Atoms
... Three isotopes of oxygen are oxygen-16, oxygen-17, and oxygen18. Write the symbol for each, including the atomic number and mass number. ...
... Three isotopes of oxygen are oxygen-16, oxygen-17, and oxygen18. Write the symbol for each, including the atomic number and mass number. ...
Chemistry Review - pams-hoey
... form new substances • Ion – a charged atom (positive or negative). • Ionization – the process of removing electrons to form ions. • The energy needed is called ionization energy. • Electron affinity – the tendency of an atom to attract electrons. • Polyatomic ion – when two elements bond first coval ...
... form new substances • Ion – a charged atom (positive or negative). • Ionization – the process of removing electrons to form ions. • The energy needed is called ionization energy. • Electron affinity – the tendency of an atom to attract electrons. • Polyatomic ion – when two elements bond first coval ...
Atomic Information
... • If electrons are added to the atom, then there are more negative charges than positive charges. The atom becomes negatively charged and is called an anion. • If electrons are removed from the atom, then there are less negative charges than positive charges. The atom becomes positively charged and ...
... • If electrons are added to the atom, then there are more negative charges than positive charges. The atom becomes negatively charged and is called an anion. • If electrons are removed from the atom, then there are less negative charges than positive charges. The atom becomes positively charged and ...
Chapter 1 - Manual Science Chemistry/Physics
... Generally nonreactive All gases o Metalloids All solids at room temperature Tend to be semiconductors Tend to be intermediate in conductivity, malleability, and luster Questions Use the periodic table to write the names for the following elements: O, S, Cu, Ag. Use the periodic table t ...
... Generally nonreactive All gases o Metalloids All solids at room temperature Tend to be semiconductors Tend to be intermediate in conductivity, malleability, and luster Questions Use the periodic table to write the names for the following elements: O, S, Cu, Ag. Use the periodic table t ...
Dalton`s Atomic Theory Atomic Theory II
... An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of the element. All atoms are made up of three kinds of particles called subatomic particles. These particles are: 1. Electrons – negatively charged particles found outside the nucleus of the atom 2. Protons – positively char ...
... An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of the element. All atoms are made up of three kinds of particles called subatomic particles. These particles are: 1. Electrons – negatively charged particles found outside the nucleus of the atom 2. Protons – positively char ...
Chapter 5 Atomic Structure and Periodic Table 2014
... If the blue spheres are the neutrons and the burgundy spheres are the protons, are these three items isotopes of an element? By the way, how many electrons does this atom have? ...
... If the blue spheres are the neutrons and the burgundy spheres are the protons, are these three items isotopes of an element? By the way, how many electrons does this atom have? ...
- Lexington JHS
... • They are never found uncombined in nature and very reactive. • Alkaline earth metals include magnesium and calcium, among others. ...
... • They are never found uncombined in nature and very reactive. • Alkaline earth metals include magnesium and calcium, among others. ...
can be determined without changing the identity of matter
... Conservation of mass - During any chemical or physical process, the overall amount of mass remains constant, even if the chemical identity or physical state of the matter involved ...
... Conservation of mass - During any chemical or physical process, the overall amount of mass remains constant, even if the chemical identity or physical state of the matter involved ...
10-1
... from. For example, one atom of gold has the same properties(density, melting point etc.) as a bar of gold does. Atoms are made up of smaller parts but these do not have the same properties as the material it came from. Every atom has a nucleus or center. Inside the nucleus are protons and neutrons. ...
... from. For example, one atom of gold has the same properties(density, melting point etc.) as a bar of gold does. Atoms are made up of smaller parts but these do not have the same properties as the material it came from. Every atom has a nucleus or center. Inside the nucleus are protons and neutrons. ...
Name Date Class DEFINING THE ATOM Section Review Objectives
... 11. The atomic number of an element is the sum of the protons and electrons in an atom of that element. 12. The atomic number of an atom is the total number of protons in an atom of that element. 13. An atom of nitrogen has 7 protons and 7 neutrons. 14. Relative atomic masses are expressed in amus. ...
... 11. The atomic number of an element is the sum of the protons and electrons in an atom of that element. 12. The atomic number of an atom is the total number of protons in an atom of that element. 13. An atom of nitrogen has 7 protons and 7 neutrons. 14. Relative atomic masses are expressed in amus. ...
File - Mrs. Wernau`s Pre
... John Dalton’s atomic theory: 1. All matter is made up of very tiny particles called atoms 2. Atoms of the same element are alike…same size, mass, and other properties. 3. Atoms are not subdivided, created, or destroyed. 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form che ...
... John Dalton’s atomic theory: 1. All matter is made up of very tiny particles called atoms 2. Atoms of the same element are alike…same size, mass, and other properties. 3. Atoms are not subdivided, created, or destroyed. 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form che ...
Chapter 1 Chemistry: the study of the composition of matter and the
... Be able to solve for the missing value in a density problem Temperature conversion: kelvin-Celsius and reverse Chapter 5 ...
... Be able to solve for the missing value in a density problem Temperature conversion: kelvin-Celsius and reverse Chapter 5 ...
Unit 2: Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry
... atom. They will explain how nuclear changes impact the parts of the atom and its identity. Students will identify how nuclear chemistry is used in today’s society and how it can impact their lives. Expected learning outcomes: 1. Develop atomic theory in an historical perspective comparing and contra ...
... atom. They will explain how nuclear changes impact the parts of the atom and its identity. Students will identify how nuclear chemistry is used in today’s society and how it can impact their lives. Expected learning outcomes: 1. Develop atomic theory in an historical perspective comparing and contra ...
