Atoms and Molecules video guide
... 13. What does an element’s atomic mass tell about the atoms that make up that ...
... 13. What does an element’s atomic mass tell about the atoms that make up that ...
The_Atoms_Family
... The number and arrangement of electrons determines the size of the atom Electrons move around the nucleus in energy levels and each can only hold so many electrons 1. 1st: 2 electrons 2. 2nd: 8 electrons 3. 3rd: 18 electrons 4. 4th: 32 electrons The number of electrons in the outermost energy level, ...
... The number and arrangement of electrons determines the size of the atom Electrons move around the nucleus in energy levels and each can only hold so many electrons 1. 1st: 2 electrons 2. 2nd: 8 electrons 3. 3rd: 18 electrons 4. 4th: 32 electrons The number of electrons in the outermost energy level, ...
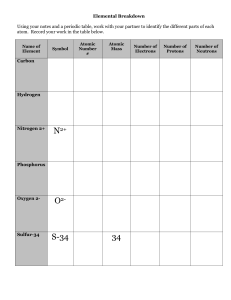
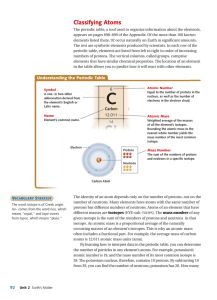
Classifying Atoms
... appears on pages 698–699 of the Appendix. Of the more than 100 known elements listed there, 92 occur naturally on Earth in significant amounts. The rest are synthetic elements produced by scientists. In each row of the periodic table, elements are listed from left to right in order of increasing num ...
... appears on pages 698–699 of the Appendix. Of the more than 100 known elements listed there, 92 occur naturally on Earth in significant amounts. The rest are synthetic elements produced by scientists. In each row of the periodic table, elements are listed from left to right in order of increasing num ...
Setting up Programmable PRS Keypad as Fixed ID Keypads
... Parser06 example6
The identity of an element is determined by the number of…
Q
Protons
Neutrons
Electrons
A molecule may consist of one atom.
Q
True
False
Molybdenum has atomic number 42. Its molar mass is 95.94 grams/mole. How many neutrons does
the most common isotope have?
Q
...
... Parser06 example
Extra Credit Test Review
... 12.One atom has 17 protons, 18 neutrons, and 17 electrons. Another atom has 17 protons, 19 neutrons and 17 electrons. Are these the same element? Yes No Explain: __________________________________________________________________ 13.Today we use Mendeleev’s arrangement, elements are arranged by incre ...
... 12.One atom has 17 protons, 18 neutrons, and 17 electrons. Another atom has 17 protons, 19 neutrons and 17 electrons. Are these the same element? Yes No Explain: __________________________________________________________________ 13.Today we use Mendeleev’s arrangement, elements are arranged by incre ...
Chemistry 102B What`s in an atom? Before “Chemistry” Other Early
... Developed the “Law of conservation of Mass”. • Joseph Proust (early 1800s) – discovered that a given compound always contained the same proportions of certain elements by mass. “Law of Definite Proportions” • John Dalton (early 1800s) – noted that elements that combined to form more than one kind of ...
... Developed the “Law of conservation of Mass”. • Joseph Proust (early 1800s) – discovered that a given compound always contained the same proportions of certain elements by mass. “Law of Definite Proportions” • John Dalton (early 1800s) – noted that elements that combined to form more than one kind of ...
Chapter 18 Notes
... Proton- P+ positive charged - in nucleus Number of P+ distinguishes one atom from another Made of 2 up quarks (+2/3 charge) and 1 down ...
... Proton- P+ positive charged - in nucleus Number of P+ distinguishes one atom from another Made of 2 up quarks (+2/3 charge) and 1 down ...
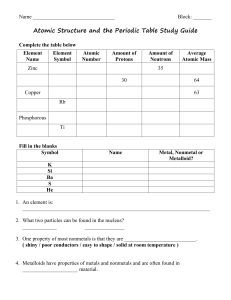
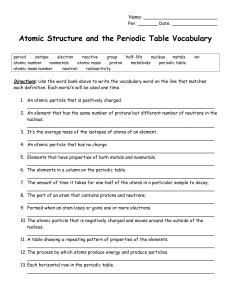
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table Vocabulary
... 2. An element that has the same number of protons but different number of neutrons in the nucleus. __________________________________________________________________ 3. It’s the average mass of the isotopes of atoms of an element. __________________________________________________________________ 4. ...
... 2. An element that has the same number of protons but different number of neutrons in the nucleus. __________________________________________________________________ 3. It’s the average mass of the isotopes of atoms of an element. __________________________________________________________________ 4. ...
Chapter 3: Atomic Theory
... Original Atomic Theory - Dalton • Atoms (matter) cannot be created nor destroyed – Chemical Reactions change the arrangement of atoms • Law of Constant Composition: a compound always contains the same proportions by mass of the elements. A given compound always has the same number & arrangement of e ...
