* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download KWL chart and chem notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
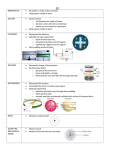
KWL CHEMISTRY CHART - On a separate piece of paper make 3 columns - Label the columns as follows: -1st column KNOW -2nd column WANT -3rd column LEARN For 7 minutes SILENTLY answer the following questions in the KNOW column and fill out the WHAT YOU WANT TO KNOW in the WANT area: 1- Explain how a chemical symbol is created. 2- Describe the atom and its structure 3- Differentiate between sub atomic particles. 4- Compare the evolution of the atom to something else in science that has evolved over time. Naming Elements Chemical Symbols -letter or pair of letters which is the abbreviation for an Element -Everyone world wide recognizes this system - both naturally occurring and man made EX- Ag= silver (Latin name) O= Oxygen (element name) Structure of the Atom Atom -smallest part of an element that retains the elements properties - comes from Greek word atmos (uncuttable) - basic building block for ALL matter EX- the element neon is made of ONLY neon atoms NUCLEUS NUCLEUS-small positively charged (+) center of an atom -contains PROTONS and NEUTRONS - MOST of the mass of the atom SUB ATOMIC PARTICLES 3 sub atomic particles are: PROTON, NEUTRON, ELECTRON PROTONS - in the NUCLEUS - have a +1 charge (positive) - number of protons is unique for each element NEUTRONS - in the NUCLEUS - NO CHARGE (electrically neutral) SUB ATOMIC PARTICLES (CON’T) ELECTRONS - Occupy the area around the nucleus - Has a -1 charge - In electron cloud moving ATOMIC MODEL - The model of the ATOM we use TODAY has EVOLVED from ideas and work of many scientists Today we use THE ELECTRON CLOUD MODEL - electron cloud is area AROUND the NUCLEUS - 100,000 times LARGER in DIAMETER than NUCLEUS (electron MUCH larger in size) - cloud is SMALLER in MASS than a single proton or neutron (electron MUCH less mass)