Today`s Powerpoint
... Emission Nebulae or H II Regions Regions of gas and dust near stars just formed. The Hydrogen is essentially fully ionized. Temperatures near 10,000 K Sizes about 1-20 pc. Hot tenuous gas => emission lines ...
... Emission Nebulae or H II Regions Regions of gas and dust near stars just formed. The Hydrogen is essentially fully ionized. Temperatures near 10,000 K Sizes about 1-20 pc. Hot tenuous gas => emission lines ...
Study Guide Astronomy
... 9. What is the relationship between surface temperature and brightness for main sequence stars on the Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram? ...
... 9. What is the relationship between surface temperature and brightness for main sequence stars on the Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram? ...
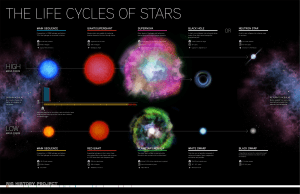
life and death of a high mass star 2
... AFTER THAT, THEY LOSE THEIR MASS AND HEAT AND BEGIN TO DIE. THIS PROCESS TAKES BILLIONS AND BILLIONS OF YEARS. ...
... AFTER THAT, THEY LOSE THEIR MASS AND HEAT AND BEGIN TO DIE. THIS PROCESS TAKES BILLIONS AND BILLIONS OF YEARS. ...
Study Guide_galaxies, Tools, and Stars Test
... 3. What is the name of the galaxy our solar system is located in? 4. What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 5. The ________ is the largest star in our solar system. 6. Name and describe the 3 types of galaxies. 7. Where is our solar system located in the Milky Way galaxy? 8. What is a light ye ...
... 3. What is the name of the galaxy our solar system is located in? 4. What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 5. The ________ is the largest star in our solar system. 6. Name and describe the 3 types of galaxies. 7. Where is our solar system located in the Milky Way galaxy? 8. What is a light ye ...
Notes: Star Formation
... • The cloud of particles in a nebula begins to collapse because of gravity. – As the cloud collapses its temperature and density increase. – Temperature and density are the highest in the center of the cloud. – protostar- a dense area of gasses in a nebula that might become a star. ...
... • The cloud of particles in a nebula begins to collapse because of gravity. – As the cloud collapses its temperature and density increase. – Temperature and density are the highest in the center of the cloud. – protostar- a dense area of gasses in a nebula that might become a star. ...
Triggered Star Formation by Massive Stars in Star
... effective. Out of 32 candidates, 24 were confirmed to be bona fide young stars, with the reaming 4 as M dwarfs and 4 as carbon stars. Other related project: Herbig Ae/Be stars in open clusters, e.g., NGC 1857; Wolf-Rayet stars in OB associations. ...
... effective. Out of 32 candidates, 24 were confirmed to be bona fide young stars, with the reaming 4 as M dwarfs and 4 as carbon stars. Other related project: Herbig Ae/Be stars in open clusters, e.g., NGC 1857; Wolf-Rayet stars in OB associations. ...
Powerpoint
... As it collapses, the center becomes hotter and hotter until nuclear fusion begins in the core. Probably new molecular clouds form continually out of less dense gas. Some collapse under their own gravity. Others may be more stable. Magnetic fields and rotation also have some influence. Gravity makes ...
... As it collapses, the center becomes hotter and hotter until nuclear fusion begins in the core. Probably new molecular clouds form continually out of less dense gas. Some collapse under their own gravity. Others may be more stable. Magnetic fields and rotation also have some influence. Gravity makes ...
1 Star Formation and Main Sequence Evolution Condensation
... but fragments into clumps with a range of masses ...
... but fragments into clumps with a range of masses ...
Structure of the Universe
... by combining smaller elements to form a larger one, specifically two hydrogen atoms form a helium atom, ...
... by combining smaller elements to form a larger one, specifically two hydrogen atoms form a helium atom, ...
Forming Planets
... How long does it take to make a solar system? A. 1 million years. B. 10 million years. C. 100 million years. D. 1 billion years. ...
... How long does it take to make a solar system? A. 1 million years. B. 10 million years. C. 100 million years. D. 1 billion years. ...
Powerpoint for today
... Remember, takes energetic UV photons to ionize H. Hot, massive stars produce huge amounts of these. Such short-lived stars spend all their lives in the stellar nursery of their birth, so emission nebulae mark sites of ongoing star formation. Many stars of lower mass are forming too, but make few UV ...
... Remember, takes energetic UV photons to ionize H. Hot, massive stars produce huge amounts of these. Such short-lived stars spend all their lives in the stellar nursery of their birth, so emission nebulae mark sites of ongoing star formation. Many stars of lower mass are forming too, but make few UV ...
Goal: To understand how stars form.
... a star to do that. • 2) Collision with another cloud of gas – this usually happens when 2 galaxies collide. • 3) Spiral arm – probably the most common. • You get a spiral density wave that shocks the gas cloud. That causes it to collapse – much like sending a seismic wave through an old house make t ...
... a star to do that. • 2) Collision with another cloud of gas – this usually happens when 2 galaxies collide. • 3) Spiral arm – probably the most common. • You get a spiral density wave that shocks the gas cloud. That causes it to collapse – much like sending a seismic wave through an old house make t ...
PPT - University of Delaware
... Question is: How big is this force vs. gravity? For the Sun, Mass lost over lifetime ~ 0.01% For hot stars (M = 10 - 50 M) mass can be reduced by ½! ...
... Question is: How big is this force vs. gravity? For the Sun, Mass lost over lifetime ~ 0.01% For hot stars (M = 10 - 50 M) mass can be reduced by ½! ...
Document
... • During the collapse, the density of the cloud increases toward the center and thus the middle region becomes optically opaque first. • Particles fall towards the centre of the sphere and the kinetic energy increases . The kinetic energy of a group of particles is the thermal kinetic energy, or tem ...
... • During the collapse, the density of the cloud increases toward the center and thus the middle region becomes optically opaque first. • Particles fall towards the centre of the sphere and the kinetic energy increases . The kinetic energy of a group of particles is the thermal kinetic energy, or tem ...
STARS and GALAXIES
... that produces tremendous amounts of heat and light. • Some stars are very old and the size of planets or moons, and some no longer emit radiation (no light). ...
... that produces tremendous amounts of heat and light. • Some stars are very old and the size of planets or moons, and some no longer emit radiation (no light). ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.