ASTRONOMY 1001 FALL SEMESTER 2004
... Giant Planets: structure, atmospheres, temperatures, rings, satellites, Tides, Io and tidal heating, Roche limit, disruption of satellites, rings Asteroids, origin, collisions and extinction; meteorites, types, origin, ages Comets, ion and dust tails, structure, nucleus, origin, behavior in orbit Or ...
... Giant Planets: structure, atmospheres, temperatures, rings, satellites, Tides, Io and tidal heating, Roche limit, disruption of satellites, rings Asteroids, origin, collisions and extinction; meteorites, types, origin, ages Comets, ion and dust tails, structure, nucleus, origin, behavior in orbit Or ...
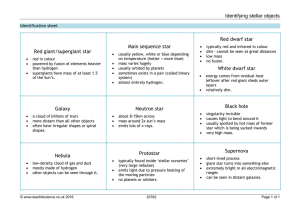
Stellar Evolution
... released. • This process is responsible for creating ALL elements found in the universe… in other words, we are all made from star dust. ...
... released. • This process is responsible for creating ALL elements found in the universe… in other words, we are all made from star dust. ...
Extension worksheet – Topic 6 - Cambridge Resources for the IB
... A large, cool cloud of gas may collapse under gravity to form a star. State where the energy comes from to heat up the star so that nuclear fusion may take place. In this question assume a mass–luminosity relation of L M 3.5 . a ...
... A large, cool cloud of gas may collapse under gravity to form a star. State where the energy comes from to heat up the star so that nuclear fusion may take place. In this question assume a mass–luminosity relation of L M 3.5 . a ...
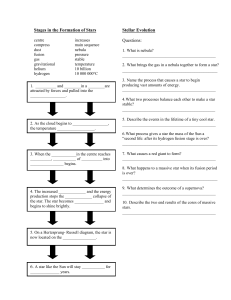
Stellar Properties and Stellar Evolution Study Guide Name Why
... 3. How does a stars surface temperature relate to its color? ...
... 3. How does a stars surface temperature relate to its color? ...
Click here for Jeopardychap16
... Give correct order of Evolution of sun-like star From young to old: ...
... Give correct order of Evolution of sun-like star From young to old: ...
Stellar Evolution
... • If the core’s mass is even greater/denser than a neutron star, it collapses. • Surface gravity is so great that no matter can escape it…not even electromagnetic ...
... • If the core’s mass is even greater/denser than a neutron star, it collapses. • Surface gravity is so great that no matter can escape it…not even electromagnetic ...
How Stars Form Powerpoint
... Star-Forming Regions • Formation happens when part of a dust cloud begins to contract under its own gravitational force • Center becomes hotter and hotter until nuclear fusion begins in the core. ...
... Star-Forming Regions • Formation happens when part of a dust cloud begins to contract under its own gravitational force • Center becomes hotter and hotter until nuclear fusion begins in the core. ...
Star Formation
... • Eventually the gas and dust are pushed away. • The star then becomes “visible.” • Prior to this it could be seen only in the radio and the infrared. ...
... • Eventually the gas and dust are pushed away. • The star then becomes “visible.” • Prior to this it could be seen only in the radio and the infrared. ...
Here
... When parts of a cloud become sufficiently massive, they collapse to form a young star, a protostar. These protostars are surrounded by disks of gas and dust in which planets may form. In these early stages the protostars also drive massive and energetic outflows which can blow away the rema ...
... When parts of a cloud become sufficiently massive, they collapse to form a young star, a protostar. These protostars are surrounded by disks of gas and dust in which planets may form. In these early stages the protostars also drive massive and energetic outflows which can blow away the rema ...
Star Life Cycle Web Quiz
... Fill in the Chart: In order for a star to continue to exist as a ball of radiant energy it must have equilibrium between two strong forces. Fill in the chart below in each of the 3 columns. What is each force? ...
... Fill in the Chart: In order for a star to continue to exist as a ball of radiant energy it must have equilibrium between two strong forces. Fill in the chart below in each of the 3 columns. What is each force? ...
Ginger Dublin 6th Grade Science
... supernova explodes causing its core to collapse. • So dense that even light can’t escape its gravity. ...
... supernova explodes causing its core to collapse. • So dense that even light can’t escape its gravity. ...
April 1st
... • The more massive a star on the main sequence, the shorter its lifetime • More massive stars do contain more hydrogen than smaller stars • However, the more massive stars have higher luminosities so they are using up their fuel at a much quicker rate than smaller stars ...
... • The more massive a star on the main sequence, the shorter its lifetime • More massive stars do contain more hydrogen than smaller stars • However, the more massive stars have higher luminosities so they are using up their fuel at a much quicker rate than smaller stars ...
Stellar Evolution
... layers are driven away • Core becomes hot enough to produce Carbon (C) • Star contracts to normal size when helium is used up • Carbon core left over, White dwarf remains ...
... layers are driven away • Core becomes hot enough to produce Carbon (C) • Star contracts to normal size when helium is used up • Carbon core left over, White dwarf remains ...
Introduction to Astronomy
... • This heat allows fusion to occur in a shell of material surrounding the core… • Due to the higher central temperature, the star’s luminosity is greater than before… • This increased energy production causes the outer part of the star to expand and cool (counterintuitive!)… • We now have a very lar ...
... • This heat allows fusion to occur in a shell of material surrounding the core… • Due to the higher central temperature, the star’s luminosity is greater than before… • This increased energy production causes the outer part of the star to expand and cool (counterintuitive!)… • We now have a very lar ...
ISM and star formation
... Some protostars not massive (< 0.08 MSun) enough to begin fusion. These are Brown Dwarfs or failed stars. Very difficult to detect because so faint. First seen in 1994 with Hubble. How many are there? ...
... Some protostars not massive (< 0.08 MSun) enough to begin fusion. These are Brown Dwarfs or failed stars. Very difficult to detect because so faint. First seen in 1994 with Hubble. How many are there? ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.