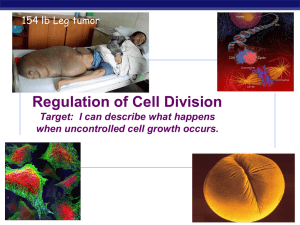
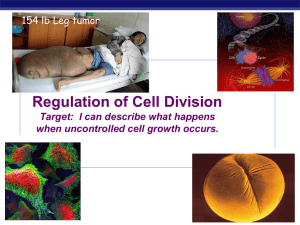
Cell Growth
... cell will have increasing difficulty moving oxygen and nutrients into the cell and moving waste products out as it increases in size. ...
... cell will have increasing difficulty moving oxygen and nutrients into the cell and moving waste products out as it increases in size. ...
PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT
... Cell Replacement Cells must divide in order for an organism to grow and develop, but cell division is also required for maintenance, cell turnover and replacement. ...
... Cell Replacement Cells must divide in order for an organism to grow and develop, but cell division is also required for maintenance, cell turnover and replacement. ...
Cells for 6th Graders - De Soto Area School District
... If cells can only get so large, how do organisms grow? Single-celled organisms divide into two new cells when they get too large. Multicellular organisms – as they grow, their cells must divide also. - each cell is a copy of the old cell - as new cells form, the organism grows larger - new cells may ...
... If cells can only get so large, how do organisms grow? Single-celled organisms divide into two new cells when they get too large. Multicellular organisms – as they grow, their cells must divide also. - each cell is a copy of the old cell - as new cells form, the organism grows larger - new cells may ...
review-cell-structur..
... Fill in the Blank Complete the statement with the best word. 20. A structure outside the plasma membrane in some cells is the ______________. 21. In a cell, the tangles of long strands of DNA form the ______________. 22. The folded system of membrane that forms a network of interconnected compartmen ...
... Fill in the Blank Complete the statement with the best word. 20. A structure outside the plasma membrane in some cells is the ______________. 21. In a cell, the tangles of long strands of DNA form the ______________. 22. The folded system of membrane that forms a network of interconnected compartmen ...
Chapter 7. The Cell: Basic Unit of Life
... Isolating organelles Cell fractionation separate organelles from cell variable density of organelles ...
... Isolating organelles Cell fractionation separate organelles from cell variable density of organelles ...
Organelles In Plant Cell
... -two primary functions: to control chemical reactions within the cytoplasm and to store information needed for cellular division. -Inside the nucleus is one or several nucleoli surrounded by a matrix called the nucleoplasm. The nucleoplasm is a liquid with a gel-like consistency (similar in this res ...
... -two primary functions: to control chemical reactions within the cytoplasm and to store information needed for cellular division. -Inside the nucleus is one or several nucleoli surrounded by a matrix called the nucleoplasm. The nucleoplasm is a liquid with a gel-like consistency (similar in this res ...
CELL PROCESSES
... substances through a cell membrane. • Endocytosis - the process in which a substance is taken into a cell by surrounding it with the _____, forming a sphere called a vesicle. • Exocytosis - the process in which the membrane of the vesicle fuses with the cell’s membrane and the vesicle’s contents are ...
... substances through a cell membrane. • Endocytosis - the process in which a substance is taken into a cell by surrounding it with the _____, forming a sphere called a vesicle. • Exocytosis - the process in which the membrane of the vesicle fuses with the cell’s membrane and the vesicle’s contents are ...
Viruses - MrKanesSciencePage
... Bacteriophage (aka phage) – virus that infects bacteria Reproduction – 2 methods o Lytic Cycle – virus enters cell, makes copies of itself, and causes cell to burst or lyse (“break open”) 1. Adsorption – virus attaches to a host cell 2. Entry – capsid contracts, injecting DNA into bacterial cell ...
... Bacteriophage (aka phage) – virus that infects bacteria Reproduction – 2 methods o Lytic Cycle – virus enters cell, makes copies of itself, and causes cell to burst or lyse (“break open”) 1. Adsorption – virus attaches to a host cell 2. Entry – capsid contracts, injecting DNA into bacterial cell ...
Volume 169 No. 3 March 1, 1989 T - The Journal of Experimental
... PREPARATION OF MANUSCRIPT Articles should conform to the style of a current issue of this journal or to the recommendations of the Council of Biology Editors Style Manual (5th edition, 1983, Council of Biology Editors, Inc., 9650 Rockville Pike, Bethesda, MD 20814) . Note that each reference should ...
... PREPARATION OF MANUSCRIPT Articles should conform to the style of a current issue of this journal or to the recommendations of the Council of Biology Editors Style Manual (5th edition, 1983, Council of Biology Editors, Inc., 9650 Rockville Pike, Bethesda, MD 20814) . Note that each reference should ...
SOLVING REAL WORLD PROBLEMS-
... Cell moves materials in opposite direction against the concentration gradient and needs energy (i.e. from an area of low concentration to an area of higher concentration) Some carrier proteins are involved in active transport and they act as ____________ that move substances against their concentrat ...
