* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 22 - Star Formation from Molecular Clouds
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Planetary system wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Directed panspermia wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
High-velocity cloud wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
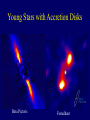
Lecture 22 - Star Formation from Molecular Clouds Gravitational contraction of gas clumps (like balloons) can’t happen in the atmosphere because you can’t get as big as the Jeans Length. But in interstellar space, it’s a different story Term: the Interstellar Medium- material in space between the stars A Star is born…. A Star is born (Part 2) … Forming stars eventually rip up the molecular cloud in which they formed. The molecular cloud is dissipated after about 30 million years. (How can we know that?) Star formation and the conservation of angular momentum You can see these phenomena in stars in the sky (T Tauri stars, HerbigHaro objects, etc) jet Accretion disk Question: • We see these processes occurring in young protostars. • We understand the physics of these processes (at least partially) • We believe the Sun formed like this. • What characteristic of the solar system can we see that is an indicator of the processes of contraction, jet formation, accretion disk formation, etc? Young Stars with Accretion Disks Beta Pictoris Fomalhaut Artist’s Conception of Fomalhaut System Summary of what we know about the formation of stars • Stars form from the massive amounts of material in cold, dark molecular clouds • Contraction from the low density molecular cloud to a dense, compact, shining star occurs through gravitational contraction (Jeans Length) • As the star contracts and “spins up”, it sheds a disk of matter, from which planets form. Where do we see this occurring? Everywhere in the sky. Particularly in the Milky Way. Check the Skalnate Pleso charts for Taurus and Auriga