Introduction to Geography
... Frost Wedging: the most important type of mechanical weathering; freeze-thaw repetition. Also responsible for city pot-holes. Personal home experiment ...
... Frost Wedging: the most important type of mechanical weathering; freeze-thaw repetition. Also responsible for city pot-holes. Personal home experiment ...
Intro to Rocks
... • Usually dark colored, but high olivine content tend to produce green colors. There are also other rare colors. • Example periodotite (intrusive) ...
... • Usually dark colored, but high olivine content tend to produce green colors. There are also other rare colors. • Example periodotite (intrusive) ...
The Rocks Beneath Our Feet
... Since the final rifting apart of Pangaea some 175 million years ago, the eastern margin of North America has remained tectonically dormant, allowing the younger rocks to weather and erode exposing the older rocks below. In and around Asheville, rocks have been weathered and eroded away exposing geol ...
... Since the final rifting apart of Pangaea some 175 million years ago, the eastern margin of North America has remained tectonically dormant, allowing the younger rocks to weather and erode exposing the older rocks below. In and around Asheville, rocks have been weathered and eroded away exposing geol ...
Evaluating Evidence of Plate Tectonics
... • Sources (at least 3, cited correctly in and out of text) • Explaining your evidence (back up each one of your pieces of evidence with reasoning for why it supports your claim) ...
... • Sources (at least 3, cited correctly in and out of text) • Explaining your evidence (back up each one of your pieces of evidence with reasoning for why it supports your claim) ...
Obs
... -- Thrust faulting in the near-surface -- Flow of weak crustal rocks at depth -- Isostatic response to thicker (buoyant) crust Mountains (Himalaya, Andes) Epeirogeny: At divergent plate boundaries and continental rifts, get: -- Thinning of the crust and lithosphere -- Hot rock brought nearer the E ...
... -- Thrust faulting in the near-surface -- Flow of weak crustal rocks at depth -- Isostatic response to thicker (buoyant) crust Mountains (Himalaya, Andes) Epeirogeny: At divergent plate boundaries and continental rifts, get: -- Thinning of the crust and lithosphere -- Hot rock brought nearer the E ...
From the Beginning The earth and the whole universe were formed
... The temperature of the surface was relatively the same or stable, but from time to time, it cooled so that ice sheets and _________________________ spread out like giant _________________________ to form deep valleys and mountains faces from rock debris. The Precambrian mountains had been worn down ...
... The temperature of the surface was relatively the same or stable, but from time to time, it cooled so that ice sheets and _________________________ spread out like giant _________________________ to form deep valleys and mountains faces from rock debris. The Precambrian mountains had been worn down ...
Chapter 6: Igneous Rocks
... • Magma is molten rock, while lava is magma on the Earth’s surface. • Igneous rocks may be either extrusive if they form at the surface (ex. basalt) or intrusive if magma solidifies underground (ex. granite). Watch Video ...
... • Magma is molten rock, while lava is magma on the Earth’s surface. • Igneous rocks may be either extrusive if they form at the surface (ex. basalt) or intrusive if magma solidifies underground (ex. granite). Watch Video ...
Chapter 4: Rocks
... grow together Are only found on the surface after layers of rock and soil that covered them have been removed by erosion It takes a long time for them too cool, therefore mineral grains are large ...
... grow together Are only found on the surface after layers of rock and soil that covered them have been removed by erosion It takes a long time for them too cool, therefore mineral grains are large ...
Appalachian Mountains - Brief Geologic History The Earth is
... Eventually, about 270 million years ago, the continents ancestral to North America and Africa collided. Huge masses of rock were pushed west-ward along the margin of North America and piled up to form the mountains that we know as the Appalachians. As blocks of continental crust rode across one anot ...
... Eventually, about 270 million years ago, the continents ancestral to North America and Africa collided. Huge masses of rock were pushed west-ward along the margin of North America and piled up to form the mountains that we know as the Appalachians. As blocks of continental crust rode across one anot ...
Minerals and Their Physical Properties
... Freezing/Melting point = 0°C Seawater (a mixture): Freezing/Melting point = -2°C ...
... Freezing/Melting point = 0°C Seawater (a mixture): Freezing/Melting point = -2°C ...
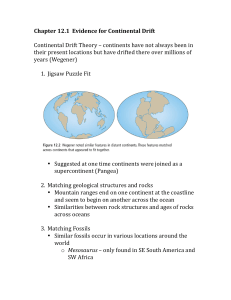
Chapter 12.1 Evidence for Continental Drift Continental Drift Theory
... Earth’s surface at a spreading ridge forming new sea floor. Process continues pushing older rock aside ...
