B 4: Photosynthesis
... that magnesium ions are needed for chlorophyll and nitrate ions are needed for amino acids ...
... that magnesium ions are needed for chlorophyll and nitrate ions are needed for amino acids ...
Chapter 2 Notes (Sections 1-4)
... substances. The surface of water in a graduated cylinder dips slightly in the center, forming a curve called a meniscus, because the adhesion between water molecules and glass molecules is stronger than the cohesion between water molecules. ...
... substances. The surface of water in a graduated cylinder dips slightly in the center, forming a curve called a meniscus, because the adhesion between water molecules and glass molecules is stronger than the cohesion between water molecules. ...
Health -- Primary Causes of Failing
... products, chemicals, food additives, preservatives, pesticides, and heavy metals, all of which are toxic and very damaging to health. In fact the accumulation of toxins from foods, water, and the environment in our blood is killing us! Blood and xenobiotic compounds Chemical compounds that are found ...
... products, chemicals, food additives, preservatives, pesticides, and heavy metals, all of which are toxic and very damaging to health. In fact the accumulation of toxins from foods, water, and the environment in our blood is killing us! Blood and xenobiotic compounds Chemical compounds that are found ...
3 The Excretory System
... How Does Filtering a Liquid Change the Liquid? 1. Your teacher will give you 50 mL of a liquid in a small container. Pour a small amount of sand into the liquid. 2. Use a glucose test strip to determine whether glucose is present in the liquid. 3. Put filter paper in a funnel. Then, put the funnel in ...
... How Does Filtering a Liquid Change the Liquid? 1. Your teacher will give you 50 mL of a liquid in a small container. Pour a small amount of sand into the liquid. 2. Use a glucose test strip to determine whether glucose is present in the liquid. 3. Put filter paper in a funnel. Then, put the funnel in ...
Honors Chapter 1 and 2 learning objectives
... 18. Describe patterns observed in data, and whether any observed trends are positive or weak 19. Develop/discuss alternative explanations for patterns in data; decide which most likely fits the data/evidence. ...
... 18. Describe patterns observed in data, and whether any observed trends are positive or weak 19. Develop/discuss alternative explanations for patterns in data; decide which most likely fits the data/evidence. ...
No Slide Title
... The contraction and relaxation of these muscles can affect the blood flow through the vessel. E.g. if the muscle runs in a circular direction around the vessel, when it contracts, it could constrict the ...
... The contraction and relaxation of these muscles can affect the blood flow through the vessel. E.g. if the muscle runs in a circular direction around the vessel, when it contracts, it could constrict the ...
Chemical Family Ketones
... Chemical Family: Ketones Ketones Ketones has an oxygen atom double bonded to a carbon atom, but always on a carbon atom that is bonded to two other carbon atoms. They are derived from secondary alcohols. Ketones with closed rings have a typical minty-camphoraceous aroma (from the menthone, camphor, ...
... Chemical Family: Ketones Ketones Ketones has an oxygen atom double bonded to a carbon atom, but always on a carbon atom that is bonded to two other carbon atoms. They are derived from secondary alcohols. Ketones with closed rings have a typical minty-camphoraceous aroma (from the menthone, camphor, ...
Glucose Regulation in Diabetes
... In a diabetic system, liver uptake and peripheral utilization of glucose is less sensitive to insulin (approximately one-half the normal state). To simulate the reduced sensitivity of liver uptake of glucose to insulin, we replace F2 with a constant. Likewise, to simulate the reduced sensitivity of ...
... In a diabetic system, liver uptake and peripheral utilization of glucose is less sensitive to insulin (approximately one-half the normal state). To simulate the reduced sensitivity of liver uptake of glucose to insulin, we replace F2 with a constant. Likewise, to simulate the reduced sensitivity of ...
FREE Sample Here
... Full file at http://emailtestbank.com/ Test-Bank-for-Human-Biology-12th-Edition--by-Mader ...
... Full file at http://emailtestbank.com/ Test-Bank-for-Human-Biology-12th-Edition--by-Mader ...
FREE Sample Here
... Full file at http://testbank360.eu/test-bank-human-biology-12th-edition-mader ...
... Full file at http://testbank360.eu/test-bank-human-biology-12th-edition-mader ...
FREE Sample Here
... Full file at http://testbankwizard.eu/Test-Bank-for-Human-Biology-12th-Edition-by-Mader ...
... Full file at http://testbankwizard.eu/Test-Bank-for-Human-Biology-12th-Edition-by-Mader ...
Biochemistry - MCQ topic quiz - Lesson element
... 15 Which monosaccharide is shown in the diagram below? ...
... 15 Which monosaccharide is shown in the diagram below? ...
Metabolism and Energy Balance
... – Making of glycogen – Making of triglycerides – Making of protein ...
... – Making of glycogen – Making of triglycerides – Making of protein ...
Section 4 pp from textbook
... Macromolecules are large molecules formed by joining smaller organic molecules together. Polymers are molecules made from repeating units of identical or nearly identical compounds linked together by a series of covalent bonds. ...
... Macromolecules are large molecules formed by joining smaller organic molecules together. Polymers are molecules made from repeating units of identical or nearly identical compounds linked together by a series of covalent bonds. ...
