chapter 2
... distillation a process used to separate components of a mixture using differences in boiling points ...
... distillation a process used to separate components of a mixture using differences in boiling points ...
I. Historical Atomic Models - Hobbs Freshman High School
... 1. 1st energy level (K) can hold up to 2 e-. 2. 2nd energy level (L) can hold up to 8 e-. 3. 3rd energy level (M) can hold up to 18 e- IF it is NOT the outermost energy level. 4. 4th energy level (N) can hold up to 32 e- IF it is NOT the outermost energy level. C. The # of energy levels of an atom d ...
... 1. 1st energy level (K) can hold up to 2 e-. 2. 2nd energy level (L) can hold up to 8 e-. 3. 3rd energy level (M) can hold up to 18 e- IF it is NOT the outermost energy level. 4. 4th energy level (N) can hold up to 32 e- IF it is NOT the outermost energy level. C. The # of energy levels of an atom d ...
Atomic Number
... 6. The _______ _________ tells us how many protons are in the nucleus. -Atomic number ...
... 6. The _______ _________ tells us how many protons are in the nucleus. -Atomic number ...
Atoms and the Periodic Table
... The elements are arranged on the periodic table by the number of protons and then grouped by other properties, such as: ...
... The elements are arranged on the periodic table by the number of protons and then grouped by other properties, such as: ...
Chemistry Curriculum Guide
... Using a periodic chart, determine the atomic number, atomic mass, the number of protons, the number of electrons, and the number of neutrons of any neutral atom of a particular element. ISOTOPES, HALF LIVES, AND RADIOACTIVE DECAY ...
... Using a periodic chart, determine the atomic number, atomic mass, the number of protons, the number of electrons, and the number of neutrons of any neutral atom of a particular element. ISOTOPES, HALF LIVES, AND RADIOACTIVE DECAY ...
2 IONS
... #1 ATOMIC SIZE – decreases across and increases down the periodic table #2 IONSLeft side of the periodic table forms positive ions. Group 1- charge of +1 (lose an electron) Group 2- charge of +2 (lose 2 electrons) Groups 3-12 (form positive ions with varying charges) Group 17-charge of -1 (gain an ...
... #1 ATOMIC SIZE – decreases across and increases down the periodic table #2 IONSLeft side of the periodic table forms positive ions. Group 1- charge of +1 (lose an electron) Group 2- charge of +2 (lose 2 electrons) Groups 3-12 (form positive ions with varying charges) Group 17-charge of -1 (gain an ...
Darlington High School EDI Lesson Plan Teacher: L. Grooms
... PS2.1 Compare the subatomic particles, protons, neutrons and electrons in regard to the mass, location, and charge and explain how these particles affect the properties of an atom. PS 2.3 Explain the trends of the periodic table based on the elements’ valence electrons and atomic number. PS 2.4 Use ...
... PS2.1 Compare the subatomic particles, protons, neutrons and electrons in regard to the mass, location, and charge and explain how these particles affect the properties of an atom. PS 2.3 Explain the trends of the periodic table based on the elements’ valence electrons and atomic number. PS 2.4 Use ...
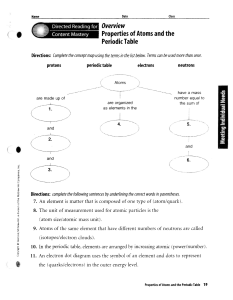
Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... Directions: complete the following sentences by underlining the correct words in parentheses, 7. An element is matter that is composed of one type of (atom/quark). 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit), 9. Atoms of the same element that have differe ...
... Directions: complete the following sentences by underlining the correct words in parentheses, 7. An element is matter that is composed of one type of (atom/quark). 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit), 9. Atoms of the same element that have differe ...
John Dalton is known as the father of modern atomic theory because
... Dalton performed a series of experiments on mixtures of gases. Based on his findings, he developed the hypothesis that the sizes of the particles making up different gases must be different. This lead him to an idea that contradicted the current thinking of alchemists who believed it was possible to ...
... Dalton performed a series of experiments on mixtures of gases. Based on his findings, he developed the hypothesis that the sizes of the particles making up different gases must be different. This lead him to an idea that contradicted the current thinking of alchemists who believed it was possible to ...
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... atoms present and subscripts are used to indicate the relative numbers of atoms. CO2 indicates each molecule contains 1 atom of carbon and 2 atoms of oxygen. Structural Formula: In which the individual bonds are shown by lines. It may or may not indicates the actual shape of the molecules. O=C=O ...
... atoms present and subscripts are used to indicate the relative numbers of atoms. CO2 indicates each molecule contains 1 atom of carbon and 2 atoms of oxygen. Structural Formula: In which the individual bonds are shown by lines. It may or may not indicates the actual shape of the molecules. O=C=O ...
