Nature of Matter
... • Proton: +, nucleus • Neutrons: neutral, nucleus • Electrons: negative, cloud around nucleus; organization inside cloud – into shells ...
... • Proton: +, nucleus • Neutrons: neutral, nucleus • Electrons: negative, cloud around nucleus; organization inside cloud – into shells ...
Atoms and the Periodic Table
... table by increasing atomic number. 1. In the late 1800’s, Dmitri Mendeleev devised the first periodic table based on atomic mass. 2. In 1913, Henry G.J. Moseley arranged the elements by atomic number rather than atomic mass. ...
... table by increasing atomic number. 1. In the late 1800’s, Dmitri Mendeleev devised the first periodic table based on atomic mass. 2. In 1913, Henry G.J. Moseley arranged the elements by atomic number rather than atomic mass. ...
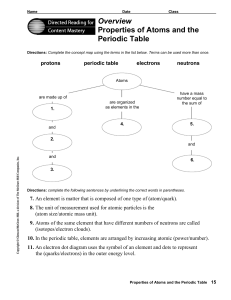
Overview Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called (isotopes/electron clouds). 10. In the periodic table, elements are arranged by increasing atomic (power/number). 11. An electron dot diagram uses the symbol of an element and dots to represent the (quarks/electrons) in ...
... 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called (isotopes/electron clouds). 10. In the periodic table, elements are arranged by increasing atomic (power/number). 11. An electron dot diagram uses the symbol of an element and dots to represent the (quarks/electrons) in ...
Chemistry Honors Semester One Final Exam Review 2014 1. Define
... 58. A prospector finds 39.39 g of pure gold (atomic mass 196.9665 amu). How many atoms are there? 59. Visible light, X rays, infrared radiation, and radio waves all have the same ________. 60. For electromagnetic radiation, what does c (the speed of light) equal? 61. Because c, the speed of electrom ...
... 58. A prospector finds 39.39 g of pure gold (atomic mass 196.9665 amu). How many atoms are there? 59. Visible light, X rays, infrared radiation, and radio waves all have the same ________. 60. For electromagnetic radiation, what does c (the speed of light) equal? 61. Because c, the speed of electrom ...
Note taker: ATOMS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE
... In ___________, this Greek philosopher suggested that the universe was made of _________ ...
... In ___________, this Greek philosopher suggested that the universe was made of _________ ...
Vocabulary
... • Valence electron – The electrons in an atom’s outermost orbitals; determine the chemical properties of an element. • Molecule – Forms when two or more atoms covalently bond • Covalent bond – A chemical bond that results from the sharing of valence electrons – “co-” means to share – “-valent” refer ...
... • Valence electron – The electrons in an atom’s outermost orbitals; determine the chemical properties of an element. • Molecule – Forms when two or more atoms covalently bond • Covalent bond – A chemical bond that results from the sharing of valence electrons – “co-” means to share – “-valent” refer ...
Unit 4 Test REVIEW
... 31. What is the mass number of an atom that has 20 protons, 22 neutrons and 20 electrons? 32. The word atom comes from the Greek word atomos meaning __________________. 33. In the synthesis of sulfur trifluoride, 33.0 g of sulfur combines with 24.0 g of fluorine. How many grams of sulfur trifluoride ...
... 31. What is the mass number of an atom that has 20 protons, 22 neutrons and 20 electrons? 32. The word atom comes from the Greek word atomos meaning __________________. 33. In the synthesis of sulfur trifluoride, 33.0 g of sulfur combines with 24.0 g of fluorine. How many grams of sulfur trifluoride ...
Radioactive Isotopes and Nuclear Equations
... Atoms are composed of three subatomic particles: protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of an atom. The total number of protons and neutrons determines an atom’s mass. The number of protons defines the element. Some nuclei are unstable, so they decompose (or " ...
... Atoms are composed of three subatomic particles: protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of an atom. The total number of protons and neutrons determines an atom’s mass. The number of protons defines the element. Some nuclei are unstable, so they decompose (or " ...
File - Cynthia Campbell
... An atom is the smallest particle of an element. An atom of any given element is made up of a certain number of protons, an equal number of electrons, and approximately the same number of neutrons. (The exception is hydrogen, which can have zero neutrons.) Protons and neutrons form the nucleus of an ...
... An atom is the smallest particle of an element. An atom of any given element is made up of a certain number of protons, an equal number of electrons, and approximately the same number of neutrons. (The exception is hydrogen, which can have zero neutrons.) Protons and neutrons form the nucleus of an ...
Structure - Mole Cafe
... Atoms are solid, homogeneous, indestructible, and indivisible Different atoms have different sizes and shapes The differing properties of matter are due to the size, shape, and movement of atoms Changes in matter result from changes in the groupings of atoms and not the atoms ...
... Atoms are solid, homogeneous, indestructible, and indivisible Different atoms have different sizes and shapes The differing properties of matter are due to the size, shape, and movement of atoms Changes in matter result from changes in the groupings of atoms and not the atoms ...
Chapter 3 - WordPress.com
... particles at a very thin sheet of gold foil. • Based on Thomson’s model of the atom he expected the alpha particles to pass through the foil but not all did! ...
... particles at a very thin sheet of gold foil. • Based on Thomson’s model of the atom he expected the alpha particles to pass through the foil but not all did! ...
