Placental Transporters Relevant to Drug Distribution across the
... fetus is also of serious health concern. One of the pivotal functions of the placenta is to provide essential nutrients to the developing fetus from the mother, but it is generally assumed that the placental barrier protects the fetus by restricting the passage of harmful chemicals. Unfortunately, t ...
... fetus is also of serious health concern. One of the pivotal functions of the placenta is to provide essential nutrients to the developing fetus from the mother, but it is generally assumed that the placental barrier protects the fetus by restricting the passage of harmful chemicals. Unfortunately, t ...
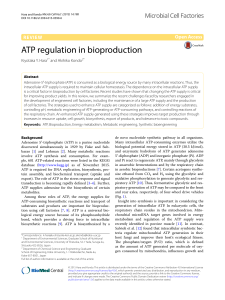
THE ATP SYNTHASE—A SPLENDID MOLECULAR MACHINE
... with subunits and stoichiometry designated as a, b2 , and c9−12 , with masses of about 30, 17, and 8 kDa, respectively. The stalk region is composed of subunits from both F1 and F0 . The F0 in higher organisms is considerably more complex. The enzyme from all sources has multiple copies of a subunit ...
... with subunits and stoichiometry designated as a, b2 , and c9−12 , with masses of about 30, 17, and 8 kDa, respectively. The stalk region is composed of subunits from both F1 and F0 . The F0 in higher organisms is considerably more complex. The enzyme from all sources has multiple copies of a subunit ...
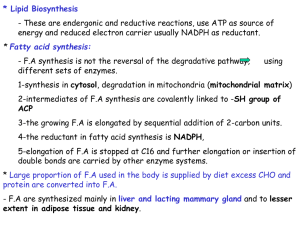
13synthesis
... Reducing power of NADH is converted into NADPH Oxaloacetate Malate Pyruvate - The other NADPH are produced pentose phosphate pathway ...
... Reducing power of NADH is converted into NADPH Oxaloacetate Malate Pyruvate - The other NADPH are produced pentose phosphate pathway ...
Disorders of mitochondrial function
... glucose enter the Krebs cycle at different sites, which are used therapeutically in some pre-Krebs cycle mitochondrial diseases [e.g. a high-fat, ketogenic diet in some cases of pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) deficiency]. For simplicity, amino acids are not shown; different amino acids enter the Krebs ...
... glucose enter the Krebs cycle at different sites, which are used therapeutically in some pre-Krebs cycle mitochondrial diseases [e.g. a high-fat, ketogenic diet in some cases of pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) deficiency]. For simplicity, amino acids are not shown; different amino acids enter the Krebs ...
6 PUFA - SENS Research Foundation
... myocardium of senescent rats vs young, due to the agerelated differences in total omega-6 PUFA. ...
... myocardium of senescent rats vs young, due to the agerelated differences in total omega-6 PUFA. ...
THE CITRIC ACID CYCLE
... electrons are transferred to O2—the final electron acceptor—via a chain of electron-carrying molecules known as the respiratory chain. In the course of electron transfer, the large amount of energy released is conserved in the form of ATP, by a process called oxidative phosphorylation (Chapter 19). ...
... electrons are transferred to O2—the final electron acceptor—via a chain of electron-carrying molecules known as the respiratory chain. In the course of electron transfer, the large amount of energy released is conserved in the form of ATP, by a process called oxidative phosphorylation (Chapter 19). ...
22. pyruvate oxidation and citric acid cycle
... cycle (TCA) was given to it some years after Krebs postulated the cycle because it was then not certain whether citric acid or some other tricarboxylic acid (e.g., isocitric acid) was first product of the cycle. Since we now know with certainty that citric acid is indeed the first tricarboxylic acid ...
... cycle (TCA) was given to it some years after Krebs postulated the cycle because it was then not certain whether citric acid or some other tricarboxylic acid (e.g., isocitric acid) was first product of the cycle. Since we now know with certainty that citric acid is indeed the first tricarboxylic acid ...
metabolism - Garland Science
... nitrogen only from organic compounds and thus are completely dependent on plants for their nutrition. Plants obtain the major elements that make up the plant body—carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen—mainly as carbon dioxide, water, and nitrate. They also take up and use many other minerals and el ...
