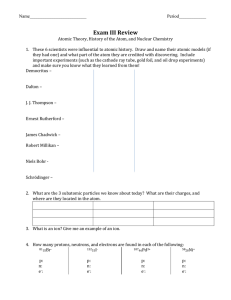
Exam III Review
... c. Positive charges are concentrated in a very small core at the atom’s center. d. Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus. 16. Today scientists have determined that electrons a. Move in the space around the nucleus. b. Have a mass equal to the mass of protons. c. Orbit the nucleus in a well ...
... c. Positive charges are concentrated in a very small core at the atom’s center. d. Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus. 16. Today scientists have determined that electrons a. Move in the space around the nucleus. b. Have a mass equal to the mass of protons. c. Orbit the nucleus in a well ...
Page 233 - ClassZone
... he called atoms. Democritus said that all atoms were made of the same material. The objects of the world differed because each was made of atoms of different sizes and shapes. How does the modern view of atoms differ from this ancient view? How is it similar? ...
... he called atoms. Democritus said that all atoms were made of the same material. The objects of the world differed because each was made of atoms of different sizes and shapes. How does the modern view of atoms differ from this ancient view? How is it similar? ...
Summative Assessment Study Guide Name: Due date: SPS1
... SPS5. Students will compare and contrast the phases of matter as they relate to atomic and molecular motion. a. Compare and contrast the atomic/molecular motion of solids, liquids, gases and plasmas. b. Relate temperature, pressure, and volume of gases to the behavior of gases. ...
... SPS5. Students will compare and contrast the phases of matter as they relate to atomic and molecular motion. a. Compare and contrast the atomic/molecular motion of solids, liquids, gases and plasmas. b. Relate temperature, pressure, and volume of gases to the behavior of gases. ...
Chemistry: The Nature of Matter
... Different states of energy are called energy levels or electron shells o 1st shell is closest to the nucleus, has the lowest energy, and holds only 2 electrons o 2nd shell has a little more energy and holds 8 electrons o 3rd shell has even more energy, etc. ______________________________________ ...
... Different states of energy are called energy levels or electron shells o 1st shell is closest to the nucleus, has the lowest energy, and holds only 2 electrons o 2nd shell has a little more energy and holds 8 electrons o 3rd shell has even more energy, etc. ______________________________________ ...
(null): 096.AtomReview
... a. Each specific color tells us about the structure of specific electrons inside the atom b. Zinc spectrum s different from ANY other element (compare to sulfur and helium on same slide) E. Atomic structure basics (see AtomOverview.ppt) – what we’ve learned by seeing without seeing … 1. PROTONS: a. ...
... a. Each specific color tells us about the structure of specific electrons inside the atom b. Zinc spectrum s different from ANY other element (compare to sulfur and helium on same slide) E. Atomic structure basics (see AtomOverview.ppt) – what we’ve learned by seeing without seeing … 1. PROTONS: a. ...
Introduction to Atomic Theory
... 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3. Atoms of different elements can combine with one another in single whole number ratios to form compounds. 4. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearra ...
... 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3. Atoms of different elements can combine with one another in single whole number ratios to form compounds. 4. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearra ...
Science Outline - cloudfront.net
... EX: All Hydrogen has 1 proton in its nucleus. Therefore, its atomic number is always 1. How many protons does an element with an atomic number of 94 have? What is this element? Most matter contains only a few kinds of elements o Ex: hamburgers, gasoline and paper are all made up of: __________ ...
... EX: All Hydrogen has 1 proton in its nucleus. Therefore, its atomic number is always 1. How many protons does an element with an atomic number of 94 have? What is this element? Most matter contains only a few kinds of elements o Ex: hamburgers, gasoline and paper are all made up of: __________ ...
Test Review: Unit 1 - Ms. Hill`s Pre
... 28. Nuclear Chemistry…ch 21 pg 681 a. Fusion: The combination of smaller molecule into larger ones. This happens on the sun. b. Fission: The splitting of large molecules into smaller radioactive daughter isotopes (“Mean Girls”) we do this in nuclear reactor and bombs! c. The big picture….both nuclea ...
... 28. Nuclear Chemistry…ch 21 pg 681 a. Fusion: The combination of smaller molecule into larger ones. This happens on the sun. b. Fission: The splitting of large molecules into smaller radioactive daughter isotopes (“Mean Girls”) we do this in nuclear reactor and bombs! c. The big picture….both nuclea ...
