Codes of Life
... start to use helium as a fuel producing carbon. It also begins burning hydrogen in its atmosphere and will expand 100 times to become the red giant • When this happens to our Sun (in about 4 billion years) all inner planets and the Earth will be incinerated. ...
... start to use helium as a fuel producing carbon. It also begins burning hydrogen in its atmosphere and will expand 100 times to become the red giant • When this happens to our Sun (in about 4 billion years) all inner planets and the Earth will be incinerated. ...
Space Test: Practice Questions and Answers 1. Who discovered
... 21. Why could the big bang explode faster than the speed of light? Because the speed of matter is limited to the speed of light, but much of the Big Bang was empty space, which does not have ...
... 21. Why could the big bang explode faster than the speed of light? Because the speed of matter is limited to the speed of light, but much of the Big Bang was empty space, which does not have ...
Galaxies and Stars Questions KEY
... 2. What are the types or categories for galaxies? There are three major types of galaxies: spiral, irregular, and elliptical. Also, there is a quasar galaxy. 3. What is a nebula? A nebula is a cloud of interstellar gas and dust from which stars form. 4. Where do stars begin their life? Stars begin t ...
... 2. What are the types or categories for galaxies? There are three major types of galaxies: spiral, irregular, and elliptical. Also, there is a quasar galaxy. 3. What is a nebula? A nebula is a cloud of interstellar gas and dust from which stars form. 4. Where do stars begin their life? Stars begin t ...
Astronomy 360 Physics/Geology 360
... Pleiades has several meanings in different cultures and traditions. The cluster is dominated by hot blue and extremely luminous stars that have formed within the last 100 million years. Dust that forms a faint reflection nebulosity around the brightest stars was thought at first to be left over from ...
... Pleiades has several meanings in different cultures and traditions. The cluster is dominated by hot blue and extremely luminous stars that have formed within the last 100 million years. Dust that forms a faint reflection nebulosity around the brightest stars was thought at first to be left over from ...
Chapter 19 Star Formation
... containing up to a million solar masses of gas (and 1% dust--it is just part of the ISM. That is a lot of self-gravity! The most massive clouds have gravity that can overcome the thermal pressure trying to resist gravity, and the cloud must collapse. The cloud shown to the right above is a moderatel ...
... containing up to a million solar masses of gas (and 1% dust--it is just part of the ISM. That is a lot of self-gravity! The most massive clouds have gravity that can overcome the thermal pressure trying to resist gravity, and the cloud must collapse. The cloud shown to the right above is a moderatel ...
Chapter 19 Star Formation
... Individual cloud fragments begin to collapse. Once the density is high enough, there is no further fragmentation. Reason: the star has become opaque to its own radiation: It has a photosphere! After this, the ‘trapped radiation heats the interior of the object as it contracts. Stage 3: Object become ...
... Individual cloud fragments begin to collapse. Once the density is high enough, there is no further fragmentation. Reason: the star has become opaque to its own radiation: It has a photosphere! After this, the ‘trapped radiation heats the interior of the object as it contracts. Stage 3: Object become ...
Chapter 19 Star Formation
... Individual cloud fragments begin to collapse. Once the density is high enough, there is no further fragmentation. Reason: the star has become opaque to its own radiation: It has a photosphere! After this, the ‘trapped radiation heats the interior of the object as it contracts. Stage 3: Object become ...
... Individual cloud fragments begin to collapse. Once the density is high enough, there is no further fragmentation. Reason: the star has become opaque to its own radiation: It has a photosphere! After this, the ‘trapped radiation heats the interior of the object as it contracts. Stage 3: Object become ...
Chapter 13 Notes – The Deaths of Stars
... VIII. The Deaths of Massive Stars: Supernovae Final stages of fusion in high-mass stars ( ___________ solar masses) leading to the formation of an ___________ core, happen extremely rapidly: _________ burning only lasts for about _______ day Iron core ultimately _________________, triggering an ...
... VIII. The Deaths of Massive Stars: Supernovae Final stages of fusion in high-mass stars ( ___________ solar masses) leading to the formation of an ___________ core, happen extremely rapidly: _________ burning only lasts for about _______ day Iron core ultimately _________________, triggering an ...
