Chapter 2 Notes - Waterford Public Schools
... • Atoms are ionized at low pressure in the gas phase • The cations that form are accelerated toward a magnetic field • The extent to which the cation beam is deflected is inversely related to the mass of the cation • The resulting data is plotted with abundance on the y-axis and mass on the x-axis ...
... • Atoms are ionized at low pressure in the gas phase • The cations that form are accelerated toward a magnetic field • The extent to which the cation beam is deflected is inversely related to the mass of the cation • The resulting data is plotted with abundance on the y-axis and mass on the x-axis ...
Ch 18 - Atoms and Elements
... Each element is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element are identical. Atoms of different elements have different properties, including mass and chemical reactivity. Atoms are not changed by chemical reactions, but merely rearranged into different compounds. ...
... Each element is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element are identical. Atoms of different elements have different properties, including mass and chemical reactivity. Atoms are not changed by chemical reactions, but merely rearranged into different compounds. ...
Solute
... Can be elements or compounds Element – substances made up of only one kind of atom Every element has a unique atomic number Atomic number – number of protons in the nucleus ...
... Can be elements or compounds Element – substances made up of only one kind of atom Every element has a unique atomic number Atomic number – number of protons in the nucleus ...
Chapter 4 Review “Atomic Structure
... the characteristics of subatomic particles. A fictitious element “X” has 10.0 % of the isotope with mass 55 amu, 20.0 % of the isotope with mass 56 amu, and 70.0 % of the isotope with mass 57 amu. Calculate the average atomic mass of element X. ...
... the characteristics of subatomic particles. A fictitious element “X” has 10.0 % of the isotope with mass 55 amu, 20.0 % of the isotope with mass 56 amu, and 70.0 % of the isotope with mass 57 amu. Calculate the average atomic mass of element X. ...
Chemistry 30A Chapter 2- Atoms and the Periodic Table Laney
... The elements of the Periodic Table can be grouped into four types: metals, nonmetals, metalloids, and noble gases. Metals occupy the left and bottom regions, nonmetals occupy the upper right region, and metalloids – which behave chemically as either metals or nonmetals – are along the line separatin ...
... The elements of the Periodic Table can be grouped into four types: metals, nonmetals, metalloids, and noble gases. Metals occupy the left and bottom regions, nonmetals occupy the upper right region, and metalloids – which behave chemically as either metals or nonmetals – are along the line separatin ...
Structure of the Atom
... • The atomic number is the number of protons in the atom • The atomic number tells us WHO the atom is. The atomic number (and therefore the protons) NEVER change! (if they did it would be a different element!) ...
... • The atomic number is the number of protons in the atom • The atomic number tells us WHO the atom is. The atomic number (and therefore the protons) NEVER change! (if they did it would be a different element!) ...
Periodic Table
... Arranged in order of increasing ______________ Columns are called ________ or ____________ There are _____ columns numbered from left to ________ Columns also have names for their families. On your periodic table, write the names above each column. Rows are called ___________ There are _ ...
... Arranged in order of increasing ______________ Columns are called ________ or ____________ There are _____ columns numbered from left to ________ Columns also have names for their families. On your periodic table, write the names above each column. Rows are called ___________ There are _ ...
Atoms, compounds and elements - Mrs. Tes de Luna`s Science Class
... Puzzle activity ◦Your group is given a box of puzzle to put together. ◦Once done, you are to tell, which part represents the atoms, elements, compounds and matter. ◦Work collaboratively and avoid arguments. ◦The more pieces put together, the higher grade you get! ...
... Puzzle activity ◦Your group is given a box of puzzle to put together. ◦Once done, you are to tell, which part represents the atoms, elements, compounds and matter. ◦Work collaboratively and avoid arguments. ◦The more pieces put together, the higher grade you get! ...
Chemistry Of Life
... • Two or more elements together • Fixed ratio (always the same ratio) • Emergent properties – behavior of compound may be drastically different than the behavior of the individual elements ...
... • Two or more elements together • Fixed ratio (always the same ratio) • Emergent properties – behavior of compound may be drastically different than the behavior of the individual elements ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Foundations: Elements, Atoms, and Ions
... isotopes) 3. The atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element. 4. Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form compounds. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. 5. Atoms are indivisible in chemical processes. That ...
... isotopes) 3. The atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element. 4. Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form compounds. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. 5. Atoms are indivisible in chemical processes. That ...
Ch 3 Outline- Intro to Atom and Periodic Table
... d. Elements with atomic numbers over 95 such as Curium (Cm), Einsteinium (Es) and others can only be synthesized using a particle accelerator i. Special machine that move atomic nuclei at extremely high speeds ii. When particles collide with a uranium nucleus with so much force and speed they them i ...
... d. Elements with atomic numbers over 95 such as Curium (Cm), Einsteinium (Es) and others can only be synthesized using a particle accelerator i. Special machine that move atomic nuclei at extremely high speeds ii. When particles collide with a uranium nucleus with so much force and speed they them i ...