Atom Models - Democritus, Dalton, Thompson, Rutherford, Bohr
... • It breaks down, releasing radioactivity. • These types of isotopes are called radioisotopes Q- Sometimes an isotope is written without its atomic number - e.g. 35S (or S-35). Why? Q- Draw B-R diagrams for the two Li isotopes. ...
... • It breaks down, releasing radioactivity. • These types of isotopes are called radioisotopes Q- Sometimes an isotope is written without its atomic number - e.g. 35S (or S-35). Why? Q- Draw B-R diagrams for the two Li isotopes. ...
Chapter 4: Introduction to Earth Chemistry Section 1 Notes
... _________________ a subatomic particle that has a _________________ charge _________________ a subatomic particle that has _________________ charge and that is located in the nucleus of an atom The Nucleus The protons and neutrons of an atom form the _______________________. The __________ charged n ...
... _________________ a subatomic particle that has a _________________ charge _________________ a subatomic particle that has _________________ charge and that is located in the nucleus of an atom The Nucleus The protons and neutrons of an atom form the _______________________. The __________ charged n ...
Posttest answers - Aurora City Schools
... electrons, so it has a charge (happens during chemical reactions). It’s written with the charge in the upper right hand corner 59. - 60. What is an isotope and how is the symbol written differently? ...
... electrons, so it has a charge (happens during chemical reactions). It’s written with the charge in the upper right hand corner 59. - 60. What is an isotope and how is the symbol written differently? ...
Outline Chapter 10 The Periodic Law
... • The inert gases are inactive nonmetals. They are in group 8. 10-7. The Periodic Table Formulated by Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in ~1869 Periodic law=states that when elements are listed in order of atomic number, elements with similar chemical and physical properties appear at regular interv ...
... • The inert gases are inactive nonmetals. They are in group 8. 10-7. The Periodic Table Formulated by Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in ~1869 Periodic law=states that when elements are listed in order of atomic number, elements with similar chemical and physical properties appear at regular interv ...
Early Atomic Theorists
... o Rays and particles emitted by radioactive materials are called radiation o Unstable nuclei decay until they form stable nonradioactive nuclei ...
... o Rays and particles emitted by radioactive materials are called radiation o Unstable nuclei decay until they form stable nonradioactive nuclei ...
Early Atomic Theorists
... o Rays and particles emitted by radioactive materials are called radiation o Unstable nuclei decay until they form stable nonradioactive nuclei ...
... o Rays and particles emitted by radioactive materials are called radiation o Unstable nuclei decay until they form stable nonradioactive nuclei ...
Atoms
... Ernest Rutherford – 1911 Gold Foil Experiment ‘As if you had fired a 15 – inch shell at a piece of tissue paper And it came back to hit you.’ ...
... Ernest Rutherford – 1911 Gold Foil Experiment ‘As if you had fired a 15 – inch shell at a piece of tissue paper And it came back to hit you.’ ...
Valence electrons and Lewis Dot Structures
... The _________ _________ basically says that an atom wants to have 8 electrons in the s and p orbitals. It will gain, lose or share electrons in order to achieve this configuration. ...
... The _________ _________ basically says that an atom wants to have 8 electrons in the s and p orbitals. It will gain, lose or share electrons in order to achieve this configuration. ...
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... Has all the parts that the Bohr atom had but has fine structure added to explain bright line spectra. Has protons, electrons, and neutrons. Discusses the position of electrons in terms of probability of finding them in a location. Has sublevels(s, p, d, f, g, h…) inside the main energy levels ...
... Has all the parts that the Bohr atom had but has fine structure added to explain bright line spectra. Has protons, electrons, and neutrons. Discusses the position of electrons in terms of probability of finding them in a location. Has sublevels(s, p, d, f, g, h…) inside the main energy levels ...
Periodic_Table
... - term comes from noble people, did not associate with anyone other then their kind - characterized by an octet of electrons in the outermost energy level; (happy) - exception of helium - very stable, (unreactive) - colorless, odorless - practical applications: balloons, illumination ...
... - term comes from noble people, did not associate with anyone other then their kind - characterized by an octet of electrons in the outermost energy level; (happy) - exception of helium - very stable, (unreactive) - colorless, odorless - practical applications: balloons, illumination ...
atomic numbers
... than the proton 3. Found moving around the nucleus at near the speed of light. - sometimes called _______________________ or charge cloud electron cloud ______________________ 4. The Quantum Mechanical Model - currently accepted model of the atom (Chapter 11) - for now we will use the Bohr model, ri ...
... than the proton 3. Found moving around the nucleus at near the speed of light. - sometimes called _______________________ or charge cloud electron cloud ______________________ 4. The Quantum Mechanical Model - currently accepted model of the atom (Chapter 11) - for now we will use the Bohr model, ri ...
The Structure of the Atom
... Protons : + charge, relative mass = 1.007 atomic mass units (amu); round to 1 Neutrons: = charge, relative mass = 1.009 atomic mass units (amu); round to 1 Electrons: - charge, relative mass = 0.0005 atomic mass units (amu); round to 0 (not factored in when figuring total mass of an atom) ...
... Protons : + charge, relative mass = 1.007 atomic mass units (amu); round to 1 Neutrons: = charge, relative mass = 1.009 atomic mass units (amu); round to 1 Electrons: - charge, relative mass = 0.0005 atomic mass units (amu); round to 0 (not factored in when figuring total mass of an atom) ...