... Earth’s surface at a spreading ridge forming new sea floor. Process continues pushing older rock aside ...
7 - English River School
... 2. When the edges of two plates slide alongside each other, the result is a a) diverging boundary b) converging boundary c) transform boundary d) none of the above 3. The way the surface of a mineral looks in the light is called a) colour b) lustre c) streak ...
... 2. When the edges of two plates slide alongside each other, the result is a a) diverging boundary b) converging boundary c) transform boundary d) none of the above 3. The way the surface of a mineral looks in the light is called a) colour b) lustre c) streak ...
Classifying rocks
... _______________ is the most abundant o Texture: depends on _______________ and shape of mineral crystals Small crystals: Lava cools _______________ _______________ rock o _______________ o Obsidian: no _______________ Large crystals: _______________ cooling lava _______________ rock o ____ ...
... _______________ is the most abundant o Texture: depends on _______________ and shape of mineral crystals Small crystals: Lava cools _______________ _______________ rock o _______________ o Obsidian: no _______________ Large crystals: _______________ cooling lava _______________ rock o ____ ...
Vocabulary Review
... the area where one lithospheric plate slides under another at convergent plate boundaries; some crust is destroyed boundary between plates that are sliding past each other at one time in geologic history the continents were joined together in one large landmass called by this name ...
... the area where one lithospheric plate slides under another at convergent plate boundaries; some crust is destroyed boundary between plates that are sliding past each other at one time in geologic history the continents were joined together in one large landmass called by this name ...
geology exam is - Spring Branch ISD
... _________________ 6. The density of a mineral is how much mass is contained in a given volume of that mineral. _________________ 7. Minerals that form irregular surfaces when they break apart have a property called cleavage. ...
... _________________ 6. The density of a mineral is how much mass is contained in a given volume of that mineral. _________________ 7. Minerals that form irregular surfaces when they break apart have a property called cleavage. ...
... water may have been involved and the small valleys on Oyama flanks may be related to this transport. Flows have also formed valleys after the deposition of these layers. These rocks have likely recorded a long and complex presence of liquid water. A fresh crater closer to the ellipse has likely exhu ...
geography - KCPE-KCSE
... Dynamic/kinetic (due to pressure changes) Thermal/contact metamorphism (due to intense heat) Thermal dynamic/region (combination of heat and pressure) Metasomatism (due to hot and molten rocks) ...
... Dynamic/kinetic (due to pressure changes) Thermal/contact metamorphism (due to intense heat) Thermal dynamic/region (combination of heat and pressure) Metasomatism (due to hot and molten rocks) ...
Introduction - Big Concepts in Geology
... Radioactive Decay of Uranium to Lead - 238U > 206Pb Carbon 14 Dating - produced by cosmic radiation in upper atmosphere - half of 14C decays to 14N in 5,730 years - method good for material up to ~50,000 years old (e.g. 15,000 year old moccasins from Missouri cave) ...
... Radioactive Decay of Uranium to Lead - 238U > 206Pb Carbon 14 Dating - produced by cosmic radiation in upper atmosphere - half of 14C decays to 14N in 5,730 years - method good for material up to ~50,000 years old (e.g. 15,000 year old moccasins from Missouri cave) ...
Introduction - Big Concepts in Geology
... Radioactive Decay of Uranium to Lead - 238U > 206Pb Carbon 14 Dating - produced by cosmic radiation in upper atmosphere - half of 14C decays to 14N in 5,730 years - method good for material up to ~50,000 years old (e.g. 15,000 year old moccasins from Missouri cave) ...
... Radioactive Decay of Uranium to Lead - 238U > 206Pb Carbon 14 Dating - produced by cosmic radiation in upper atmosphere - half of 14C decays to 14N in 5,730 years - method good for material up to ~50,000 years old (e.g. 15,000 year old moccasins from Missouri cave) ...
Weathering and Erosion - School District 67 Okanagan Skaha
... • Lichens that grow on rocks produce weak acids that chemically weather rock • Acids are formed when plants and animals decay ...
... • Lichens that grow on rocks produce weak acids that chemically weather rock • Acids are formed when plants and animals decay ...
Week 11 – SEDIMENTARY ROCKS
... c. The type and size of the sediment controls the texture of the rock. ...
... c. The type and size of the sediment controls the texture of the rock. ...
Composition of Mars

The composition of Mars covers the branch of the geology of Mars that describes the make-up of the planet Mars.