Chemistry Notes
... Gain valence electrons when they bond Properties of metalloids Elements that touch stair-step line between metals and nonmetals Have characteristics of metals and nonmetals Family/Group – columns of elements Same physical and chemical properties Same number of valence electrons Period – ro ...
... Gain valence electrons when they bond Properties of metalloids Elements that touch stair-step line between metals and nonmetals Have characteristics of metals and nonmetals Family/Group – columns of elements Same physical and chemical properties Same number of valence electrons Period – ro ...
Matter and the Periodic Table
... atomic number of an element is the number of protons in each atom of that element. For example, every atom of chlorine has 17 protons. Its atomic number is 17. ...
... atomic number of an element is the number of protons in each atom of that element. For example, every atom of chlorine has 17 protons. Its atomic number is 17. ...
Chapter 4.1
... 1. Protons – positive particles in the nucleus -charge is +1 -# protons = atomic # 2. Electrons – negative particles on orbits around the nucleus -charge is -1 -# electons = # protons= atomic # 3. Neutrons – neutral particles in the nucleus -charge is 0 -#neutrons= mass-atomic # ...
... 1. Protons – positive particles in the nucleus -charge is +1 -# protons = atomic # 2. Electrons – negative particles on orbits around the nucleus -charge is -1 -# electons = # protons= atomic # 3. Neutrons – neutral particles in the nucleus -charge is 0 -#neutrons= mass-atomic # ...
Pre-Knowledge: Chemistry and Physics Vocabulary Atomic Number
... The sum of the number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus of an atom. Nucleus The small “core” of the atom, where most of its mass and all of its positive charge is concentrated. Except for ordinary hydrogen (which has only a proton), atomic nuclei consist of protons and neutrons. For this reason ...
... The sum of the number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus of an atom. Nucleus The small “core” of the atom, where most of its mass and all of its positive charge is concentrated. Except for ordinary hydrogen (which has only a proton), atomic nuclei consist of protons and neutrons. For this reason ...
Chemistry I Lecture Notes – Atomic Structure
... Chemistry I Lecture Notes – Atomic Structure Dalton’s Atomic Theory (1808) All matter is made up of atoms. Atoms are indivisible (cannot be broken down into smaller pieces!) All atoms of a given element are exactly alike in size, mass and shape. Atoms of different elements can combine in sim ...
... Chemistry I Lecture Notes – Atomic Structure Dalton’s Atomic Theory (1808) All matter is made up of atoms. Atoms are indivisible (cannot be broken down into smaller pieces!) All atoms of a given element are exactly alike in size, mass and shape. Atoms of different elements can combine in sim ...
Radioisotopes
... • Isotopes are any of the different types of atoms (Nuclides) of the same chemical element, each having a different atomic mass (mass number) • Isotopes of an element have nuclei with the same number of protons (the same atomic number) but different numbers of neutrons. • Therefore, isotopes have di ...
... • Isotopes are any of the different types of atoms (Nuclides) of the same chemical element, each having a different atomic mass (mass number) • Isotopes of an element have nuclei with the same number of protons (the same atomic number) but different numbers of neutrons. • Therefore, isotopes have di ...
Atomic Mass
... Atomic masses can be different for atoms of the same element if they have different numbers of neutrons Atoms with different masses are called Isotopes or Nuclides ...
... Atomic masses can be different for atoms of the same element if they have different numbers of neutrons Atoms with different masses are called Isotopes or Nuclides ...
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... Neutral atom – the number of positive charges equal the number of negative charges All elements on periodic table are stable atoms. ...
... Neutral atom – the number of positive charges equal the number of negative charges All elements on periodic table are stable atoms. ...
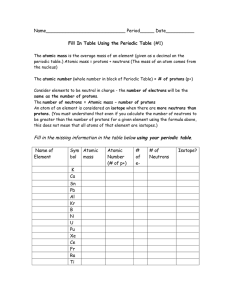
Periodic Table Fill in Table 1
... The atomic mass is the average mass of an element (given as a decimal on the periodic table.) Atomic mass = protons + neutrons (The mass of an atom comes from the nucleus) The atomic number (whole number in block of Periodic Table) = # of protons (p+) Consider elements to be neutral in charge - the ...
... The atomic mass is the average mass of an element (given as a decimal on the periodic table.) Atomic mass = protons + neutrons (The mass of an atom comes from the nucleus) The atomic number (whole number in block of Periodic Table) = # of protons (p+) Consider elements to be neutral in charge - the ...
Unit 1: Atomic Structure AP Chemistry
... experiment 1.60 x 10-19 From this and Thomson’s value, the mass was calculated to be 9.11 x 10-28g ...
... experiment 1.60 x 10-19 From this and Thomson’s value, the mass was calculated to be 9.11 x 10-28g ...
