The Hidden Lives of Galaxies NSTA 2001
... diagram, meaning that they are cool but luminous (bright). •Their luminosity is high because they are very large, and so have a big surface area to radiate from. Typically they may have a radius one hundred times that of the Sun. ...
... diagram, meaning that they are cool but luminous (bright). •Their luminosity is high because they are very large, and so have a big surface area to radiate from. Typically they may have a radius one hundred times that of the Sun. ...
Characteristics of Stars
... Classification • H-R diagram • Absolute magnitude vs. temperature • For most stars the brightness increases as surface temp increases • Main sequence stars are band in center ...
... Classification • H-R diagram • Absolute magnitude vs. temperature • For most stars the brightness increases as surface temp increases • Main sequence stars are band in center ...
universe_pp_4 - Cobb Learning
... universe were moving away from us…which would mean at one time they were all together at one point •The Hubble Telescope was named in his honor ...
... universe were moving away from us…which would mean at one time they were all together at one point •The Hubble Telescope was named in his honor ...
giant molecular clouds
... Triggering Star Formation (1) Previous star formation can trigger further star formation through: a) Shocks from ...
... Triggering Star Formation (1) Previous star formation can trigger further star formation through: a) Shocks from ...
Document
... Giant Molecular Clouds •How do the star-forming dark nebulae distribute in our galaxy? •Distant dark nebulae are hard to observe, because they do not emit visible light •However, dark nebulae can be detected using microwave observation, because the molecules in nebulae emit at ...
... Giant Molecular Clouds •How do the star-forming dark nebulae distribute in our galaxy? •Distant dark nebulae are hard to observe, because they do not emit visible light •However, dark nebulae can be detected using microwave observation, because the molecules in nebulae emit at ...
Stars - Images
... Vary in size, color, and temperature Color can indicate the size, temperature, and life span of the star. Pass through stages (Depends on its mass) Consist mainly of helium and hydrogen ...
... Vary in size, color, and temperature Color can indicate the size, temperature, and life span of the star. Pass through stages (Depends on its mass) Consist mainly of helium and hydrogen ...
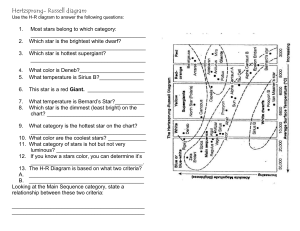
Hertzsprung - Russel Diagram
... Hertzsprung- Russell diagram Use the H-R diagram to answer the following questions: ...
... Hertzsprung- Russell diagram Use the H-R diagram to answer the following questions: ...
PowerPoint - Chandra X
... have important implications for the formation of planets around these stars. According to some theoretical models, large flares could produce strong turbulence in a planet-forming disk around a young star. Such turbulence might affect the position of rocky, Earth-like planets as they form and preven ...
... have important implications for the formation of planets around these stars. According to some theoretical models, large flares could produce strong turbulence in a planet-forming disk around a young star. Such turbulence might affect the position of rocky, Earth-like planets as they form and preven ...
Section 2
... distance from the earth. temperature is based on the color of the star • Blue or blue white is the hottest and red is the coolest ...
... distance from the earth. temperature is based on the color of the star • Blue or blue white is the hottest and red is the coolest ...
Star Birth
... – Molecular H is hard to detect, since they do not emit light (radiation) – However, carbon monoxide present in these clouds emit millimeter wavelength light, and thus can be detected by radio telescopes. – these giant clouds have masses ranging from 105 - 106M. ...
... – Molecular H is hard to detect, since they do not emit light (radiation) – However, carbon monoxide present in these clouds emit millimeter wavelength light, and thus can be detected by radio telescopes. – these giant clouds have masses ranging from 105 - 106M. ...
Lecture4
... The visible-light spectrum of the Sun is wrapped here end to end from red to blue. The dark “lines” are wavelengths that are absorbed by atoms in the Sun’s outer layers. There are millions of “lines” in the Sun’s spectrum. ...
... The visible-light spectrum of the Sun is wrapped here end to end from red to blue. The dark “lines” are wavelengths that are absorbed by atoms in the Sun’s outer layers. There are millions of “lines” in the Sun’s spectrum. ...
