* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earth - Capital High School
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Gamma-ray burst wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Shape of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
Fine-tuned Universe wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Ultimate fate of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Expansion of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Flatness problem wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic microwave background wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Observable universe wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
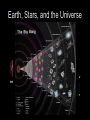
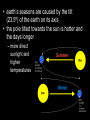
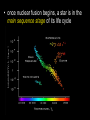
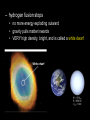
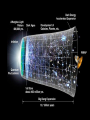
Earth, Stars, and the Universe Earth • tends to be hotter at the equator because the sun’s energy is perpendicular to the earth and therefore more concentrated • earth’s seasons are caused by the tilt (23.5º) of the earth on its axis • the pole tilted towards the sun is hotter and the days longer – more direct sunlight and higher temperatures Stars • life cycle varies depending on the size • all begin life inside a huge cloud of gas (mostly hydrogen) and dust called a nebula • then turns into a protostar – H is converted to He – gravity squeezes the atoms of a star so tight that the electrons are stripped away and the bare nuclei of atoms almost touch each other • once nuclear fusion begins, a star is in the main sequence stage of its life cycle • for average, Sun-sized stars – eventually runs out of H – gets hotter making C and O atoms – expands outwards making a red giant – hydrogen fusion stops • no more energy exploding outward • gravity pulls matter inwards • VERY high density, bright, and is called a white dwarf • for larger stars – larger elements (up to iron) of the periodic table are fused together – eventually may turn into a supernova • quickly collapses because run out of energy and gravity is now the strongest force – core collapses and then rebounds outward with a shock wave that makes a bright explosion (supernova) – at this point, heavier elements are created • if the leftover core is very, very dense, it may form a very small neutron star or a black hole with VERY powerful gravity Universe (The Big Bang) The Hubble Ultra Deep Field, or HUDF, is an image of a small region of space in the constellation Fornax, composited from Hubble Space Telescope data accumulated over a period from September 3, 2003 through January 16, 2004. It is the deepest image of the universe ever taken in visible light, looking back in time more than 13 billion years. The HUDF contains an estimated 10,000 galaxies. The total field of view represents only 1 ten millionth of the total sky. THIS MAY NOT BE TRUE, I JUST FOUND IT ON THE INTERNET • consists of all matter, empty space, and energy that exists • objects are so far away, we are seeing what they looked like millions of years ago – it takes one year for light to travel 5+ trillion miles (a light year) • around 10-20 billion years old • Evidence 1. is expanding, therefore must have been smaller at one point • evident by galaxies’ red shift – most look red because they are moving away from us • if they were moving towards us, they would look bluer (blue shift) 2. cosmic background radiation – scientists found “noise” in our galaxy that was the cosmic microwave background radiation predicted by the Big Bang theory 3. most elements in universe are H and He – when stars reach the end of their life cycle, they spread out C, O, and Fe into the universe • if the universe was older, there would be more C, O, and Fe