Ch L14 Atoms Elements the Mole
... Atoms, elements, names, and symbols. “Atom” comes from Greek for indivisible The atom is recognized as the fundamental unit of matter Atoms contain smaller parts, known as protons, neutrons, and electrons ...
... Atoms, elements, names, and symbols. “Atom” comes from Greek for indivisible The atom is recognized as the fundamental unit of matter Atoms contain smaller parts, known as protons, neutrons, and electrons ...
document
... 5. Ionic Bond I E. States that all elements want either a full outer shell or eight 6. Subscript H electrons in their outer electron shell. 7. Polyatomic Ion J F. A multiplier. It is used to balance equations. 8. Synthesis Reaction L G. A reaction in which two reactant compounds switch ions. 9. Deco ...
... 5. Ionic Bond I E. States that all elements want either a full outer shell or eight 6. Subscript H electrons in their outer electron shell. 7. Polyatomic Ion J F. A multiplier. It is used to balance equations. 8. Synthesis Reaction L G. A reaction in which two reactant compounds switch ions. 9. Deco ...
Atomic Theory
... All atoms of one element are alike in mass and other properties, but the atoms of one element are different that the atoms of other elements. Compounds are formed when atoms of elements unite in fixed proportions. No atoms are created, destroyed, or broken apart in chemical reactions. Atoms ar ...
... All atoms of one element are alike in mass and other properties, but the atoms of one element are different that the atoms of other elements. Compounds are formed when atoms of elements unite in fixed proportions. No atoms are created, destroyed, or broken apart in chemical reactions. Atoms ar ...
Chapter 3
... 18. Cathode rays have _____________________ properties regardless of the element used to produce them. Therefore, it was concluded that ____________________ are present in atoms of all elements. 19. Which American physicist measured the charge of the electron? ______________________________ ...
... 18. Cathode rays have _____________________ properties regardless of the element used to produce them. Therefore, it was concluded that ____________________ are present in atoms of all elements. 19. Which American physicist measured the charge of the electron? ______________________________ ...
notes 4.1 & 4.2
... • Outermost ones are called valence electrons. They are responsible for how elements react with each other and the physical and chemical properties. ...
... • Outermost ones are called valence electrons. They are responsible for how elements react with each other and the physical and chemical properties. ...
Pre-AP Chemistry
... Section Objectives Students know protons and neutrons in the nucleus are held together by nuclear forces that overcome the electromagnetic repulsion between the protons. (11a) Students know the nucleus of the atom is much smaller than the atom yet contains most of its mass. (1e) Students recog ...
... Section Objectives Students know protons and neutrons in the nucleus are held together by nuclear forces that overcome the electromagnetic repulsion between the protons. (11a) Students know the nucleus of the atom is much smaller than the atom yet contains most of its mass. (1e) Students recog ...
Atoms, Elements, and Ions
... to form new compounds; they are not created, destroyed, or changed into atoms of any other elements. Yes, except for nuclear reactions that can change atoms of one element to a different element ...
... to form new compounds; they are not created, destroyed, or changed into atoms of any other elements. Yes, except for nuclear reactions that can change atoms of one element to a different element ...
Neutron - Piscataway High School
... Atom: the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that element Atomic mass: the weighted average of the masses of the isotopes of an element Atomic mass unit: one-twelfth the mass of a carbon atom having 6 protons and 6 neutrons Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucl ...
... Atom: the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that element Atomic mass: the weighted average of the masses of the isotopes of an element Atomic mass unit: one-twelfth the mass of a carbon atom having 6 protons and 6 neutrons Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucl ...
Sample Exam 1 Key
... a) Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons. b) Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of protons. c) Atoms of the same element can have different mass numbers. d) Atoms of two different elements can have the same number of neutrons. 2. Which of the following is ...
... a) Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons. b) Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of protons. c) Atoms of the same element can have different mass numbers. d) Atoms of two different elements can have the same number of neutrons. 2. Which of the following is ...
Atomic Structure_Tre..
... 5) Importance: The number of electrons located in the last energy level determine the chemical activity of the element. ...
... 5) Importance: The number of electrons located in the last energy level determine the chemical activity of the element. ...
ch19 - Otterville R-VI School District
... • Lab procedures were developed, but alchemists did not perform controlled experiments like true scientists. ...
... • Lab procedures were developed, but alchemists did not perform controlled experiments like true scientists. ...
The Atom
... Contains most of mass of atom 1 amu (atomic mass unit) 6 x 10 23 protons equal one gram Contains Proton Positive charge 1 amu Neutron No charge 1amu Electron Cloud Surrounds the small nucleus Contains mostly empty space Largest part of atom Contains very little (considered no) mass Electron Cloud & ...
... Contains most of mass of atom 1 amu (atomic mass unit) 6 x 10 23 protons equal one gram Contains Proton Positive charge 1 amu Neutron No charge 1amu Electron Cloud Surrounds the small nucleus Contains mostly empty space Largest part of atom Contains very little (considered no) mass Electron Cloud & ...