Name_________________________________
... Go to http://sciencespot.net/ and click the Kid Zone graphic! Part 2: Go to the “Matter and Atoms” Section under Chemistry. Click on “Science is Fun” under General Sites. Go to the “ChemTime Clock” area to find the answers. 1) All materials, whether solid, liquid or gas, are made of ____________. ...
... Go to http://sciencespot.net/ and click the Kid Zone graphic! Part 2: Go to the “Matter and Atoms” Section under Chemistry. Click on “Science is Fun” under General Sites. Go to the “ChemTime Clock” area to find the answers. 1) All materials, whether solid, liquid or gas, are made of ____________. ...
CHAPTER 3: The Building Blocks of Matter
... I. Early Atomic Theory□Democritus (400 B.C.)- suggested that the world was made of two things: -empty space and -tiny, indivisible particles called ‘____________’. □Dalton (early 1800s)- using the experimental observations of others, including Lavoisier and Proust, he proposed□Dalton’s Atomic Theory ...
... I. Early Atomic Theory□Democritus (400 B.C.)- suggested that the world was made of two things: -empty space and -tiny, indivisible particles called ‘____________’. □Dalton (early 1800s)- using the experimental observations of others, including Lavoisier and Proust, he proposed□Dalton’s Atomic Theory ...
Study Guide - Honors Chemistry
... one nucleus is broken into multiple (2 in this case) nuclei by force (an alpha particle is used to break it up) one nucleus is broken into multiple (2 in this case) nuclei on its own. No force is needed. one nucleus is transformed into another nucleus by bombarding a particle into it. A particle may ...
... one nucleus is broken into multiple (2 in this case) nuclei by force (an alpha particle is used to break it up) one nucleus is broken into multiple (2 in this case) nuclei on its own. No force is needed. one nucleus is transformed into another nucleus by bombarding a particle into it. A particle may ...
Chapter 2
... • Metals – left side; majority of elements; good conductors; lose electrons (+ ions) • Nonmetals – right side; poor conductors; gain electrons (- ions) • Metalloids – stair-step line • Groups – columns; grouped by similar properties • 18 – each has a name ...
... • Metals – left side; majority of elements; good conductors; lose electrons (+ ions) • Nonmetals – right side; poor conductors; gain electrons (- ions) • Metalloids – stair-step line • Groups – columns; grouped by similar properties • 18 – each has a name ...
Atomic Theory - rlhonorschem4
... » 1.All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. » 2. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties.' » 3.Atoms cannot be subdivided, created or destroyed. » 4.Atoms of different ...
... » 1.All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. » 2. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties.' » 3.Atoms cannot be subdivided, created or destroyed. » 4.Atoms of different ...
PP 04 Atoms_ molecules_ ions
... Groups or Families: Columns which indicate the number of electrons in the outermost energy level determining charge & reactivity ...
... Groups or Families: Columns which indicate the number of electrons in the outermost energy level determining charge & reactivity ...
Chemistry10AtomicTheory
... Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form chemical compounds; a given compound always has the same relative numbers of types of atoms. Atoms cannot be created, divided into smaller particles, nor destroyed in the chemical process; a chemical reaction simply changes th ...
... Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form chemical compounds; a given compound always has the same relative numbers of types of atoms. Atoms cannot be created, divided into smaller particles, nor destroyed in the chemical process; a chemical reaction simply changes th ...
Subject Area Standard Area Organizing Category Course Standard
... 3.2.C.A5: MODELS Recognize discoveries from Dalton (atomic theory), Thomson (the electron), Rutherford (the nucleus), and Bohr (planetary model of atom), and understand how each discovery leads to modern theory. Describe Rutherford’s “gold foil” experiment that led to the discovery of the nuclear at ...
... 3.2.C.A5: MODELS Recognize discoveries from Dalton (atomic theory), Thomson (the electron), Rutherford (the nucleus), and Bohr (planetary model of atom), and understand how each discovery leads to modern theory. Describe Rutherford’s “gold foil” experiment that led to the discovery of the nuclear at ...
Exemplar exam question – Chapter 2
... The first answer is probably worthy of only 1 mark as it does not make clear that isotopes are different atoms of the same element. The second answer would probably score 0. Although the idea of the same element and different number of neutrons is mentioned, the student has not mentioned different a ...
... The first answer is probably worthy of only 1 mark as it does not make clear that isotopes are different atoms of the same element. The second answer would probably score 0. Although the idea of the same element and different number of neutrons is mentioned, the student has not mentioned different a ...










![Atomic Structure [PowerPoint]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000122096_1-1d100da6540d2f26db122fc51f672fe5-300x300.png)