KWL chart and chem notes
... KNOW column and fill out the WHAT YOU WANT TO KNOW in the WANT area: 1- Explain how a chemical symbol is created. 2- Describe the atom and its structure 3- Differentiate between sub atomic particles. 4- Compare the evolution of the atom to something else in science that has evolved over time. ...
... KNOW column and fill out the WHAT YOU WANT TO KNOW in the WANT area: 1- Explain how a chemical symbol is created. 2- Describe the atom and its structure 3- Differentiate between sub atomic particles. 4- Compare the evolution of the atom to something else in science that has evolved over time. ...
Understanding Atomic Structure of an Element
... -Valence electrons are those that are contained in the outer most shell/energy level -They play a very important role in understanding how a element will react with other elements in a reaction -A Valence electron shell is only happy when it contains a full amount of electrons ...
... -Valence electrons are those that are contained in the outer most shell/energy level -They play a very important role in understanding how a element will react with other elements in a reaction -A Valence electron shell is only happy when it contains a full amount of electrons ...
Ch. 18 Notes Atoms and Elements
... The number of protons Determines the type of element Can only be changed with extremely high energy ...
... The number of protons Determines the type of element Can only be changed with extremely high energy ...
Atoms and the Periodic Table Study Guide
... 3) What two subatomic particles are responsible for the mass of the atom? ...
... 3) What two subatomic particles are responsible for the mass of the atom? ...
Learning Objectives
... of atomic structure. 4. Distinguish between each of the following pairs of terms: a. neutron and proton b. atomic number and mass number c. atomic weight and mass number 5. Explain how the atomic number and mass number of an atom can be used to determine the number of neutrons. 6. Explain how two is ...
... of atomic structure. 4. Distinguish between each of the following pairs of terms: a. neutron and proton b. atomic number and mass number c. atomic weight and mass number 5. Explain how the atomic number and mass number of an atom can be used to determine the number of neutrons. 6. Explain how two is ...
Review for Periodic - Mr-Durands
... 1. Find Scandium (Sc) on the table what is the atomic number? 2. What is the atomic mass of Chromium (Cr)? 3. What is the number of neutrons for Cesium (Cs)? 4. What is the difference between atomic mass and number? 5. How do isotopes affect the atomic mass of an element? 6. What is a group on the p ...
... 1. Find Scandium (Sc) on the table what is the atomic number? 2. What is the atomic mass of Chromium (Cr)? 3. What is the number of neutrons for Cesium (Cs)? 4. What is the difference between atomic mass and number? 5. How do isotopes affect the atomic mass of an element? 6. What is a group on the p ...
Chapter 4 4.1 Defining the Atom • Early Models of the Atom atom
... ratios to form compounds. 4) Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated from each other, joined, or rearranged in a different combination. Atoms of one element, however, are never changed into atoms of another element as a result of a chemical reaction. ...
... ratios to form compounds. 4) Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated from each other, joined, or rearranged in a different combination. Atoms of one element, however, are never changed into atoms of another element as a result of a chemical reaction. ...
04 Atoms_ molecules _ ions
... all the isotopes of an element • average of relative abundance x mass number for each ...
... all the isotopes of an element • average of relative abundance x mass number for each ...
Structure of the Atom
... • The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. • Atoms can have different numbers of neutrons. • Atoms that have different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. ...
... • The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. • Atoms can have different numbers of neutrons. • Atoms that have different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. ...
HONORS EARTH SCIENCE HOMEWORK, Ch2, Sec 1 Atoms and
... 5. Particles with a negative charge are called ________ and they exist outside the nucleus. 6. In an atom, electrons can be grouped into _________ levels, each holding only a specific number of electrons. 7. All atoms of the same element have the same number of ________ . 8. The number of protons in ...
... 5. Particles with a negative charge are called ________ and they exist outside the nucleus. 6. In an atom, electrons can be grouped into _________ levels, each holding only a specific number of electrons. 7. All atoms of the same element have the same number of ________ . 8. The number of protons in ...
200
... •Q All atoms of the same element have what in common? •A The atomic number or number of protons ...
... •Q All atoms of the same element have what in common? •A The atomic number or number of protons ...