the chorio-allantoic ...
The blood sugar concentration or blood glucose
... All forms of glucose are colorless and easily soluble in water, acetic acid, and several other solvents. They are only sparingly soluble in methanol and ethanol. The open-chain form is thermodynamically unstable, and it spontaneously isomerizes to the cyclic forms. (Although the ring closure reactio ...
... All forms of glucose are colorless and easily soluble in water, acetic acid, and several other solvents. They are only sparingly soluble in methanol and ethanol. The open-chain form is thermodynamically unstable, and it spontaneously isomerizes to the cyclic forms. (Although the ring closure reactio ...
PENTOSE PHOSPHATE PATHWAY AND FRUCTOSE METABOLISM
... • Provide reduced NADP for synthetic reactions, e.g. fatty acid synthesis and reduction of ...
... • Provide reduced NADP for synthetic reactions, e.g. fatty acid synthesis and reduction of ...
New Functions for Parts of the Krebs Cycle in Procyclic
... long slender bloodstream form has the simplest pathway for the degradation of glucose, viz. glycolysis, and excretes pyruvate as the sole end product (2– 4). However, the glycosomal and mitochondrial metabolism of T. brucei changes significantly upon transformation from the long slender bloodstream ...
... long slender bloodstream form has the simplest pathway for the degradation of glucose, viz. glycolysis, and excretes pyruvate as the sole end product (2– 4). However, the glycosomal and mitochondrial metabolism of T. brucei changes significantly upon transformation from the long slender bloodstream ...
Constitutively Active CaMKKa Stimulates Skeletal Muscle
... cellular and metabolic processes in muscle, including the regulation of contractile activity and glucose uptake. Importantly, studies have shown that stimulation of isolated rodent muscles with low doses of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release agents, caffeine or N-(6-amino-hexyl)-5-chloro-1-napt ...
... cellular and metabolic processes in muscle, including the regulation of contractile activity and glucose uptake. Importantly, studies have shown that stimulation of isolated rodent muscles with low doses of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release agents, caffeine or N-(6-amino-hexyl)-5-chloro-1-napt ...
Biochemistry2 2016 Lecture Glycogen Metabolism
... The path from insulin to GSK3 and glycogen synthase. Insulin binding to its receptor activates a tyrosine protein kinase receptor, which phosphorylates insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1). The phosphotyrosine in this protein is then bound by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI-3K), which converts ph ...
... The path from insulin to GSK3 and glycogen synthase. Insulin binding to its receptor activates a tyrosine protein kinase receptor, which phosphorylates insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1). The phosphotyrosine in this protein is then bound by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI-3K), which converts ph ...
Malonyl CoenzymeA Decarboxylase Regulates Lipid and
... for malonyl-CoA degradation is via MCD, which decarboxylates malonyl-CoA to acetyl-CoA. MCD inhibition has been proposed as a novel strategy to treat ischemic heart disease and obesity, namely by allowing full oxidation of glucose rather than elevated lactic acid and proton production leading to dim ...
... for malonyl-CoA degradation is via MCD, which decarboxylates malonyl-CoA to acetyl-CoA. MCD inhibition has been proposed as a novel strategy to treat ischemic heart disease and obesity, namely by allowing full oxidation of glucose rather than elevated lactic acid and proton production leading to dim ...
Chemistry of Carbohydrates
... + produced at reaction 5 to respiratory chain (each NADH2+ ++molecule produce 2.5 ATP molecules) +5 ATP molecules generated by entrance of two NADH2+ molecules (produced from conversion of two molecules of pyruvate into two molecules of acetyl-CoA / one molecule of glucose) to respiratory chain. + 2 ...
... + produced at reaction 5 to respiratory chain (each NADH2+ ++molecule produce 2.5 ATP molecules) +5 ATP molecules generated by entrance of two NADH2+ molecules (produced from conversion of two molecules of pyruvate into two molecules of acetyl-CoA / one molecule of glucose) to respiratory chain. + 2 ...
Synergistic Inhibitory Effects of Hypoxia and Iron
... Hypoxia results in stabilization of hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs), transcription factors that control a wide range of physiologic processes. HIF-1 and -2 form heterodimeric DNA binding complexes composed of a- and b-subunits (3). HIF-1a and HIF-2a are highly structurally homologous; however, the ...