Homework #7 (Ch. 19)
... because the entire process occurs deep inside a molecular cloud, which itself is deep inside a dark, dense dust cloud. Visible light cannot escape from this environment but long ...
... because the entire process occurs deep inside a molecular cloud, which itself is deep inside a dark, dense dust cloud. Visible light cannot escape from this environment but long ...
08 October: Stellar life after the Main Sequence
... Why mass is destiny: the more mass, the more fuel, but more massive stars use up their fuel at much higher rates ...
... Why mass is destiny: the more mass, the more fuel, but more massive stars use up their fuel at much higher rates ...
ORIGIN OF THE UNIVERSE
... stars, comets, etc are the debris that is still drifting outward from this explosion. * There are many flaws to this theory, but scientifically it is the most supported answer. Inflation Theory (IUT) is gaining ground. * The Universe is estimated to be 13.7 Billion Years ...
... stars, comets, etc are the debris that is still drifting outward from this explosion. * There are many flaws to this theory, but scientifically it is the most supported answer. Inflation Theory (IUT) is gaining ground. * The Universe is estimated to be 13.7 Billion Years ...
Compare the following sets of stars using the words: BRIGHTER or
... 22. What determines the life cycle path the star will take in the above diagram? The mass of the gas cloud (nebula) 23. Name the forces involved in the following processes: A. Gas/dust from a stellar nursery come together to form stars: Gravity B. Stars are made of gas, but keep a size/shape (equili ...
... 22. What determines the life cycle path the star will take in the above diagram? The mass of the gas cloud (nebula) 23. Name the forces involved in the following processes: A. Gas/dust from a stellar nursery come together to form stars: Gravity B. Stars are made of gas, but keep a size/shape (equili ...
Section 3-3(rev04) 2
... nubula. It is the source of all stars. Gravity pulls the gases closer together and they heat up. This is called a protostar. A star is born when the gases and dust become hot enough for nuclear fusion to take place. Nuclear fusion is the process in which hydrogen is changed to helium. Other elements ...
... nubula. It is the source of all stars. Gravity pulls the gases closer together and they heat up. This is called a protostar. A star is born when the gases and dust become hot enough for nuclear fusion to take place. Nuclear fusion is the process in which hydrogen is changed to helium. Other elements ...
Review 2
... Internal structure of our Sun and its chemical composition. What is the convection zone on the Sun and what are the granules and supergranules? What is the temperature in the Sun’s core? What is the photosphere, chromosphere and corona? What is their temperature and what causes their color? What is ...
... Internal structure of our Sun and its chemical composition. What is the convection zone on the Sun and what are the granules and supergranules? What is the temperature in the Sun’s core? What is the photosphere, chromosphere and corona? What is their temperature and what causes their color? What is ...
CBradleyLoutl
... star becomes a red supergiant. - This is determined primarily by the mass of the star: . <.08 Solar Masses: The temperature and pressure weren’t great enough to cause any hydrogen fusion at all, the star passes through the main sequence and becomes a white dwarf, slowly cooling. . ~.08 - .3 Solar Ma ...
... star becomes a red supergiant. - This is determined primarily by the mass of the star: . <.08 Solar Masses: The temperature and pressure weren’t great enough to cause any hydrogen fusion at all, the star passes through the main sequence and becomes a white dwarf, slowly cooling. . ~.08 - .3 Solar Ma ...
Life Cycles of Stars
... • Remaining core of a supergiant that was more than 40 times the size of our Sun • The core of the supergiant, after a supernova, is so dense that its gravitational pull sucks in space, time, light and matter • Thought to be at the centre of all galaxies ...
... • Remaining core of a supergiant that was more than 40 times the size of our Sun • The core of the supergiant, after a supernova, is so dense that its gravitational pull sucks in space, time, light and matter • Thought to be at the centre of all galaxies ...
Astronomy 115 Homework Set #1 – Due: Thursday, Feb
... How does that compare to the escape velocity from the Sun itself? How might this difference affect the winds coming off each star? ...
... How does that compare to the escape velocity from the Sun itself? How might this difference affect the winds coming off each star? ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.