File
... are separated, joined or rearranged. Atoms of one element are not changed into atoms of another! ...
... are separated, joined or rearranged. Atoms of one element are not changed into atoms of another! ...
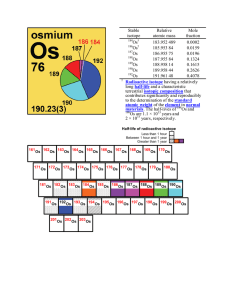
Stable isotope Relative atomic mass Mole fraction Os 183.952 489
... by an atomic nucleus undergoing radioactive decay. The energies of gamma rays are higher than those of X-rays; thus, gamma rays have greater penetrating power. half-life (radioactive) – the time interval that it takes for the total number of atoms of any radioactive isotope to decay and leave only o ...
... by an atomic nucleus undergoing radioactive decay. The energies of gamma rays are higher than those of X-rays; thus, gamma rays have greater penetrating power. half-life (radioactive) – the time interval that it takes for the total number of atoms of any radioactive isotope to decay and leave only o ...
Notetaking Workshee
... and ____________ neutrons. B. Protons Identify the Element 1. The number of __________________ in an atom is equal to a number called the ___________________________________. 2. The mass number of an atom is the sum of _________________ and ___________________________ in the nucleus of an atom. C. I ...
... and ____________ neutrons. B. Protons Identify the Element 1. The number of __________________ in an atom is equal to a number called the ___________________________________. 2. The mass number of an atom is the sum of _________________ and ___________________________ in the nucleus of an atom. C. I ...
Chapter 2 Law of Dalton`s Atomic Theory Law of Multiple
... • Arranged in order of increasing atomic number, the periodic table looks like this. • The columns are called groups – elements in the same group have similar chemical properties. • The rows are called periods. ...
... • Arranged in order of increasing atomic number, the periodic table looks like this. • The columns are called groups – elements in the same group have similar chemical properties. • The rows are called periods. ...
Chapter 14: Inside the Atom
... • Strong nuclear force holds protons together that are tightly packed in the nucleus. ...
... • Strong nuclear force holds protons together that are tightly packed in the nucleus. ...
Chemistry and elements 1. The rows of the periodic table are called
... d. All of the above 12. The atomic mass of an element is: a. Protons + Neutrons b. Protons + Electrons c. Neutrons + Electrons d. Just protons 15. Inside the atom’s nucleus are the: a. Protons and electrons b. Neutrons and electrons c. Protons and Neutrons d. Just the electrons 18. O is the atomic s ...
... d. All of the above 12. The atomic mass of an element is: a. Protons + Neutrons b. Protons + Electrons c. Neutrons + Electrons d. Just protons 15. Inside the atom’s nucleus are the: a. Protons and electrons b. Neutrons and electrons c. Protons and Neutrons d. Just the electrons 18. O is the atomic s ...
Models of the Atom Intro
... elements. After you have created each model, draw each model on your chart. • Hint to make a chart, use a burrito fold, then fold the top down by 1 ½ inches. Unfold, you now have 3 columns. Label the columns: element, Bohr model, Lewis Dot. ...
... elements. After you have created each model, draw each model on your chart. • Hint to make a chart, use a burrito fold, then fold the top down by 1 ½ inches. Unfold, you now have 3 columns. Label the columns: element, Bohr model, Lewis Dot. ...
ISOTOPES
... of atomic structure we have been developing, this would mean that each atom of an element would have the same number of protons, electrons, and neutrons as every other atom of the element. Thus the atomic mass of every atom of an element would be the same. In the early twentieth century, scientists ...
... of atomic structure we have been developing, this would mean that each atom of an element would have the same number of protons, electrons, and neutrons as every other atom of the element. Thus the atomic mass of every atom of an element would be the same. In the early twentieth century, scientists ...
Chemistry Major Understandings
... difference between the potential energy of the products and potential energy of the reactants. 4.2a Heat is a transfer of energy (usually thermal energy) from a body of higher temperature to a body of lower temperature. Thermal energy is the energy associated with the random motion of atoms and mole ...
... difference between the potential energy of the products and potential energy of the reactants. 4.2a Heat is a transfer of energy (usually thermal energy) from a body of higher temperature to a body of lower temperature. Thermal energy is the energy associated with the random motion of atoms and mole ...
ATOMIC THEORY
... ATOMS CANNOT BE BROKEN DOWN INTO SMALLER PARTICLES. ALL ATOMS OF AN ELEMENT WERE EXACTLY ALIKE AND ATOMS ...
... ATOMS CANNOT BE BROKEN DOWN INTO SMALLER PARTICLES. ALL ATOMS OF AN ELEMENT WERE EXACTLY ALIKE AND ATOMS ...
Document
... Draw the electrons by adding shells (circles) around the nucleus. The first shell has only 2 electrons. But the remaining shells usually have no more than 8 electrons. ...
... Draw the electrons by adding shells (circles) around the nucleus. The first shell has only 2 electrons. But the remaining shells usually have no more than 8 electrons. ...
Terminology 1
... The weight of one molecule of the substance relative to the weight of carbon atom taken as 12 The molecular weight is the sum of the atomic weights of the elements present in one molecule of the substance When molecular weight is expressed in grams, it is termed as gram molecule Eg. 32g of O2 = ...
