A) Structure and Function of the Cell Membrane B) Cellular Transport
... Molecules such as _______________________________________________________________________ cannot pass through the membrane easily because they are TOO ...
... Molecules such as _______________________________________________________________________ cannot pass through the membrane easily because they are TOO ...
GO ontology: accession~term GO definition # genes overlapping GO
... The attachment of a cell or organism to a substrate or other organism. Any of the various filamentous elements that form the internal framework of cells, and typically remain after treatment of the cells with mild detergent to remove membrane constituents and soluble components of the cytoplasm. The ...
... The attachment of a cell or organism to a substrate or other organism. Any of the various filamentous elements that form the internal framework of cells, and typically remain after treatment of the cells with mild detergent to remove membrane constituents and soluble components of the cytoplasm. The ...
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell CONTENT I. The Microscopic world of
... 2. Cell Junctions: structures that connect cells into tissues in different ways. 3. Cell channels: open channels found in plant cells to join the cytoplasm of neighboring cells. 4. Cell wall: found in plant cells and absent in animal cells; cellulose for protection, strength & shape. III. Nucleus & ...
... 2. Cell Junctions: structures that connect cells into tissues in different ways. 3. Cell channels: open channels found in plant cells to join the cytoplasm of neighboring cells. 4. Cell wall: found in plant cells and absent in animal cells; cellulose for protection, strength & shape. III. Nucleus & ...
Unit G Rev #2 - Mr. Lesiuk
... ___ 2. There are two different types of endocytosis; name them and explainwhat makes them different from one another. ___ 3. When an amoeba ingests a paramecium what type of endocytosis would that be? ___ 4. After a white blood cell uses Endocytosis (phagocytosis) to engulf a bacterial cell, what t ...
... ___ 2. There are two different types of endocytosis; name them and explainwhat makes them different from one another. ___ 3. When an amoeba ingests a paramecium what type of endocytosis would that be? ___ 4. After a white blood cell uses Endocytosis (phagocytosis) to engulf a bacterial cell, what t ...
Compartmentalization of the Cell
... The cell also contains other organelles that are not membranebound and have specific functions Ribosomes ...
... The cell also contains other organelles that are not membranebound and have specific functions Ribosomes ...
Eukaryotic Cells - Madison County Schools
... (mainly proteins) to different parts of the cell -synthesis of cell wall components - Proteins made by ribosomes go to Golgi to be folded! ...
... (mainly proteins) to different parts of the cell -synthesis of cell wall components - Proteins made by ribosomes go to Golgi to be folded! ...
Document
... Plant cells have an additional layer surrounding them called the cell wall. The cell wall is made of nonliving material called cellulose. Color and label the cell wall brown. The centrosome (also called the "microtubule organizing center") is a small body located near the nucleus. The centrosome is ...
... Plant cells have an additional layer surrounding them called the cell wall. The cell wall is made of nonliving material called cellulose. Color and label the cell wall brown. The centrosome (also called the "microtubule organizing center") is a small body located near the nucleus. The centrosome is ...
Make protein for the cell.
... between cell and within cell. Breaks down some medicines. Makes lipids (fat). Packages proteins for release from the cell. Rough E.R. has ribosomes on it. Smooth E.R. does not have ribosomes on it. **Provides a system of transport from the nucleus to the cell.** ...
... between cell and within cell. Breaks down some medicines. Makes lipids (fat). Packages proteins for release from the cell. Rough E.R. has ribosomes on it. Smooth E.R. does not have ribosomes on it. **Provides a system of transport from the nucleus to the cell.** ...
Introduction to Stem Cells
... Embryonic stem cells • Pluripotent: pluri = many potent = capacity • At blastocyst stage cells become pluripotent. • Have the capacity to become all cell types but not placenta. • Cells of most interest to research scientists. ...
... Embryonic stem cells • Pluripotent: pluri = many potent = capacity • At blastocyst stage cells become pluripotent. • Have the capacity to become all cell types but not placenta. • Cells of most interest to research scientists. ...
Unit I File
... 3. Glycocalyx = protein and carbohydrate coat covering the extracellular surface of the plasma membrane a. Allows attachment to other cells b. Allows the cell to interact with the environment c. Gives each person’s cell a distinctive surface; allows your body to recognize foreign tissues as differen ...
... 3. Glycocalyx = protein and carbohydrate coat covering the extracellular surface of the plasma membrane a. Allows attachment to other cells b. Allows the cell to interact with the environment c. Gives each person’s cell a distinctive surface; allows your body to recognize foreign tissues as differen ...
Ch. 8 Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance (updated)
... chromosomes, resulting in two copies called sister chromatids joined by a centromere. When a cell divides, sister chromatids separate from each other, (now called chromosomes) and sort into separate daughter cells. ...
... chromosomes, resulting in two copies called sister chromatids joined by a centromere. When a cell divides, sister chromatids separate from each other, (now called chromosomes) and sort into separate daughter cells. ...
Unit 2
... 3. Describe how chromosome number changes throughout the human life cycle. DNA is partitioned among chromosomes, making it easier for the eukaryotic cell to replicate and distribute its huge amounts of DNA. As the cell prepares to divide, it duplicates each of its multiple chromosomes. A duplicated ...
... 3. Describe how chromosome number changes throughout the human life cycle. DNA is partitioned among chromosomes, making it easier for the eukaryotic cell to replicate and distribute its huge amounts of DNA. As the cell prepares to divide, it duplicates each of its multiple chromosomes. A duplicated ...
