Chapter 12. Regulation of the Cell Cycle
... forces cell into G0 resting stage keeps cell in G1 arrest causes apoptosis of damaged cell ...
... forces cell into G0 resting stage keeps cell in G1 arrest causes apoptosis of damaged cell ...
Chapter 12. Regulation of the Cell Cycle
... forces cell into G0 resting stage keeps cell in G1 arrest causes apoptosis of damaged cell ...
... forces cell into G0 resting stage keeps cell in G1 arrest causes apoptosis of damaged cell ...
CHAPTER 6 LEARNING OBJECTIVES
... 4. Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 5. Explain why there are limits to cell size. 6. Explain the advantages of compartmentalization in eukaryotic cells. The Nucleus and Ribosomes 7. Describe the structure and function of the nuclear envelope, including the role of the pore compl ...
... 4. Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 5. Explain why there are limits to cell size. 6. Explain the advantages of compartmentalization in eukaryotic cells. The Nucleus and Ribosomes 7. Describe the structure and function of the nuclear envelope, including the role of the pore compl ...
Slide 1 Cells are the fundamental structural units of life
... Cell Theory states that every living organism is composed of cells, that the cell is the basic unit of life, and that cells arise only from pre-existing cells. A cell is usually a microscopic structure containing nuclear and cytoplasmic material enclosed by a semi-permeable membrane and, in some ins ...
... Cell Theory states that every living organism is composed of cells, that the cell is the basic unit of life, and that cells arise only from pre-existing cells. A cell is usually a microscopic structure containing nuclear and cytoplasmic material enclosed by a semi-permeable membrane and, in some ins ...
Cells
... separates the chromosomes in its cell nucleus into two identical sets, in two separate nuclei. It is generally followed immediately by cytokinesis, which divides the nuclei, cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis a ...
... separates the chromosomes in its cell nucleus into two identical sets, in two separate nuclei. It is generally followed immediately by cytokinesis, which divides the nuclei, cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis a ...
Modern cell theory
... surface of the cell which separates the cell from the environment. The cytoplasm is the aqueous content within the plasma membrane. Plasma membrane : It is like any other membrane in the cell but it plays a very important function. It forms the border of a cell, so it is also called the cell membra ...
... surface of the cell which separates the cell from the environment. The cytoplasm is the aqueous content within the plasma membrane. Plasma membrane : It is like any other membrane in the cell but it plays a very important function. It forms the border of a cell, so it is also called the cell membra ...
Cell biology
... ● Multicellular organisms have properties that emerge from the interaction of their cellular ...
... ● Multicellular organisms have properties that emerge from the interaction of their cellular ...
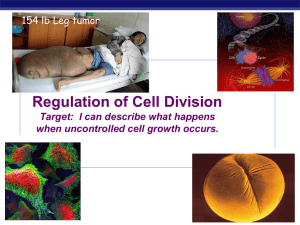
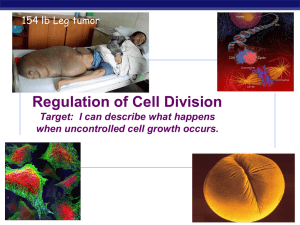
Mitotic Division in Cancer Cells
... in cancer cells is altered. You may have heard of cancer cells being “runaway” which have no controls on their rate of reproduction. It is this characteristic that allows some cancer cells to grow and spread quite rapidly. OBJECTIVE: Analyze data to determine the differences in timing of mitosis bet ...
... in cancer cells is altered. You may have heard of cancer cells being “runaway” which have no controls on their rate of reproduction. It is this characteristic that allows some cancer cells to grow and spread quite rapidly. OBJECTIVE: Analyze data to determine the differences in timing of mitosis bet ...
Lifecycle for planting cell-celebration churches
... As the private worship gatherings increase in frequency, believers will be mobilized for ministry to prepare for public celebrations. Identifying and training coaches will be a primary task in this phase. ...
... As the private worship gatherings increase in frequency, believers will be mobilized for ministry to prepare for public celebrations. Identifying and training coaches will be a primary task in this phase. ...
Cells
... c. Anaphase: i. chromatids are pulled apart at the centromere and are pulled toward the poles by the spindle fibers ii. complete when chromosomes reach the poles d. Telophase: i. Essentially prophase in reverse ii. chromosomes uncoil and become chromatin again iii. spindle breaks down and nuclear me ...
... c. Anaphase: i. chromatids are pulled apart at the centromere and are pulled toward the poles by the spindle fibers ii. complete when chromosomes reach the poles d. Telophase: i. Essentially prophase in reverse ii. chromosomes uncoil and become chromatin again iii. spindle breaks down and nuclear me ...
