* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Astronomy 360 Physics/Geology 360
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Globular cluster wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Open cluster wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
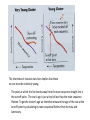
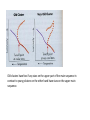
Astronomy 360 Physics/Geology 360 Measuring the Age of Star Clusters A star only uses hydrogen in its core (available fuel is 0.1 times the star’s mass. t = 1010 M/L years Where M is in solar masses and L is in solar luminosities where t is the main sequence lifetime(see page 381) In a star cluster all stars form at approximately the same time and at their birth all a burning hydrogen in their core. All stars at their birth lie on the main sequence. Calculate the main sequence lifetime of a star of 2 M and 20L How about 1 M and 1 L? The shortness of massive stars lives implies that those we see must be relatively young. The point at which the line bends away from the main sequence straight line is the turnoff point. The star’s age is just a tiny bit less than the main sequence lifetime. To get the cluster’s age we therefore measure the age of the star at the turnoff point by calculating its main sequence lifetime from its mass and luminosity. Old clusters have few if any stars on the upper part of the main sequence in contrast to young clusters on the other hand have stars on the upper main sequence. In astronomy, the Pleiades, or Seven Sisters (Messier object 45), is an open star cluster containing middle-aged hot B-type stars located in the constellation of Taurus. It is among the nearest star clusters to Earth and is the cluster most obvious to the naked eye in the night sky. Pleiades has several meanings in different cultures and traditions. The cluster is dominated by hot blue and extremely luminous stars that have formed within the last 100 million years. Dust that forms a faint reflection nebulosity around the brightest stars was thought at first to be left over from the formation of the cluster (hence the alternate name Maia Nebula after the star Maia), but is now known to be an unrelated dust cloud in the interstellar medium that the stars are currently passing through. Astronomers estimate that the cluster will survive for about another 250 million years, after which it will disperse due to gravitational interactions with its galactic neighborhood. The fate of a star like our sun The fate of a one solar mass one Luminosity Star