Life Processes - DronStudy.com
... • On the other hand, when guard cells lose water, they shrink, become straight and close the stomatal pores. How the plants obtain water for photosynthesis? • The water required by the plants for photosynthesis is absorbed by the root of the plants from the soil through the process of osmosis. • Th ...
... • On the other hand, when guard cells lose water, they shrink, become straight and close the stomatal pores. How the plants obtain water for photosynthesis? • The water required by the plants for photosynthesis is absorbed by the root of the plants from the soil through the process of osmosis. • Th ...
CHAPTER 15
... (1) In the IUPAC nomenclature system, an aldehyde group has priority over a ketone group. (2) Addition of an alcohol molecule across the carbon-oxygen double bond of an aldehyde produces a compound in which the carbonyl carbon atom bears both an alkoxy group and a hydroxy group. (3) 2-Propenal conta ...
... (1) In the IUPAC nomenclature system, an aldehyde group has priority over a ketone group. (2) Addition of an alcohol molecule across the carbon-oxygen double bond of an aldehyde produces a compound in which the carbonyl carbon atom bears both an alkoxy group and a hydroxy group. (3) 2-Propenal conta ...
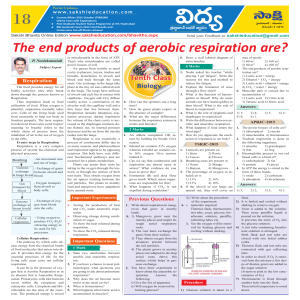
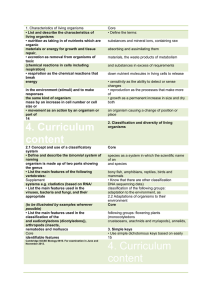
1. Characteristics of living organisms Core • List and describe the
... • Describe the role of enzymes in the biological washing products and in the food • Outline the use of microorganisms and penicillin and enzymes for use in biological • Describe the role of the fungus Penicillium in 6. Nutrition • Define nutrition as taking in of nutrients ions, containing raw mater ...
... • Describe the role of enzymes in the biological washing products and in the food • Outline the use of microorganisms and penicillin and enzymes for use in biological • Describe the role of the fungus Penicillium in 6. Nutrition • Define nutrition as taking in of nutrients ions, containing raw mater ...
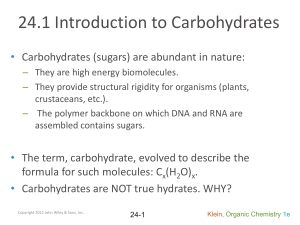
24.1 Introduction to Carbohydrates
... – The polymer backbone on which DNA and RNA are assembled contains sugars. ...
... – The polymer backbone on which DNA and RNA are assembled contains sugars. ...
Foundation Tier, Unit 1
... (b) Many newborn babies are fed breast milk by their mothers for the first few months after birth. The breast milk contains antibodies. ...
... (b) Many newborn babies are fed breast milk by their mothers for the first few months after birth. The breast milk contains antibodies. ...
ch13[1].
... in the pure state by dipole-dipole interactions. • They have higher boiling points and are more soluble in water than nonpolar compounds of comparable molecular weight. ...
... in the pure state by dipole-dipole interactions. • They have higher boiling points and are more soluble in water than nonpolar compounds of comparable molecular weight. ...
The end products of aerobic respiration are?
... Respiration includes inhalation, expiration processes during inspiration the volume of the chest cavity is increased as the diaphragm contracts dome flattens out, its internal pressure decreases and the air from the outside rushes into the lungs. Respiration is not essentially a process of combustio ...
... Respiration includes inhalation, expiration processes during inspiration the volume of the chest cavity is increased as the diaphragm contracts dome flattens out, its internal pressure decreases and the air from the outside rushes into the lungs. Respiration is not essentially a process of combustio ...
C-OH
... acids contain a carboxyl group … . -COOH It’s a combination of a carbonyl (C=O) and a hydroxyl (-OH) group ...
... acids contain a carboxyl group … . -COOH It’s a combination of a carbonyl (C=O) and a hydroxyl (-OH) group ...
Organic Chemistry - Coastal Bend College
... Organic Chemistry: Carbohydrates Monosaccharides (MS) Mono 1 Saccharide Sugar • MS’s usually have from 3 to 6 C’s in their make-up. Those w/6 are the most essential to humans – These include: – Glucose – Fructose – Galactose • These are isomers of each other AP1: Ch. 2: Chemical Basis of Life ...
... Organic Chemistry: Carbohydrates Monosaccharides (MS) Mono 1 Saccharide Sugar • MS’s usually have from 3 to 6 C’s in their make-up. Those w/6 are the most essential to humans – These include: – Glucose – Fructose – Galactose • These are isomers of each other AP1: Ch. 2: Chemical Basis of Life ...