... nitrogen only from organic compounds and thus are completely dependent on plants for their nutrition. Plants obtain the major elements that make up the plant body—carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen—mainly as carbon dioxide, water, and nitrate. They also take up and use many other minerals and el ...
Cu(II)–disulfide complexes display simultaneous superoxide
... [30]. Briefly, rat duodenal epithelium-isolated mitochondria were incubated for 30 min with DHE (10 μM). After incubation, mitochondria were centrifuged for 10 min (14,000 g, 4 °C) and resuspended in phosphate buffer (20 mM, pH 7.4) containing NADH (65 μM), coenzyme Q (32.5 μM), diclofenac (500 μM) a ...
... [30]. Briefly, rat duodenal epithelium-isolated mitochondria were incubated for 30 min with DHE (10 μM). After incubation, mitochondria were centrifuged for 10 min (14,000 g, 4 °C) and resuspended in phosphate buffer (20 mM, pH 7.4) containing NADH (65 μM), coenzyme Q (32.5 μM), diclofenac (500 μM) a ...
Thesis - HuVetA
... Based on the chemiosmotic coupling hypothesis, introduced by Nobel Prize winner Peter D. Mitchell and Moyle (1965), the electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation are coupled by a proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane. According to this, the free energy generated during ...
... Based on the chemiosmotic coupling hypothesis, introduced by Nobel Prize winner Peter D. Mitchell and Moyle (1965), the electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation are coupled by a proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane. According to this, the free energy generated during ...
Chapter 8: Energy generation:glycolysis
... proteins. Some enzyme cofactors are also activated carrier molecules. These include NAD+ and NADP+, each of which can carry energy in the form of a pair of electrons and a proton (H+ ion), converting the molecules into their reduced forms referred to as NADH and NADPH. The chemical equations for red ...
... proteins. Some enzyme cofactors are also activated carrier molecules. These include NAD+ and NADP+, each of which can carry energy in the form of a pair of electrons and a proton (H+ ion), converting the molecules into their reduced forms referred to as NADH and NADPH. The chemical equations for red ...
SODIUM-COUPLED TRANSPORTERS FOR KREBS CYCLE
... uptake at pH 5.5. This study is consistent with electrogenic transport of divalent citrate in pig intestine and supports a coupling stoichiometry of 3 Na+:1 divalent anion substrate (69). Interestingly, another study of succinate transport in pig intestine reported very low rates of sodium-coupled t ...
... uptake at pH 5.5. This study is consistent with electrogenic transport of divalent citrate in pig intestine and supports a coupling stoichiometry of 3 Na+:1 divalent anion substrate (69). Interestingly, another study of succinate transport in pig intestine reported very low rates of sodium-coupled t ...
Camp 1 - University of California, Santa Cruz
... recognize that glycolysis needs a continuing supply of NAD+. • If no oxygen is present to reoxidize NADH to NAD+, then another way must be found to reoxidize it. ...
... recognize that glycolysis needs a continuing supply of NAD+. • If no oxygen is present to reoxidize NADH to NAD+, then another way must be found to reoxidize it. ...
Electron transport chain
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of compounds that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions, and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons (H+ ions) across a membrane. This creates an electrochemical proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis, or the generation of chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The final acceptor of electrons in the electron transport chain is molecular oxygen.Electron transport chains are used for extracting energy via redox reactions from sunlight in photosynthesis or, such as in the case of the oxidation of sugars, cellular respiration. In eukaryotes, an important electron transport chain is found in the inner mitochondrial membrane where it serves as the site of oxidative phosphorylation through the use of ATP synthase. It is also found in the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast in photosynthetic eukaryotes. In bacteria, the electron transport chain is located in their cell membrane.In chloroplasts, light drives the conversion of water to oxygen and NADP+ to NADPH with transfer of H+ ions across chloroplast membranes. In mitochondria, it is the conversion of oxygen to water, NADH to NAD+ and succinate to fumarate that are required to generate the proton gradient. Electron transport chains are major sites of premature electron leakage to oxygen, generating superoxide and potentially resulting in increased oxidative stress.