Cholera as a prokaryote1.61 MB
... • Bacteria belong to a large group of organisms called prokaryotes which lack a nucleus. • All organisms that have a well defined membrane - bound nucleus are called eukaryotes e.g. animals, plants, fungi and some single-celled organisms. ...
... • Bacteria belong to a large group of organisms called prokaryotes which lack a nucleus. • All organisms that have a well defined membrane - bound nucleus are called eukaryotes e.g. animals, plants, fungi and some single-celled organisms. ...
Cells Study Guide
... - cell wall: provides structure in plant cells - chloroplast: traps light to make glucose for plant - cytoskeleton: support and give cell its shape - centrosome: makes microtubules and contains centriole - flagella: tail that helps cell move - cilia: hairs around cell that help it move 9. distinguis ...
... - cell wall: provides structure in plant cells - chloroplast: traps light to make glucose for plant - cytoskeleton: support and give cell its shape - centrosome: makes microtubules and contains centriole - flagella: tail that helps cell move - cilia: hairs around cell that help it move 9. distinguis ...
Organelle Functions WS
... Which organelle has malfunctioned? Use the word bank to match to the malfunction. Terms may be repeated. Organelle ...
... Which organelle has malfunctioned? Use the word bank to match to the malfunction. Terms may be repeated. Organelle ...
2. Internal and external cues help regulate the cell cycle
... • The timing and rates of cell division in different parts of an animal or plant are crucial for normal growth, development, and maintenance. • The frequency of cell division varies with cell type. • Some human cells divide frequently throughout life (skin cells), others have the ability to divide, ...
... • The timing and rates of cell division in different parts of an animal or plant are crucial for normal growth, development, and maintenance. • The frequency of cell division varies with cell type. • Some human cells divide frequently throughout life (skin cells), others have the ability to divide, ...
Characteristics of Life
... Characteristics of Living Things • Must include ALL eight of the following in order to be considered. ...
... Characteristics of Living Things • Must include ALL eight of the following in order to be considered. ...
7th Grade Life Science: Activity Outline
... proteins and can also be found floating elsewhere in the cytoplasm. The golgi apparatus receives materials from the ER and packages them for transport to other parts of the cell. The “powerhouses” of the cell are the mitochondria, which convert food energy to usable energy. Water, food, and other ma ...
... proteins and can also be found floating elsewhere in the cytoplasm. The golgi apparatus receives materials from the ER and packages them for transport to other parts of the cell. The “powerhouses” of the cell are the mitochondria, which convert food energy to usable energy. Water, food, and other ma ...
Classification - De Anza College
... Endosymbiotic Theory • Eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes • Supported by similarities between prokaryotes & organelles in eukaryotes • Mitochondria & chloroplasts same size as prokaryote cell – Contain DNA, 70S ribosomes ...
... Endosymbiotic Theory • Eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes • Supported by similarities between prokaryotes & organelles in eukaryotes • Mitochondria & chloroplasts same size as prokaryote cell – Contain DNA, 70S ribosomes ...
3.5.3 - OpenStudy
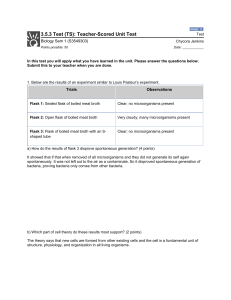
... a) How do the results of flask 3 disprove spontaneous generation? (4 points) It showed that if that when removed of all microorganisms and they did not generate its self again spontaneously. It was not left out to the air as a contaminate. So it disproved spontaneous generation of bacteria, proving ...
... a) How do the results of flask 3 disprove spontaneous generation? (4 points) It showed that if that when removed of all microorganisms and they did not generate its self again spontaneously. It was not left out to the air as a contaminate. So it disproved spontaneous generation of bacteria, proving ...
Procaryotic and Eucaryotic cell
... Nuclear region is primitive in procaryotic cell, i.e. bacteria. Procaryotic cells DO NOT possess a true nucleus. The functions of the nucleus are carried out by a single long strand of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) The nuclear region where the DNA is present is sometimes known as a nucleoid, NOT a nuc ...
... Nuclear region is primitive in procaryotic cell, i.e. bacteria. Procaryotic cells DO NOT possess a true nucleus. The functions of the nucleus are carried out by a single long strand of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) The nuclear region where the DNA is present is sometimes known as a nucleoid, NOT a nuc ...
CH 3 Part 2 - Catherine Huff`s Site
... • May be rough or smooth depending on if it contains ribosomes or not. • Rough ER is involved in production of protein assembled by ribosomes • New Proteins are moved inside ER into passageways. • Cisternae -Location of protein modification before being moved to Golgi. • Smooth ER is connected to Ro ...
... • May be rough or smooth depending on if it contains ribosomes or not. • Rough ER is involved in production of protein assembled by ribosomes • New Proteins are moved inside ER into passageways. • Cisternae -Location of protein modification before being moved to Golgi. • Smooth ER is connected to Ro ...
Bio 1 Unit 2
... Objective 2.12: I can relate the function of a cell to its organization in tissues, organs, and organ systems. Which of the following best describes the sequence of organization in a frog’s body from simplest to most complex? a. Cells → tissues → organs → organ systems b. Organs → organ systems → or ...
... Objective 2.12: I can relate the function of a cell to its organization in tissues, organs, and organ systems. Which of the following best describes the sequence of organization in a frog’s body from simplest to most complex? a. Cells → tissues → organs → organ systems b. Organs → organ systems → or ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.