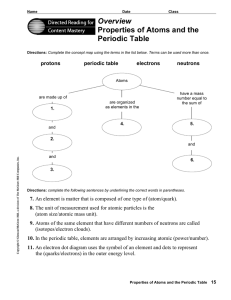
Reading Assignment Worksheet on Atoms - District 196 e
... 7. An element is matter that is composed of one type of (atom/quark). 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit). 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called (isotopes/electron clouds). 10. In the periodic table, eleme ...
... 7. An element is matter that is composed of one type of (atom/quark). 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit). 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called (isotopes/electron clouds). 10. In the periodic table, eleme ...
Chapter 2 Outline 3rd PERIOD
... Atomic Weight: atoms of almost all elements exhibit two or more structural variations Isotopes have the same number of protons and electrons but vary in the number of neutrons they contain Heavier isotopes of certain atoms are unstable and tend to decompose to be more stable, these are called ...
... Atomic Weight: atoms of almost all elements exhibit two or more structural variations Isotopes have the same number of protons and electrons but vary in the number of neutrons they contain Heavier isotopes of certain atoms are unstable and tend to decompose to be more stable, these are called ...
ATOMIC THEORY WORKSHEET 1. Which of the following
... All atoms of a given element have the same number of protons in the nucleus. They may differ in the number of neutrons. Chemically the atoms of a given element are virtually indistinguishable: the types of chemical reactions are the same; the rates may slightly differ for different isotopes. ...
... All atoms of a given element have the same number of protons in the nucleus. They may differ in the number of neutrons. Chemically the atoms of a given element are virtually indistinguishable: the types of chemical reactions are the same; the rates may slightly differ for different isotopes. ...
ATOMIC THEORY WORKSHEET 1.
... All atoms of a given element have the same number of protons in the nucleus. They may differ in the number of neutrons. Chemically the atoms of a given element are virtually indistinguishable: the types of chemical reactions are the same; the rates may slightly differ for different isotopes. ...
... All atoms of a given element have the same number of protons in the nucleus. They may differ in the number of neutrons. Chemically the atoms of a given element are virtually indistinguishable: the types of chemical reactions are the same; the rates may slightly differ for different isotopes. ...
Study Island Copyright © 2012 Study Island
... A. The properties of a compound are the same as the properties of its elements. B. The elements all share identical properties, but their properties are different than the compound's properties. C. The properties of a compound are different than the properties of its elements. D. The compound shares ...
... A. The properties of a compound are the same as the properties of its elements. B. The elements all share identical properties, but their properties are different than the compound's properties. C. The properties of a compound are different than the properties of its elements. D. The compound shares ...
Chemistry - Rainhill High School
... Describe why the new evidence from the scattering experiment led to a change in the atomic model. ...
... Describe why the new evidence from the scattering experiment led to a change in the atomic model. ...
Six Weeks Review PPT
... Democritus, 460 BC – proposes particles so small they can not be destroyed or divided, and describes them as “atomos” (uncuttable) John Dalton, early 1800’s - first to use “atom”; proposes that atoms of the same element are identical, and atoms of different elements have different weights/masses; So ...
... Democritus, 460 BC – proposes particles so small they can not be destroyed or divided, and describes them as “atomos” (uncuttable) John Dalton, early 1800’s - first to use “atom”; proposes that atoms of the same element are identical, and atoms of different elements have different weights/masses; So ...
Ch 4 - USD305.com
... charge because of the unequal # of electrons and protons – NaCl- Sodium(11 protons/11 electrons), Chlorine (17 protons/17electrons). Sodium gives up electron, now a positive charge. Chlorine gains electron now a negative charge ...
... charge because of the unequal # of electrons and protons – NaCl- Sodium(11 protons/11 electrons), Chlorine (17 protons/17electrons). Sodium gives up electron, now a positive charge. Chlorine gains electron now a negative charge ...
Bohr´s atomic model (1913)
... Between the nucleus and the electron shell there is empty space. Most of the atom is empty space. The nucleus of an atom is positively charged and contains almost all the mass of the atom. We know now that it is composed of protons and neutrons. Electrons orbit around the nucleus in circular orbits. ...
... Between the nucleus and the electron shell there is empty space. Most of the atom is empty space. The nucleus of an atom is positively charged and contains almost all the mass of the atom. We know now that it is composed of protons and neutrons. Electrons orbit around the nucleus in circular orbits. ...
Study Guide for test - Madison County Schools
... c. Describe his model of the atom. d. Why was his theory accepted so well? 3) J. J. Thomson a. His experiments first provided evidence of what? b. What device did he use to make his discovery, and what evidence did he find? c. What did people call his atomic model? d. What do we call the particle th ...
... c. Describe his model of the atom. d. Why was his theory accepted so well? 3) J. J. Thomson a. His experiments first provided evidence of what? b. What device did he use to make his discovery, and what evidence did he find? c. What did people call his atomic model? d. What do we call the particle th ...
600 $600
... As one moves down the elements in the first column of the periodic table, the A. Atomic number of the elements increases. ...
... As one moves down the elements in the first column of the periodic table, the A. Atomic number of the elements increases. ...