... The weight of one molecule of the substance relative to the weight of carbon atom taken as 12 The molecular weight is the sum of the atomic weights of the elements present in one molecule of the substance When molecular weight is expressed in grams, it is termed as gram molecule Eg. 32g of O2 = ...
ScienceHelpNotes-UnitB3 - JA Williams High School
... into the periodic table. The periodic table is separated by a staircase, with metals on the left of the staircase and nonmetals on the right. Metals have some similarities in their chemical properties because they all lose electrons to form positive ions. Typically, metal are shiny, flexible, and ...
... into the periodic table. The periodic table is separated by a staircase, with metals on the left of the staircase and nonmetals on the right. Metals have some similarities in their chemical properties because they all lose electrons to form positive ions. Typically, metal are shiny, flexible, and ...
Chemistry in Focus 3rd edition Tro
... – Specified with n, the orbit’s quantum number • Fixed energies • Fixed radii • Maximum number of electrons based on n • This model is an oversimplification (as are most models). ...
... – Specified with n, the orbit’s quantum number • Fixed energies • Fixed radii • Maximum number of electrons based on n • This model is an oversimplification (as are most models). ...
Atom Study Guide
... indestructible particles. (not true because there are smaller parts within the atom) Atoms of the same element are exactly alike. Atoms of different elements are different. Compounds are formed by the joining of atoms of two or more elements. ...
... indestructible particles. (not true because there are smaller parts within the atom) Atoms of the same element are exactly alike. Atoms of different elements are different. Compounds are formed by the joining of atoms of two or more elements. ...
Study Guide 1st Semester
... 31. What is a valence electron? 32. Where are the alkali metal elements found? How do their electron configurations end? What are some typical behaviors of alkali metals? 33. Where are the alkaline earth metals found? How do their electron configurations end? What are some typical behaviors of alkal ...
... 31. What is a valence electron? 32. Where are the alkali metal elements found? How do their electron configurations end? What are some typical behaviors of alkali metals? 33. Where are the alkaline earth metals found? How do their electron configurations end? What are some typical behaviors of alkal ...
Grade 9 Science Unit 1 Review.notebook
... NO new bonds have been made (no new substance has formed) Physical Properties: characteristics of matter that are often observed or measured. Law: most laws are supported by different and robust experimental evidence. Atomic Number: this number represents the number of protons in an atom. It also re ...
... NO new bonds have been made (no new substance has formed) Physical Properties: characteristics of matter that are often observed or measured. Law: most laws are supported by different and robust experimental evidence. Atomic Number: this number represents the number of protons in an atom. It also re ...
File
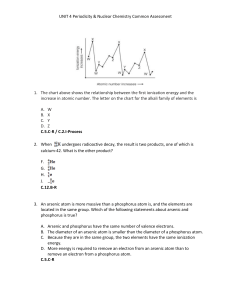
... phosphorus is true? A. Arsenic and phosphorus have the same number of valence electrons. B. The diameter of an arsenic atom is smaller than the diameter of a phosphorus atom. C. Because they are in the same group, the two elements have the same ionization energy. D. More energy is required to remove ...
... phosphorus is true? A. Arsenic and phosphorus have the same number of valence electrons. B. The diameter of an arsenic atom is smaller than the diameter of a phosphorus atom. C. Because they are in the same group, the two elements have the same ionization energy. D. More energy is required to remove ...
ch3 B - Manasquan Public Schools
... Credited with discovering nucleus. and atoms are mostly empty space. ...
... Credited with discovering nucleus. and atoms are mostly empty space. ...
Document
... 4. atoms combine in certain whole-number ratios YES! Called the Law of Definite Proportions 5. In a chemical reaction, atoms are merely rearranged to form new compounds; they are not created, destroyed, or changed into atoms of any other elements. Yes, except for nuclear reactions that can change at ...
... 4. atoms combine in certain whole-number ratios YES! Called the Law of Definite Proportions 5. In a chemical reaction, atoms are merely rearranged to form new compounds; they are not created, destroyed, or changed into atoms of any other elements. Yes, except for nuclear reactions that can change at ...
Early Atomic Theory
... • At this point, this completes our look at the early contributors into Atomic Theory and Structure. • You were given a lot of names, but here are the ones I want you to focus on: • Democritus, Dalton, Thompson, Rutherford • When we get to other topics, we will explore a few more of them in detail s ...
... • At this point, this completes our look at the early contributors into Atomic Theory and Structure. • You were given a lot of names, but here are the ones I want you to focus on: • Democritus, Dalton, Thompson, Rutherford • When we get to other topics, we will explore a few more of them in detail s ...
The atom
... 2. Atoms can be neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions 3. All atoms of a given element are identical 4. Atoms chemically combine in definite whole-number ratios to form compounds 5. Atoms of different elements have different masses ...
... 2. Atoms can be neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions 3. All atoms of a given element are identical 4. Atoms chemically combine in definite whole-number ratios to form compounds 5. Atoms of different elements have different masses ...
Unit2StudyGuide
... Which two particles have the same mass? What particles make up the nucleus? What particles are NOT in the nucleus? What particles make up the atomic mass? What particles have insignificant mass, but take up most of the space of an atom? Atoms of the same element but have a different mass are _______ ...
... Which two particles have the same mass? What particles make up the nucleus? What particles are NOT in the nucleus? What particles make up the atomic mass? What particles have insignificant mass, but take up most of the space of an atom? Atoms of the same element but have a different mass are _______ ...