File - thebiotutor.com
... 10 (a) Name four examples of compounds which are classed as carbohydrate. (b) What elements are present in carbohydrates? 11 Write the formula for glucose. 12 If represents a glucose molecule draw (a) a maltose molecule, (b) part of a starch molecule. 13 Select the most appropriate words from the li ...
... 10 (a) Name four examples of compounds which are classed as carbohydrate. (b) What elements are present in carbohydrates? 11 Write the formula for glucose. 12 If represents a glucose molecule draw (a) a maltose molecule, (b) part of a starch molecule. 13 Select the most appropriate words from the li ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... “Others” Category – Foods not included in the five food groups because of their low nutrient content. Some of these foods are sweets, fats and oils, chips and related products. Protein – Protein is needed to build and maintain body tissue, to regulate body processes, and to supply energy. The best s ...
... “Others” Category – Foods not included in the five food groups because of their low nutrient content. Some of these foods are sweets, fats and oils, chips and related products. Protein – Protein is needed to build and maintain body tissue, to regulate body processes, and to supply energy. The best s ...
Sweet Facts about Maltitol
... them to sucrose, as it is the most widely used sweetener in the world. In their purest forms, both sucrose and maltitol are white powders consisting of anhydrous crystals with similar crystalline structures. Crystalline maltitol has a molecular weight (MW) very close to that of sucrose— the differen ...
... them to sucrose, as it is the most widely used sweetener in the world. In their purest forms, both sucrose and maltitol are white powders consisting of anhydrous crystals with similar crystalline structures. Crystalline maltitol has a molecular weight (MW) very close to that of sucrose— the differen ...
16 Chapter
... of proteins used in your cells. • Most of these amino acids can be made in your body’s cells, but essential amino acids have to be supplied by the foods you eat. ...
... of proteins used in your cells. • Most of these amino acids can be made in your body’s cells, but essential amino acids have to be supplied by the foods you eat. ...
Aerobic respiration
... (e) One student concluded that bile contains enzymes that digest fats. Which of the results shows that this conclusion is incorrect? Explain your answer. ...
... (e) One student concluded that bile contains enzymes that digest fats. Which of the results shows that this conclusion is incorrect? Explain your answer. ...
ExamView Pro - Chapter 03.bnk
... 1. You are given four test tubes containing purified biological macromolecules. The test tubes are unlabeled except for a number between 1 and 4. You are told that one test tube contains a protein, one contains a lipid, one contains a carbohydrate, and one contains a nucleic acid. You then perform s ...
... 1. You are given four test tubes containing purified biological macromolecules. The test tubes are unlabeled except for a number between 1 and 4. You are told that one test tube contains a protein, one contains a lipid, one contains a carbohydrate, and one contains a nucleic acid. You then perform s ...
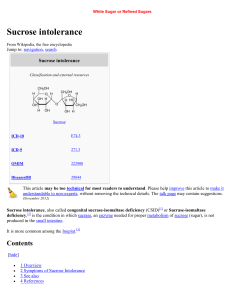
Sucrose intolerance
... Human beings have long sought sugars, but aside from wild honey, have not had access to the large quantities that characterize the modern diet. Studies have indicated potential links between consumption of free sugars including sucrose (particularly prevalent in processed foods) and health hazards, ...
... Human beings have long sought sugars, but aside from wild honey, have not had access to the large quantities that characterize the modern diet. Studies have indicated potential links between consumption of free sugars including sucrose (particularly prevalent in processed foods) and health hazards, ...
Carbohydrate
A carbohydrate is a biological molecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen:oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water); in other words, with the empirical formula Cm(H2O)n (where m could be different from n). Some exceptions exist; for example, deoxyribose, a sugar component of DNA, has the empirical formula C5H10O4. Carbohydrates are technically hydrates of carbon; structurally it is more accurate to view them as polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones.The term is most common in biochemistry, where it is a synonym of saccharide, a group that includes sugars, starch, and cellulose. The saccharides are divided into four chemical groups: monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. In general, the monosaccharides and disaccharides, which are smaller (lower molecular weight) carbohydrates, are commonly referred to as sugars. The word saccharide comes from the Greek word σάκχαρον (sákkharon), meaning ""sugar."" While the scientific nomenclature of carbohydrates is complex, the names of the monosaccharides and disaccharides very often end in the suffix -ose. For example, grape sugar is the monosaccharide glucose, cane sugar is the disaccharide sucrose and milk sugar is the disaccharide lactose (see illustration).Carbohydrates perform numerous roles in living organisms. Polysaccharides serve for the storage of energy (e.g., starch and glycogen) and as structural components (e.g., cellulose in plants and chitin in arthropods). The 5-carbon monosaccharide ribose is an important component of coenzymes (e.g., ATP, FAD and NAD) and the backbone of the genetic molecule known as RNA. The related deoxyribose is a component of DNA. Saccharides and their derivatives include many other important biomolecules that play key roles in the immune system, fertilization, preventing pathogenesis, blood clotting, and development.In food science and in many informal contexts, the term carbohydrate often means any food that is particularly rich in the complex carbohydrate starch (such as cereals, bread and pasta) or simple carbohydrates, such as sugar (found in candy, jams, and desserts).