... Original Atomic Theory - Dalton • Atoms (matter) cannot be created nor destroyed – Chemical Reactions change the arrangement of atoms • Law of Constant Composition: a compound always contains the same proportions by mass of the elements. A given compound always has the same number & arrangement of e ...
Vocabulary for Periodic Table
... 12) Period: a horizontal row in the periodic table of elements that have varying properties. 13) Reactive: indicates how likely an element is to undergo a chemical change. 14) Metal: an element that tends to be shiny, easily shaped, and a good conductor of electricity and heat. 15) Nonmetal: an elem ...
... 12) Period: a horizontal row in the periodic table of elements that have varying properties. 13) Reactive: indicates how likely an element is to undergo a chemical change. 14) Metal: an element that tends to be shiny, easily shaped, and a good conductor of electricity and heat. 15) Nonmetal: an elem ...
BC1 Atoms Unit Standards
... periodic table based on properties, number of protons, or electron configuration) Create visual models for atoms of different elements that shows the location of electrons and their relative distance from the nucleus. 4a Draw a Bohr model for a given element 4b Write an electron configuration to des ...
... periodic table based on properties, number of protons, or electron configuration) Create visual models for atoms of different elements that shows the location of electrons and their relative distance from the nucleus. 4a Draw a Bohr model for a given element 4b Write an electron configuration to des ...
File
... composition that is uniform throughout, all the way down to the molecular level. • Hydrocarbon-any molecule consisting of only hydrogen and carbon atoms, typically fossil fuels and other compounds derived from them. • Ion- a charged atom, it has either gained or lost an electron. • Isotope-any varie ...
... composition that is uniform throughout, all the way down to the molecular level. • Hydrocarbon-any molecule consisting of only hydrogen and carbon atoms, typically fossil fuels and other compounds derived from them. • Ion- a charged atom, it has either gained or lost an electron. • Isotope-any varie ...
Atomic Models
... Democritus (400 BC) - thought that matter was made of particles called ________, but we couldn’t prove this until 2000 years later! Antoine Lavoisier (1743-1794) - French chemist - developed.. - his law stated that matter cannot be ___________________________ in a chemical reaction, only changes for ...
... Democritus (400 BC) - thought that matter was made of particles called ________, but we couldn’t prove this until 2000 years later! Antoine Lavoisier (1743-1794) - French chemist - developed.. - his law stated that matter cannot be ___________________________ in a chemical reaction, only changes for ...
Periodic Table Vocab page 7
... Mass number: the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. Mass number = protons + neutrons Valence #: The number of outermost electrons in an atom. Periodic Table: An arrangement of elements in order of increasing atomic numbers that demonstrates the periodic patterns that occur amo ...
... Mass number: the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. Mass number = protons + neutrons Valence #: The number of outermost electrons in an atom. Periodic Table: An arrangement of elements in order of increasing atomic numbers that demonstrates the periodic patterns that occur amo ...
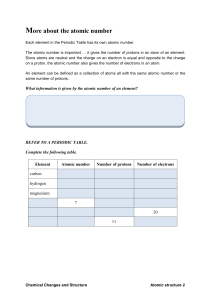
14 more about the atomic number
... Each element in the Periodic Table has its own atomic number. The atomic number is important it gives the number of protons in an atom of an element. Since atoms are neutral and the charge on an electron is equal and opposite to the charge on a proton, the atomic number also gives the number of elec ...
... Each element in the Periodic Table has its own atomic number. The atomic number is important it gives the number of protons in an atom of an element. Since atoms are neutral and the charge on an electron is equal and opposite to the charge on a proton, the atomic number also gives the number of elec ...
PP - myndrs.com
... the nucleus of an atom in orbits or shells. • Each orbit is a certain distance from the nucleus and contains a definite number of electrons. • The orbits are filled in a routine way: – First orbit: 2 electrons – Second orbit: 8 electrons – Third orbit: 8 electrons ...
... the nucleus of an atom in orbits or shells. • Each orbit is a certain distance from the nucleus and contains a definite number of electrons. • The orbits are filled in a routine way: – First orbit: 2 electrons – Second orbit: 8 electrons – Third orbit: 8 electrons ...
Structure of an Atom structure_of_atom
... the nucleus of an atom in orbits or shells. • Each orbit is a certain distance from the nucleus and contains a definite number of electrons. • The orbits are filled in a routine way: – First orbit: 2 electrons – Second orbit: 8 electrons – Third orbit: 8 electrons ...
... the nucleus of an atom in orbits or shells. • Each orbit is a certain distance from the nucleus and contains a definite number of electrons. • The orbits are filled in a routine way: – First orbit: 2 electrons – Second orbit: 8 electrons – Third orbit: 8 electrons ...