* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atoms and the Periodic Table Test
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
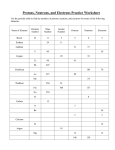
Practice Test for Equipment, Atoms & Periodic Table Name: Hour: Word Bank For #1- 14 Proton, Neutron, Electron, mass number, atomic mass, atomic number, isotope, ion, amu, element 1. Which subatomic particles are nucleons? Protons & neutrons 2. Which subatomic particle has almost no mass? electron 3. Which subatomic particles have a mass of 1 amu? Protons & neutron 4. Atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons are called ___isotopes_________________ 5. Atoms that have gained or lost electrons are called______ions_________________ 6. Which subatomic particle is neutral neutron 7. What subatomic particle has a charge of +1 Proton 8. What subatomic particle has a charge of -1 electron 9. The unit of mass used to indicate the mass of an atomic nucleus is the a.m.u. 10. You change the number of protons in an atom then the atom changes into a new ____element_____________ 11. The weighted average mass of the different isotopes of an element is called the ____atomic mass_________________. 12. An atom is neutral when it has the same number of __protons_____________ as _____electrons_______________ 13. Atoms of the same element that have different masses must have different numbers of __neutrons_______________ 14. The exact mass of a particular atom is calculated by adding protons + neutrons. This is called the _mass number 15. How many electrons can fit in the first energy level? Second? Third? 2 8 18 16. The lowest energy electrons are the electrons in the _first___________ energy level. Word Bank for # 17 – 26 Bohr, Chadwick, Democrates, Dalton, Lavosier, Mendeleev, Rutherford, Thomson 17. This scientist who led a series of experiments that used high-speed positively–charged helium atoms to bombard very thin pieces of gold foil. Rutherford 18. Named the atom Democrates 21.Discovered the neutron Chadwick 19.Wrote the law of Definite proportions Lavosier 22.First periodic table Mendeleev 24.Solar system model, discovered proton and nucleus Rutherford 20.Found that electrons formed different energy levels Bohr 23.Discovered the electron Thompson 25.Plum pudding model Thompson 26. Used a cathode ray tube to ‘see’ the path of particles? Thompson 27. When Thompson discovered negative particles, what did this tell him about what was in the rest of a neutral atom? There must be positive parts to balance out the negative parts since atoms are neutral 28. Who was the first person to state that the smallest piece of matter was an atom? Democrates 29. What is the most modern Theory about the structure of an atom? a. Plum pudding c. wave model b. Solar system model d. Bohr model 30. Label each of the following diagrams with the name of the scientist that came up with that model of the atom? a Thompson = Plum pudding b. Rutherford =solar system/planetary c. d. Bohr Democrates & Dalton they had no idea what was in an atom 32. How many different elements are included in the following list? CaSOFeMn 5 Fill in the following Table: Substance Symbol Atomic # Mass # Protons 24 12 Magnesium Mg 12 Sulfur S-2 16 32 Fluorine F 9 Aluminum Al - 23 13 Neutrons Electrons 12 12 16 16 18 (bcs -2) 19 9 10 9 23 13 10 13 Draw a Bohr Model and a Lewis dot diagram for oxygen, how many valence electrons does oxygen have? Draw a Bohr Model and a Lewis dot diagram for Beryllium. How many valence electrons does Beryllium have? 1) To determine safe driving distances at 25mph, 50 mph, and 70 mph, scientists measure how far a car travels before stopping. a. What is the independent variable? b. What is the dependent variable? c. What are some controlled variables? a. Speed in mph b. stopping distance c. same car, same road conditions, same driver 2) An experiment is run to see if a new type of salt will melt ice better then sodium chloride. The salt is sprinkled on 30 sheets of ice and the time it takes for the ice to melt is recorded. a. What is the experimental variable being tested. b. What would you do for a control set-up? c. What things need to be kept the same between the control set-up and the experimental set-up? d. What is the dependent variable? a. New salt b. try same set-up using sodium chloride amount of salt, same thickness of ice sheets, d. time c. same temperature, same On the periodic table below label: metals, non-metals, metalloids, hydrogen, alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, halogens, nobel gasses. Write in group numbers, and oxidation numbers Which families of metals are most reactive? Which metals are highly radioactive? Which family is inert? Which metals have different oxidation numbers depending on their environment? Which non-metals are highly reactive? What are valence electrons? How can you use the periodic table to tell you how many valence electrons an element has? How can you use the periodic table to tell how many energy levels an element has?