... Hypoxia results in stabilization of hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs), transcription factors that control a wide range of physiologic processes. HIF-1 and -2 form heterodimeric DNA binding complexes composed of a- and b-subunits (3). HIF-1a and HIF-2a are highly structurally homologous; however, the ...
Full Text - Harvard University
... conducted a systematic evaluation of biochemical changes after an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) in a community-based population. Metabolic profiling was performed on 377 nondiabetic Framingham Offspring cohort participants (mean age 57 years, 42% women, BMI 30 kg/m2) before and after OGTT. Chang ...
... conducted a systematic evaluation of biochemical changes after an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) in a community-based population. Metabolic profiling was performed on 377 nondiabetic Framingham Offspring cohort participants (mean age 57 years, 42% women, BMI 30 kg/m2) before and after OGTT. Chang ...
Identification of the Human Erythrocyte Glucose Transporter (GLUT1
... facilitative glucose transporters selectively pump ...
... facilitative glucose transporters selectively pump ...
Gluconeogenesis differs in developing chick embryos derived from
... significant treatment effect with standard α (0.05) and power (80%) was determined to be 5 based on measured SD of various response variables from a similar study from our laboratory. To obtain a minimum sample size of 5 at each sampling time point (day of development) and to account for potential h ...
... significant treatment effect with standard α (0.05) and power (80%) was determined to be 5 based on measured SD of various response variables from a similar study from our laboratory. To obtain a minimum sample size of 5 at each sampling time point (day of development) and to account for potential h ...
21. glycolysis
... Fig, 21–5. Hexokinase not only acts on glucose but also on some other common hexoses such as fructose and mannose. The activity of hexokinase is inhibited by the product of the raction (i.e., glucose 6-phosphate) which binds the enzyme at an allosteric site. Hexokinase has a high affinity (i.e., low ...
... Fig, 21–5. Hexokinase not only acts on glucose but also on some other common hexoses such as fructose and mannose. The activity of hexokinase is inhibited by the product of the raction (i.e., glucose 6-phosphate) which binds the enzyme at an allosteric site. Hexokinase has a high affinity (i.e., low ...
The aconitase of Escherichia cok purification of the
... 10 mM-MgSO,. The cultures were concentrated 20-fold in 10 mMMgS04 for phage adsorption (15 min at room temperature with an m.0.i. of 2) and diluted into 20ml prewarmed LB broth containing 10 m~-MgsO,. The infected bacteria were incubated at 37 "C with shaking, and samples (1.5 ml) were pelleted (150 ...
... 10 mM-MgSO,. The cultures were concentrated 20-fold in 10 mMMgS04 for phage adsorption (15 min at room temperature with an m.0.i. of 2) and diluted into 20ml prewarmed LB broth containing 10 m~-MgsO,. The infected bacteria were incubated at 37 "C with shaking, and samples (1.5 ml) were pelleted (150 ...
Lac operon

lac operon (lactose operon) is an operon required for the transport and metabolism of lactose in Escherichia coli and many other enteric bacteria. Although glucose is the preferred carbon source for most bacteria, the lac operon allows for the effective digestion of lactose when glucose is not available. Gene regulation of the lac operon was the first genetic regulatory mechanism to be understood clearly, so it has become a foremost example of prokaryotic gene regulation. It is often discussed in introductory molecular and cellular biology classes at universities for this reason.Bacterial operons are polycistronic transcripts that are able to produce multiple proteins from one mRNA transcript. In this case, when lactose is required as a sugar source for the bacterium, the three genes of the lac operon can be expressed and their subsequent proteins translated: lacZ, lacY, and lacA. The gene product of lacZ is β-galactosidase which cleaves lactose, a disaccharide, into glucose and galactose. LacY encodes lactose permease, a protein which becomes embedded in the cytoplasmic membrane to enable transport of lactose into the cell. Finally, lacA encodes galactoside O-acetyltransferase. Layout of the lac operon.It would be wasteful to produce the enzymes when there is no lactose available or if there is a more preferable energy source available, such as glucose. The lac operon uses a two-part control mechanism to ensure that the cell expends energy producing the enzymes encoded by the lac operon only when necessary. In the absence of lactose, the lac repressor halts production of the enzymes encoded by the lac operon. In the presence of glucose, the catabolite activator protein (CAP), required for production of the enzymes, remains inactive, and EIIAGlc shuts down lactose permease to prevent transport of lactose into the cell. This dual control mechanism causes the sequential utilization of glucose and lactose in two distinct growth phases, known as diauxie.