Solving the Mystery of Massive Star Birth
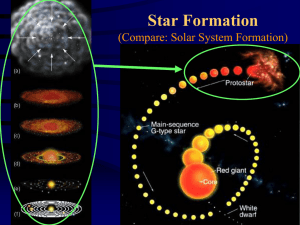
... collapse of the cloud, which begins to shrink under the pull of its own gravity. As the cloud gets smaller, it gets clumpy. The clumps may eventually become so compact that they begin to heat up, growing hotter and hotter, until eventually they begin “burning” at their core. When the temperature at ...
... collapse of the cloud, which begins to shrink under the pull of its own gravity. As the cloud gets smaller, it gets clumpy. The clumps may eventually become so compact that they begin to heat up, growing hotter and hotter, until eventually they begin “burning” at their core. When the temperature at ...
transition
... photons and small pieces of slightly clumped matter. The Universe remains ionized as the electrons can not yet recombine with the protons to make neutral hydrogen. When the temperature cools to 3000K, recombination happens, the surface of last scattering is reached, and the radiation dominated era i ...
... photons and small pieces of slightly clumped matter. The Universe remains ionized as the electrons can not yet recombine with the protons to make neutral hydrogen. When the temperature cools to 3000K, recombination happens, the surface of last scattering is reached, and the radiation dominated era i ...
22.2 Stars Change Over Their Life Cycles
... • Try this! Close one eye at a time and focus on a single object. Blink back and forth quickly. What happens!? Does the object appear to move? ...
... • Try this! Close one eye at a time and focus on a single object. Blink back and forth quickly. What happens!? Does the object appear to move? ...
Chapter 3: the Sun - University of Waterloo
... Rotation of the cloud means this collapsing material forms a disk. Eventually T becomes high enough that molecular hydrogen dissociates; this absorbs some of the energy supporting the protostar, so the core begins to collapse further, until it becomes ~30% larger than the present ...
... Rotation of the cloud means this collapsing material forms a disk. Eventually T becomes high enough that molecular hydrogen dissociates; this absorbs some of the energy supporting the protostar, so the core begins to collapse further, until it becomes ~30% larger than the present ...
22 October: The Formation of Stars
... • Now, how to stars form? What do they form from? Space seems to be empty. Where does the material come from? ...
... • Now, how to stars form? What do they form from? Space seems to be empty. Where does the material come from? ...
Formation of Stars
... Gravity works to compress a cloud. As an interstellar cloud collapses, it heats up. The rise in internal temperature and pressure works to counter gravity and stop the compression. ...
... Gravity works to compress a cloud. As an interstellar cloud collapses, it heats up. The rise in internal temperature and pressure works to counter gravity and stop the compression. ...
Document
... are about to form new stars. They also create the heavier elements (such as gold, silver, lead, and uranium) and distribute these as well. Their remnants generate the cosmic rays which lead to mutation and evolution in living cells. These supernovae, then, are key to the evolution of the Universe an ...
... are about to form new stars. They also create the heavier elements (such as gold, silver, lead, and uranium) and distribute these as well. Their remnants generate the cosmic rays which lead to mutation and evolution in living cells. These supernovae, then, are key to the evolution of the Universe an ...
Lecture11
... Above the protostar, the rest of the cloud is still in free-fall. Rotation of the cloud means this collapsing material forms a disk. Eventually T becomes high enough that molecular hydrogen dissociates; this absorbs some of the energy supporting the protostar, so the core begins to collapse further, ...
... Above the protostar, the rest of the cloud is still in free-fall. Rotation of the cloud means this collapsing material forms a disk. Eventually T becomes high enough that molecular hydrogen dissociates; this absorbs some of the energy supporting the protostar, so the core begins to collapse further, ...
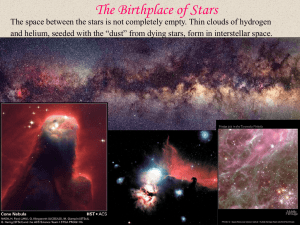
molecular clouds
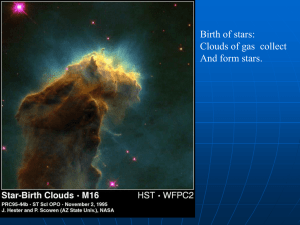
... GMCs typically have diameters of 100 light-years, masses of up to 6 million solar masses, and an average interior temperature of 10 K. The nearest nebula to the Sun where massive stars are being formed is the Orion nebula, 1,300 ly away. ...
... GMCs typically have diameters of 100 light-years, masses of up to 6 million solar masses, and an average interior temperature of 10 K. The nearest nebula to the Sun where massive stars are being formed is the Orion nebula, 1,300 ly away. ...
Day-5
... 1¼ seconds to arrive from the Moon. 8.3 minutes to arrive from the Sun. 5.5 hours to get to Pluto from the Sun. 4.3 years (yr) to get to the nearest star. 100,000 yr to cross the galaxy. 2.9 million yr to get to the nearest big galaxy. 10 billion yr to come from distant galaxies. ...
... 1¼ seconds to arrive from the Moon. 8.3 minutes to arrive from the Sun. 5.5 hours to get to Pluto from the Sun. 4.3 years (yr) to get to the nearest star. 100,000 yr to cross the galaxy. 2.9 million yr to get to the nearest big galaxy. 10 billion yr to come from distant galaxies. ...
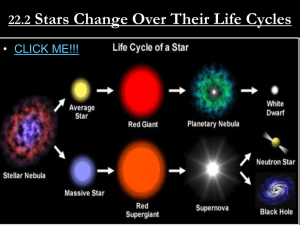
The Evolutionary Cycle of Stars
... White Dwarf The final evolutionary state whose mass is not too high. This is the last stage of stellar evolution. ...
... White Dwarf The final evolutionary state whose mass is not too high. This is the last stage of stellar evolution. ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... • Cloud contracts/warms, begins radiating; almost all radiated energy escapes • Cloud becomes dense opaque to radiation radiated energy trapped core heats up ...
... • Cloud contracts/warms, begins radiating; almost all radiated energy escapes • Cloud becomes dense opaque to radiation radiated energy trapped core heats up ...
Class 12 : Star formation I : The Interstellar Medium (ISM)
... A very large gas cloud will fragment into small pieces, each of which is equal to the Jeans Mass As a gas cloud collapses and increases in density, the Jeans Mass decreases… the gas fragments into yet smaller pieces ...
... A very large gas cloud will fragment into small pieces, each of which is equal to the Jeans Mass As a gas cloud collapses and increases in density, the Jeans Mass decreases… the gas fragments into yet smaller pieces ...
Lecture 22 - Star Formation from Molecular Clouds
... • We understand the physics of these processes (at least partially) • We believe the Sun formed like this. • What characteristic of the solar system can we see that is an indicator of the processes of contraction, jet formation, accretion disk formation, etc? ...
... • We understand the physics of these processes (at least partially) • We believe the Sun formed like this. • What characteristic of the solar system can we see that is an indicator of the processes of contraction, jet formation, accretion disk formation, etc? ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.