... Cell moves materials in opposite direction against the concentration gradient and needs energy (i.e. from an area of low concentration to an area of higher concentration) Some carrier proteins are involved in active transport and they act as ____________ that move substances against their concentrat ...
Cell Organelles 12-13
... Helps make membranes & other antibodies such as insulin Located close to the nucleus Internet resources (Biologyabout.com) ...
... Helps make membranes & other antibodies such as insulin Located close to the nucleus Internet resources (Biologyabout.com) ...
Cell project guidelines
... Menu You must use the menu appropriately. Choose one appetizer, one entree, and one dessert. You will lose points for not following directions. On time Projects must be turned in ON TIME! You will lose points if your project is late. All projects need to be in the science lab by the start of school ...
... Menu You must use the menu appropriately. Choose one appetizer, one entree, and one dessert. You will lose points for not following directions. On time Projects must be turned in ON TIME! You will lose points if your project is late. All projects need to be in the science lab by the start of school ...
... To Teacher: The students will decide on their own to implement the plans, along with the specific procedures for building the model. The students will then exchange procedures/plans with another group (two students maximum). Allow the students have total creativity for choosing the materials they wi ...
Notes – Chapter 5
... Notes – Cells I. Evolution of the current cell theory A. Anton von Leeuwenhoek invented the first Microscope in the 17th century. He used it to become the first person to observe and describe microscopic organisms and living cells. B. Robert Hooke used the microscope to describe the empty chambers o ...
... Notes – Cells I. Evolution of the current cell theory A. Anton von Leeuwenhoek invented the first Microscope in the 17th century. He used it to become the first person to observe and describe microscopic organisms and living cells. B. Robert Hooke used the microscope to describe the empty chambers o ...
HMH 3.1 Notes
... 1838: Schleiden was the first to note that plants are made of cells. 1839: Schwann concluded that all living things are made of cells. 1855: Virchow proposed that all cells come from other cells. ...
... 1838: Schleiden was the first to note that plants are made of cells. 1839: Schwann concluded that all living things are made of cells. 1855: Virchow proposed that all cells come from other cells. ...
File
... When a white blood cell engulfs and kills one of our own cells that have been infected by a virus, it prevents that virus from reproducing many other viruses within the normal cell and then spreading those reproduced viruses to other normal cells in our body after that one infected cell bursts. So e ...
... When a white blood cell engulfs and kills one of our own cells that have been infected by a virus, it prevents that virus from reproducing many other viruses within the normal cell and then spreading those reproduced viruses to other normal cells in our body after that one infected cell bursts. So e ...
1) A student investigated whether ants dig more tunnels in the light
... 5) Explain the proper way to evaluate someone’s work to assure it is accurately evaluated without bias? 6) Define the following terms: discuss 7) Control group: 8) Variable/experimental group: 9) Dependent variable: 10) Independent variable: 11) What is the difference between a hypothesis and a theo ...
... 5) Explain the proper way to evaluate someone’s work to assure it is accurately evaluated without bias? 6) Define the following terms: discuss 7) Control group: 8) Variable/experimental group: 9) Dependent variable: 10) Independent variable: 11) What is the difference between a hypothesis and a theo ...
Name
... part of a large brick wall. Each individual “brick” is one cell. The outer covering of the plant cell is the cell wall. The cell wall surrounds the cell membrane in a plant cell. It is stiff and rigid and provides support to the cell. 8. Note the small green organelles inside each cell. These are ch ...
... part of a large brick wall. Each individual “brick” is one cell. The outer covering of the plant cell is the cell wall. The cell wall surrounds the cell membrane in a plant cell. It is stiff and rigid and provides support to the cell. 8. Note the small green organelles inside each cell. These are ch ...
File
... 69. What kingdoms contain organisms that are capable of capturing and using energy from the Sun? _____________________________________________________________________________ 70. What kingdoms include organisms credited for breaking down dead plants and animals into rich soil? ______________________ ...
... 69. What kingdoms contain organisms that are capable of capturing and using energy from the Sun? _____________________________________________________________________________ 70. What kingdoms include organisms credited for breaking down dead plants and animals into rich soil? ______________________ ...
View PDF
... 18. Make a table to show what happens to plant and animal cells that are placed in the following types of solutions: hypotonic, isotonic, and hypertonic. ...
... 18. Make a table to show what happens to plant and animal cells that are placed in the following types of solutions: hypotonic, isotonic, and hypertonic. ...
Chapter 12. Regulation of the Cell Cycle
... forces cell into G0 resting stage keeps cell in G1 arrest causes apoptosis of damaged cell ...
... forces cell into G0 resting stage keeps cell in G1 arrest causes apoptosis of damaged cell ...
Chapter 12. Regulation of the Cell Cycle
... forces cell into G0 resting stage keeps cell in G1 arrest causes apoptosis of damaged cell ...
... forces cell into G0 resting stage keeps cell in G1 arrest causes apoptosis of damaged cell ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.