* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Solution to Problem Set 1 1. The total number of nucleons in one
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Planetary nebula wikipedia , lookup
Nucleosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
X-ray astronomy detector wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear drip line wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Microplasma wikipedia , lookup
Hayashi track wikipedia , lookup
Standard solar model wikipedia , lookup
Main sequence wikipedia , lookup
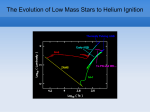
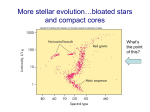
Solution to Problem Set 1 1. The total number of nucleons in one kilogram of matter is N = 1/ mp = 5.99 × 1026 . Each nucleon releases = 8.8 MeV, so the total energy released is N = 8.4 × 1014 J. 2. The age for a main sequence star is approximately τ = 1010 yr M M −2.5 (1) For a 6M star, this gives τ = 1.1 × 108 yr. So the age of Pleiades is about 1.1 × 108 yr. 3. From the definition of the apparent magnitude, we have, at the limit of the d naked eye, 6 = 4.7 + 5 log 10 pc , which gives d = 18.2 pc. The flux is then f = L/(4πd2 ) = 9.6 × 10−11 W m−2 . Assuming the area of the eyes is about A = 1 cm2 , then the total energy received in a time period of t = 1s is E = f At = 9.6 × 10−15 J. The photons are mostly in the visible range, so have a wavelength λ ≈ 5500Å. Each photon has an energy of = hc/λ = 3.6 × 10−19 J, so the total number of photons is then E/ = 2.7 × 104 photons. 4. See the lecture notes (Figs. 9 and 10). The most luminous stars are on the top, while the reddest stars are to the right. The stellar masses are in the range of 0.1 − 100M [1 mark] At the lower limit, the gravity is balanced by the degenerate pressure of electrons, and the central temperature is too low to initiate the nuclear burning. [2 marks] Very massive stars are dominated by radiation pressure, such radiation dominated stars are unstable to radial perturbations, and hence this provides an upper limit on the stellar mass. [2 marks] At the late evolutionary stage of the Sun, helium nuclear burning occurs in a degenerate core. The energy generation rate is extremely sensitive to the temperature: ∝ ρ2He T 40 When the helium burning reaction starts, the energy liberated increases the temperature locally, but because of the degeneracy, the rising temperature does not increase the pressure, the latter means the core cannot expand and cool itself. The increasing temperature means the reaction 3α →12 C runs faster, and so on, so we have a thermal runaway, called helium flash. [5 marks]