PDHPE Student Activity Sheet (1.1 MB)
... the body’s physiological responses to exercise and consider why these changes occur. You will have the opportunity to participate in a number of tests, including vertical jump performance, maximal aerobic uptake (VO2max), and maximal power. Each of these tests has been included to assist you in your ...
... the body’s physiological responses to exercise and consider why these changes occur. You will have the opportunity to participate in a number of tests, including vertical jump performance, maximal aerobic uptake (VO2max), and maximal power. Each of these tests has been included to assist you in your ...
The Chemical Level of Organization
... Disaccharides Formed from two simple sugars through condensation (dehydration) Sucrose, lactose, maltose Can be broken down to form simple sugars Hydrolysis rxn ...
... Disaccharides Formed from two simple sugars through condensation (dehydration) Sucrose, lactose, maltose Can be broken down to form simple sugars Hydrolysis rxn ...
Chapter 10: Chemistry of Living Systems
... a polar molecule. A polar molecule is a molecule that has a positive end and a negative end because of unequal sharing of electrons. A nonpolar molecule is a molecule that shares electrons equally and does not have oppositely charged ends. Figure 5 shows the molecular structure of a water molecule. ...
... a polar molecule. A polar molecule is a molecule that has a positive end and a negative end because of unequal sharing of electrons. A nonpolar molecule is a molecule that shares electrons equally and does not have oppositely charged ends. Figure 5 shows the molecular structure of a water molecule. ...
Naming Aldehydes & Ketones
... IUPAC Rules for Naming Ketones 3. If the chain is longer than four carbons, it is numbered so that the carbonyl group has the smallest number possible; this number is prefixed to the parent name of the ketone. 4. Other groups attached to the parent chain are named and numbered as we have done befor ...
... IUPAC Rules for Naming Ketones 3. If the chain is longer than four carbons, it is numbered so that the carbonyl group has the smallest number possible; this number is prefixed to the parent name of the ketone. 4. Other groups attached to the parent chain are named and numbered as we have done befor ...
Herbs - NaturesTools
... Dandelion anemia, liver, age spots, blood cleanser, endurance, hypoglycemia Devil’s Claw deep muscle & tissue cleanser, relieves disease & aching in the body Dong Quai hot flashes, hormone balance, nervousness, brain nourishment Echinacea Purpurea antibiotic, infections, blood purifier/builder, lymp ...
... Dandelion anemia, liver, age spots, blood cleanser, endurance, hypoglycemia Devil’s Claw deep muscle & tissue cleanser, relieves disease & aching in the body Dong Quai hot flashes, hormone balance, nervousness, brain nourishment Echinacea Purpurea antibiotic, infections, blood purifier/builder, lymp ...
www.theallpapers.com
... 40 The levels of carbon dioxide in the Earth’s atmosphere have increased during the last one hundred years. What is the most likely cause of this? A ...
... 40 The levels of carbon dioxide in the Earth’s atmosphere have increased during the last one hundred years. What is the most likely cause of this? A ...
Nutrition
... Individuals should consume 5 servings of fruits and vegetables and 6 servings of grain, cereal, pasta, rice daily. Fiber intake should be 20-35 grams daily. Digestion and Metabolism of COH all, except for fiber; COH is broken down into monosaccharides then absorbed - converted to glucose, glucose ar ...
... Individuals should consume 5 servings of fruits and vegetables and 6 servings of grain, cereal, pasta, rice daily. Fiber intake should be 20-35 grams daily. Digestion and Metabolism of COH all, except for fiber; COH is broken down into monosaccharides then absorbed - converted to glucose, glucose ar ...
respiration - Learn Biology
... Anaerobic = without oxygen (O2) Sometimes we need to produce energy very quickly – i.e. explosive activities like sprinting. So, anaerobic respiration takes place when there isn’t enough oxygen (O2) available to supply the body (e.g. muscles) with the O2 required for ‘normal’ aerobic respiration. ...
... Anaerobic = without oxygen (O2) Sometimes we need to produce energy very quickly – i.e. explosive activities like sprinting. So, anaerobic respiration takes place when there isn’t enough oxygen (O2) available to supply the body (e.g. muscles) with the O2 required for ‘normal’ aerobic respiration. ...
Ex ploring the Hu an Body - The Canadian Sugar Institute
... environment is safe or not. Taste, for example, can help you detect if a food is fresh and good to eat or spoiled and dangerous to your health. We inherited a natural liking for foods rich in carbohydrates (starches and sugars) from our ancestors. Early humans relied on their taste buds as important ...
... environment is safe or not. Taste, for example, can help you detect if a food is fresh and good to eat or spoiled and dangerous to your health. We inherited a natural liking for foods rich in carbohydrates (starches and sugars) from our ancestors. Early humans relied on their taste buds as important ...