Stars
... The number of stars visible to the naked eye from earth has been estimated to total 8000, of which 4000 are visible from the northern hemisphere and 4000 from the southern hemisphere. At any one time in either hemisphere, only about 2000 stars are visible. The other 2000 are located in the daytime s ...
... The number of stars visible to the naked eye from earth has been estimated to total 8000, of which 4000 are visible from the northern hemisphere and 4000 from the southern hemisphere. At any one time in either hemisphere, only about 2000 stars are visible. The other 2000 are located in the daytime s ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... is not blown off • The mass falls back on the neutron star • The gravity causes the neutron star to keep ...
... is not blown off • The mass falls back on the neutron star • The gravity causes the neutron star to keep ...
Section 15
... the zero-age main sequence (ZAMS). Of course, the true circumstances are more complex in detail than the simple Hayashi picture; protostars show circumstellar accretion disks, and outflows such as jets and stellar winds. Magnetic fields also play a role. Material falling onto the protostar generates ...
... the zero-age main sequence (ZAMS). Of course, the true circumstances are more complex in detail than the simple Hayashi picture; protostars show circumstellar accretion disks, and outflows such as jets and stellar winds. Magnetic fields also play a role. Material falling onto the protostar generates ...
Quiz # 5
... A protoplanetary disk, such as those observed around some stars in the Orion nebula. Any planet of greater mass than Jupiter. A planet orbiting a star beyond the Sun; for example, the planet orbiting the star 51 Pegasi. D) A primitive organism thought to exist on Jupiter's moon, Europa. ...
... A protoplanetary disk, such as those observed around some stars in the Orion nebula. Any planet of greater mass than Jupiter. A planet orbiting a star beyond the Sun; for example, the planet orbiting the star 51 Pegasi. D) A primitive organism thought to exist on Jupiter's moon, Europa. ...
new_qwk11
... ruler is measured to be longer than its twin ruler at rest D. The mass or inertia of an object decreases when its speed approaches the speed of light ...
... ruler is measured to be longer than its twin ruler at rest D. The mass or inertia of an object decreases when its speed approaches the speed of light ...
Earth - Capital High School
... they looked like millions of years ago – it takes one year for light to travel 5+ trillion miles (a light year) ...
... they looked like millions of years ago – it takes one year for light to travel 5+ trillion miles (a light year) ...
Unit 8 Astronomy
... A ___________________ is an _________________ that marks the end of a very massive star’s life. When it occurs, the exploding star can outshine all of the other stars in the galaxy in total for several days and may leave behind only a crushed core. ...
... A ___________________ is an _________________ that marks the end of a very massive star’s life. When it occurs, the exploding star can outshine all of the other stars in the galaxy in total for several days and may leave behind only a crushed core. ...
ASTR2050 Spring 2005 • In this class we will ...
... Example: Masses of stars “Mass Luminosity Relation” “Massive stars are much, much brighter than lighter stars.” An important goal of our study of stellar structure will be to understand how this relation comes about. Mass (in solar masses) ...
... Example: Masses of stars “Mass Luminosity Relation” “Massive stars are much, much brighter than lighter stars.” An important goal of our study of stellar structure will be to understand how this relation comes about. Mass (in solar masses) ...
Beginnings - Big Picture
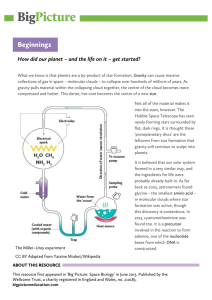
... It seems that the early solar system – including the early Earth – was laced with some of the basic chemicals from which life is built. But what turned an inanimate, prehistoric ‘soup’ of chemicals into the first organisms we would classify as alive? The most famous experiment into the origin of li ...
... It seems that the early solar system – including the early Earth – was laced with some of the basic chemicals from which life is built. But what turned an inanimate, prehistoric ‘soup’ of chemicals into the first organisms we would classify as alive? The most famous experiment into the origin of li ...
Notes: Astronomy and Groups of Stars
... The core of stars is very hot. The temperatures observed are of the outer layer of the star. ...
... The core of stars is very hot. The temperatures observed are of the outer layer of the star. ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.