Recitation 1 Solutions
... Classify each of the above organisms as unicellular or multi-cellular. Bacterial and yeast cells are unicellular whereas flies, mice and rabbits are multi-cellular. 2. You are given three different cell types, each stained with a dye that specifically binds to deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). You observ ...
... Classify each of the above organisms as unicellular or multi-cellular. Bacterial and yeast cells are unicellular whereas flies, mice and rabbits are multi-cellular. 2. You are given three different cell types, each stained with a dye that specifically binds to deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). You observ ...
Standard B-2
... ○ All living things are composed of one or more cells. ○ Cells are the basic unit of structure of all living things. ○ All presently existing cells arose from previously existing cells. Know the following organelles and their functions: ○ Nucleus contains DNA; functions in the genetic control of t ...
... ○ All living things are composed of one or more cells. ○ Cells are the basic unit of structure of all living things. ○ All presently existing cells arose from previously existing cells. Know the following organelles and their functions: ○ Nucleus contains DNA; functions in the genetic control of t ...
Optical methods for studying cell mechanics
... initiation and propagation of electromechanical signals within single neurons. Brightfield optical imaging approach has been applied to the mechanical wave visualization that associated with action potential in the fourth application. Neuron-to-neuron viability of membrane displacement was revealed ...
... initiation and propagation of electromechanical signals within single neurons. Brightfield optical imaging approach has been applied to the mechanical wave visualization that associated with action potential in the fourth application. Neuron-to-neuron viability of membrane displacement was revealed ...
I. The Cell Cycle
... offspring from a single parent using mitosis. The offspring are therefore genetically identical to each other and to their “parent”- in other words they are clones. Asexual reproduction is very common in nature, and in addition we humans have developed some new, artificial methods. The Latin terms i ...
... offspring from a single parent using mitosis. The offspring are therefore genetically identical to each other and to their “parent”- in other words they are clones. Asexual reproduction is very common in nature, and in addition we humans have developed some new, artificial methods. The Latin terms i ...
投影片 1
... dangerous cells from an organism without damaging surrounding cells and tissues Necessary for normal embryogenesis Maintenance of tissue homeostasis ...
... dangerous cells from an organism without damaging surrounding cells and tissues Necessary for normal embryogenesis Maintenance of tissue homeostasis ...
origin of life - UniMAP Portal
... right temperature, ion composition, and pH. They absorb and incorporate various substances from the surrounding solution. A protocell could have contained only RNA to function as both genetic material and enzymes. First protocells were heterotrophs using ATP as energy and carrying out a form of ferm ...
... right temperature, ion composition, and pH. They absorb and incorporate various substances from the surrounding solution. A protocell could have contained only RNA to function as both genetic material and enzymes. First protocells were heterotrophs using ATP as energy and carrying out a form of ferm ...
OP 08 Can we make new beta cells? 43 Differentiation of functional
... of human, gene editable and functional islet cells to improve through-put and translability. We aimed to establish a differentiation protocol to allow induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS) to differentiate to mature beta-cells in vitro in an industrial setting suitable for use in screening for novel ...
... of human, gene editable and functional islet cells to improve through-put and translability. We aimed to establish a differentiation protocol to allow induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS) to differentiate to mature beta-cells in vitro in an industrial setting suitable for use in screening for novel ...
Meiosis - WordPress.com
... Humans: 46 chromosomes, 23 pairs • Each of the 23 pairs is called a homologous pair: a similar pair where one came from the mother and one came from the father. ...
... Humans: 46 chromosomes, 23 pairs • Each of the 23 pairs is called a homologous pair: a similar pair where one came from the mother and one came from the father. ...
Plant Cells
... Recent evidence suggests that the cytoskeleton may help regulate biochemical activities ATP ...
... Recent evidence suggests that the cytoskeleton may help regulate biochemical activities ATP ...
Cells and Their Organelles
... rough appearance. Color and label the rough ER violet (another shade of purple). Rough ER transports materials through the cell and produces proteins in sacks called cistern which are sent to the Golgi body, or inserted into the cell membrane. The Golgi apparatus or Golgi complex is a flattened, lay ...
... rough appearance. Color and label the rough ER violet (another shade of purple). Rough ER transports materials through the cell and produces proteins in sacks called cistern which are sent to the Golgi body, or inserted into the cell membrane. The Golgi apparatus or Golgi complex is a flattened, lay ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.