Chapter Sixteen Aldehydes and Ketones
... ► Aldehydes and ketones establish equilibria with alcohols to form hemiacetals or acetals. ► Hemiacetals, which have an -OH and an -OR on what was the carbonyl carbon, result from addition of one alcohol molecule to the C=O bond. ► The more stable acetals, which have two -OR groups on what was the c ...
... ► Aldehydes and ketones establish equilibria with alcohols to form hemiacetals or acetals. ► Hemiacetals, which have an -OH and an -OR on what was the carbonyl carbon, result from addition of one alcohol molecule to the C=O bond. ► The more stable acetals, which have two -OR groups on what was the c ...
small intestine
... Obesity and Evolution • The problem of maintaining weight partly stems from our evolutionary past, when fat hoarding was a means of survival • A species of birds called petrels become obese as chicks; in order to consume enough protein from high-fat food, chicks need to consume more calories than t ...
... Obesity and Evolution • The problem of maintaining weight partly stems from our evolutionary past, when fat hoarding was a means of survival • A species of birds called petrels become obese as chicks; in order to consume enough protein from high-fat food, chicks need to consume more calories than t ...
1 - AQA
... eat a balanced diet. But what does this mean, and why is it important? Nutrients are important substances that your body needs to survive and stay healthy. There are different types of nutrients. We get most of them from food. The types of nutrient are: 1 carbohydrates, which provide energy 2 lipids ...
... eat a balanced diet. But what does this mean, and why is it important? Nutrients are important substances that your body needs to survive and stay healthy. There are different types of nutrients. We get most of them from food. The types of nutrient are: 1 carbohydrates, which provide energy 2 lipids ...
MEMBRANOGENESIS AND PLACENTAL FUNCTION LEARNING OUTCOMES
... (c) Epitheliochorial placentas have poor rates of diffusion of fatty acids and neonates (eg calf and piglet) have little body fat compared to the haemochorial model (human) 3. TAG deposits in both white and brown adipose tissue. Brown fat essential for thermogenesis in neonate 4. Crucial here are th ...
... (c) Epitheliochorial placentas have poor rates of diffusion of fatty acids and neonates (eg calf and piglet) have little body fat compared to the haemochorial model (human) 3. TAG deposits in both white and brown adipose tissue. Brown fat essential for thermogenesis in neonate 4. Crucial here are th ...
small intestine
... Food Intake Ingestion: the act of eating • Suspension feeders - many aquatic animals, which sift small food particles from the water • Substrate feeders are animals that live in or on their food source • Fluid feeders suck nutrient-rich fluid from a living ...
... Food Intake Ingestion: the act of eating • Suspension feeders - many aquatic animals, which sift small food particles from the water • Substrate feeders are animals that live in or on their food source • Fluid feeders suck nutrient-rich fluid from a living ...
10 - Animal Nutrition & Digestion Sum13
... A diet missing a certain essential part or not enough calories overall leads to malnourishment or undernourishment ...
... A diet missing a certain essential part or not enough calories overall leads to malnourishment or undernourishment ...
Carbohydrate
A carbohydrate is a biological molecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen:oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water); in other words, with the empirical formula Cm(H2O)n (where m could be different from n). Some exceptions exist; for example, deoxyribose, a sugar component of DNA, has the empirical formula C5H10O4. Carbohydrates are technically hydrates of carbon; structurally it is more accurate to view them as polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones.The term is most common in biochemistry, where it is a synonym of saccharide, a group that includes sugars, starch, and cellulose. The saccharides are divided into four chemical groups: monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. In general, the monosaccharides and disaccharides, which are smaller (lower molecular weight) carbohydrates, are commonly referred to as sugars. The word saccharide comes from the Greek word σάκχαρον (sákkharon), meaning ""sugar."" While the scientific nomenclature of carbohydrates is complex, the names of the monosaccharides and disaccharides very often end in the suffix -ose. For example, grape sugar is the monosaccharide glucose, cane sugar is the disaccharide sucrose and milk sugar is the disaccharide lactose (see illustration).Carbohydrates perform numerous roles in living organisms. Polysaccharides serve for the storage of energy (e.g., starch and glycogen) and as structural components (e.g., cellulose in plants and chitin in arthropods). The 5-carbon monosaccharide ribose is an important component of coenzymes (e.g., ATP, FAD and NAD) and the backbone of the genetic molecule known as RNA. The related deoxyribose is a component of DNA. Saccharides and their derivatives include many other important biomolecules that play key roles in the immune system, fertilization, preventing pathogenesis, blood clotting, and development.In food science and in many informal contexts, the term carbohydrate often means any food that is particularly rich in the complex carbohydrate starch (such as cereals, bread and pasta) or simple carbohydrates, such as sugar (found in candy, jams, and desserts).

![ch13[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008194698_1-d188c504eac7b7806e762a2340484910-300x300.png)