* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Compare the following sets of stars using the words: BRIGHTER or
Gamma-ray burst wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
High-velocity cloud wikipedia , lookup
Stellar classification wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
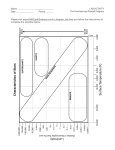
Compare the following sets of stars using the words: BRIGHTER or DIMMER, and COOLER or HOTTER. 1. Spica (dimmer and hotter) and Polaris (brighter and cooler) 2. Betelgeuse (brighter and same cool temperature) and Bernard’s star (dimmer and same cool temp.) 3. Sirius B (brighter and hotter) and Procyon B (dimmer and cooler) 4. Sun (dimmer and cooler) and Vega (brighter and hotter) 5. Alpha Centauri A (dimmer and cooler) and Canopus (brighter and hotter) 6. Describe the sun’s location on the HR diagram: Along the Main Sequence about average brightness and temperature 7. What determines the color of the stars? The temperature! Blue is the hottest & red is coolest! 8. Explain how energy is transferred from the Sun to the Earth in the vacuum of space? Electromagnetic Energy (infrared, light and ultraviolet) through waves 9. How do scientists know what elements are in stars? By looking at the star spectrums for known elements using a spectroscope. Complete the following table: Type of galaxy Sketch 10. Elliptical 12. Irregular 14 Spiral Barred Spiral 16. Description 11. Round or elliptical, old red stars 13. No Defined Shape, young stars 15. A cluster of stars in the center with arms showing rotation (spin) 17. A type of spiral with a thick band of stars through the middle 18. What type of galaxy is the Milkyway galaxy? A Barred Spiral (or spiral) 19. Where are we located in the Milkyway galaxy? We are on an arm. 20. Draw a picture and describe the process of H atoms combining to form He atoms. In the process of nuclear fusion, one atom of hydrogen (mass # = 2) and one atom of hydrogen (mass # = 3) fuse together to form Helium (mass # = 4) and one neutron. This occurs during the Main Sequence of a star. 21. Draw and label the life cycle of stars (see your star notes): Sun-like Star -> red giant -> planetary nebula -> white dwarf Massive -> Super red giant -> supernova -> neutron star (large stars) ->Black hole (extra-large stars) Stellar Nursery (Nebula) 22. What determines the life cycle path the star will take in the above diagram? The mass of the gas cloud (nebula) 23. Name the forces involved in the following processes: A. Gas/dust from a stellar nursery come together to form stars: Gravity B. Stars are made of gas, but keep a size/shape (equilibrium): Gravity (inward) and Gas Pressure (outward) 24. Put the following structures in order from smallest to largest: Universe, star, galaxy, asteroid, planet, solar system, International Space Station, Earth’s moon ISS, Asteroid, Moon, Planet, Star, Solar System, Galaxy, Universe 25. Place the following waves in order from lowest frequency (longer wavelengths) to highest frequency (shorter wavelengths): Ultraviolet, Radio, X-ray, Visible light, Gamma, Infrared Radio, Infrared, Visible light, Ultraviolet, X-ray, Gamma 26. What is wavelength and how does it determine frequency? Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive crests or troughs. The shorter the wavelength, the higher the frequency. 27. Which electromagnetic wave has the lowest energy? Radio Highest? Gamma How do you know? The higher the frequency of a wave, the more energy it has (more powerful) 28. Explain the Big Bang Theory, including the evidence that supports it: Theory of the beginning of the universe, proof is the Red Shift showing everything is expanding 29. What is a LIGHT-YEAR? Distance light travels in a year, used to measure distances outside of our solar system. 30. Why do planets in our solar system orbit the sun in a circular path? The sun’s gravitational force keeps us in our circular path. We stay in motion due to inertia. 32. What causes day and night? Earth’s rotation (24 hours) Seasons? Earth’s tilt 33. Draw and label moon phases. Neap tide Spring tide Spring tide Lunar Eclipse Solar Eclipse Neap tide