Rules for Calculating Protons, Neutrons, Electrons, Atomic Number
... Rules for Calculating Protons, Neutrons, Electrons, Atomic Number and Atomic Mass The ATOMIC NUMBER, PROTONS, and ELECTRONS are always the same. EX) If the atomic number of an atom is 15, then the number of protons is 15 and the number of electrons is 15. To calculate the number of NEUTRONS in an at ...
... Rules for Calculating Protons, Neutrons, Electrons, Atomic Number and Atomic Mass The ATOMIC NUMBER, PROTONS, and ELECTRONS are always the same. EX) If the atomic number of an atom is 15, then the number of protons is 15 and the number of electrons is 15. To calculate the number of NEUTRONS in an at ...
WAHS—Chemistry Unit 4: Atomic Structure 1 Unit Assignment #1
... 13. Write the nuclear symbol for deuterium (H-2): a. Identify the atomic number b. Identify the mass number 14. Determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in Co–59. 15. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in an atom of Ac–221? 16. How many electrons, neutrons, and protons are ...
... 13. Write the nuclear symbol for deuterium (H-2): a. Identify the atomic number b. Identify the mass number 14. Determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in Co–59. 15. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in an atom of Ac–221? 16. How many electrons, neutrons, and protons are ...
Chemistry Worksheet: Atomic Structure and Isotopes
... Use the mass number in the name of the isotope as was done in 1 - 4. e. 52 neutrons in each nucleus and a mass number of 92. f. A mass number of 112 and 48 electrons in each uncharged atom. g. A mass number of 75 and 36 electrons in each -3 anion. h. A mass number of 262 and 159 neutrons in the nucl ...
... Use the mass number in the name of the isotope as was done in 1 - 4. e. 52 neutrons in each nucleus and a mass number of 92. f. A mass number of 112 and 48 electrons in each uncharged atom. g. A mass number of 75 and 36 electrons in each -3 anion. h. A mass number of 262 and 159 neutrons in the nucl ...
I. Properties of Matter
... III. Mixtures of Matter c. Colloid – a type of mixture that never settles (particles are larger than those in solutions but not heavy enough to settle) • Example: milk (contains water, fats, and proteins in varying proportions) d. Suspension – a type of heterogeneous mixture containing particles th ...
... III. Mixtures of Matter c. Colloid – a type of mixture that never settles (particles are larger than those in solutions but not heavy enough to settle) • Example: milk (contains water, fats, and proteins in varying proportions) d. Suspension – a type of heterogeneous mixture containing particles th ...
Atom/Elements Study Guide
... 3. The atom is composed mostly of empty space. 4. Where is most of the mass of the atom located? In the nucleus 5. How many electrons can exist in the first shell? The second? 2, 8, 8,18 6. Which two subatomic particles have approximately the same mass? Neutrons and protons 7. Atoms with the same nu ...
... 3. The atom is composed mostly of empty space. 4. Where is most of the mass of the atom located? In the nucleus 5. How many electrons can exist in the first shell? The second? 2, 8, 8,18 6. Which two subatomic particles have approximately the same mass? Neutrons and protons 7. Atoms with the same nu ...
Atoms and the Periodic Table Test
... 8. What subatomic particle has a charge of -1 electron 9. The unit of mass used to indicate the mass of an atomic nucleus is the a.m.u. 10. You change the number of protons in an atom then the atom changes into a new ____element_____________ 11. The weighted average mass of the different isotopes of ...
... 8. What subatomic particle has a charge of -1 electron 9. The unit of mass used to indicate the mass of an atomic nucleus is the a.m.u. 10. You change the number of protons in an atom then the atom changes into a new ____element_____________ 11. The weighted average mass of the different isotopes of ...
Welcome to Chemistry 1001
... whole number ratios to form compounds Chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of atoms. No new atoms are created or destroyed. ...
... whole number ratios to form compounds Chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of atoms. No new atoms are created or destroyed. ...
All substances are made from atoms
... smallest particle which exists of an element. All of the atoms of any one element (say oxygen) are identical. Oxygen gas is made from trillions of identical oxygen atoms. There are just over one hundred elements in the periodic table, so there are just over one hundred types of atoms in the universe ...
... smallest particle which exists of an element. All of the atoms of any one element (say oxygen) are identical. Oxygen gas is made from trillions of identical oxygen atoms. There are just over one hundred elements in the periodic table, so there are just over one hundred types of atoms in the universe ...
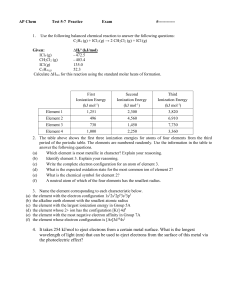
AP Chem Test 5-7 Practice Exam - mvhs
... the element with the electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p3 the alkaline earth element with the smallest atomic radius the element with the largest ionization energy in Group 5A the element whose 2+ ion has the configuration [Kr] 4d5 the element with the most negative electron affinity in Group 7A t ...
... the element with the electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p3 the alkaline earth element with the smallest atomic radius the element with the largest ionization energy in Group 5A the element whose 2+ ion has the configuration [Kr] 4d5 the element with the most negative electron affinity in Group 7A t ...
Isotope Practice Worksheet
... Most of the light elements contain different proportions of at least two isotopes. Usually one isotope is the predominantly abundant isotope. For example, the average abundance of 12C is 98.89%, while the average abundance for 13C is 1.11%. The table below outlines the average isotopic abundan ...
... Most of the light elements contain different proportions of at least two isotopes. Usually one isotope is the predominantly abundant isotope. For example, the average abundance of 12C is 98.89%, while the average abundance for 13C is 1.11%. The table below outlines the average isotopic abundan ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.